The human body is one of the most complex structures in the world, where each cell and organ starting from the tiniest cerebellum’s granule cell to the biggest muscle of the gluteus maximus, i.e., the buttock muscle, has its own work and responsibilities to make the body function actively on a regular basis.
The plasma membrane of the free end gets modified to form three types of functional junctions microvilli, Stereocilia, Cilia, or kinocilia. Stereocilia and Cilia are cytoplasmic projections. Though they both are confused about each other, in reality, Stereocilia is more similar to microvilli.
Key Takeaways
- Cilia are shorter and more numerous than stereocilia.
- Cilia are used for locomotion, while stereocilia are used for sensory reception.
- Cilia have a characteristic whip-like motion, while stereocilia have a stationary hair-like structure.
Cilia vs Stereocilia
Cilia and stereocilia are hair-like extensions from cell surfaces but serve different purposes: cilia facilitate cell movement and propel fluids, while stereocilia function in sensory perception, particularly in the inner ear. These tiny structures, although similar in appearance, play crucial roles in various biological processes.
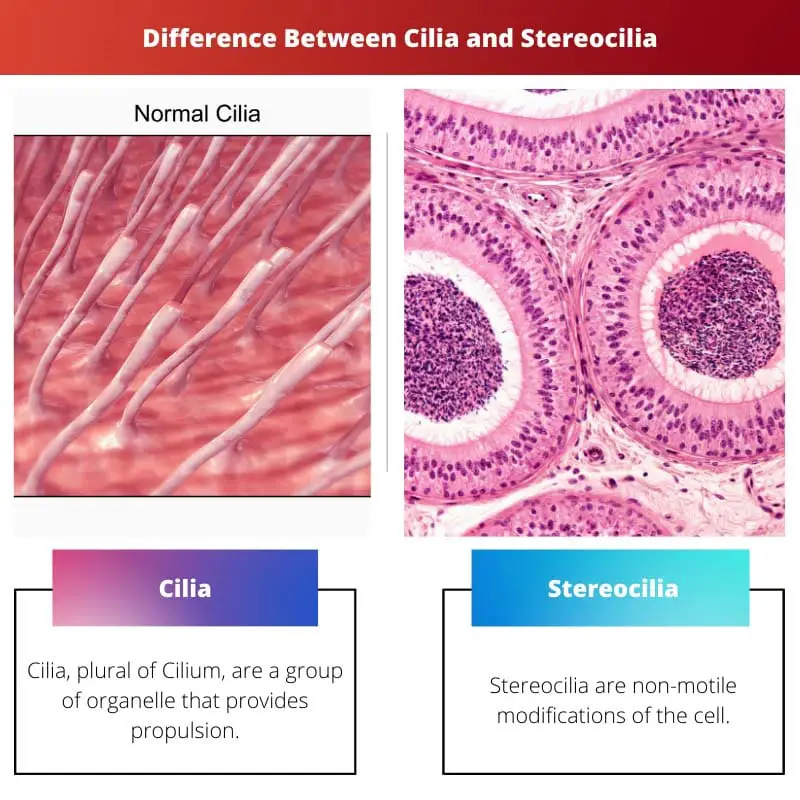
Cilla is a small projection that arises from basal granules of the body. Basal granules are a type of cellular membrane structure. They are mostly contractile motile. The function of this fibrous process is to move particles, primarily mucus, in a specific direction.
Stereocilia is a mechanosensing organelle that plays the role of increasing the in-between surface cells so that it can help them in absorption and secretion. Since there is a 9+2 arrangement in Stereocilia, they are also absent in the basal granules.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Cilia | Stereocillia |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cilia, plural of Cilium, are a group of organelle that provides propulsion. | Stereocilia are non-motile modifications of the cell. |
| Another name | Kinocilia | Stereovilli |
| Function(s) | Provide locomotion, i.e., to Move cells into a regular movement. | Turn physical force into an electric signal in the process of hearing and absorption, secretion of excess fluid in the hollow human. |
| Arrangement | 9+2 arrangement is present. | 9+2 arrangement is absent. |
| Location | In the middle ear, lungs, and respiratory tract. | In the hair cells of the inner body, ductus deferens and epididymis. |
What is Cilia?
The name “Cilia” came from a Latin word that translates into “the edge of the eyelids and of the eyelashes.” It was first discovered in 1675 by Anthony Van Leeuwenhoek, making it the first known cellular organelle.
Cilia are small hair-like structures. These cells are many in number, to be approx. Hundreds per cell. It originates all over the human body or on the peristomial region/end. A single unit of it would be called Cilium.
The arrangement of cilia fuses with each other to form membranelles and cirri or undulating membranes. The movement is fast, in a pendular type movement or sweeping movement. They are the fastest protozoans. These are located on the inner surface of the hollow organ.
Their main function is to protect the body from germs and bacteria entering the body through the mucus of the airways and from the lungs by propelling microbes.
Like the respiratory tract, whenever oxygen is inhaled into the body, there are certain dirt particles in it. There comes the use of mucus, and in that, Cilia help in tracking those dirt particles.

What is Stereocilia?
Stereocilia is a specialization of the free surface. They are the mechanosensing organelles of hair cells, which means it is a kind of receptor that has the ability to sense their microenvironment.
Though Stereocilia shares its name with Cilia, the tissues share more features with microvilli than Cilia. Its structure is long and non-motile.
They are located at the Epididymis, in the inner ear of the hearing guard, and in the Vas deferens. It can also be found in the lining of the urethra. The main function is plays of increasing the surface area for the process of secretion and absorption.
Unlike Cilia, Stereocilia does not have any ultra arrangement.
The Stereocilia of the inner ear are about 10–50 micrometres in length. They respond to fluid motions not only in humans but in various types of other animals s well.
The sound above a certain decibel can damage the Stereocilia that lie in the inner ear. But according to new studies, damaged hearing loss can be restored in the future damaged inner ear Stereocilia cause.
Main Differences Between Cilia and Stereocilia
- Stereocilia is like Cilia, but their projections are long, whereas Cilia’s projections are small in comparison to Stereocilia.
- Stereocilia are non-mobile or non-motile. On the other hand, Cilia can be motile or non-motile but are mostly motile in number.
- Their locations located in the human body are also different. Cilia is present in the basal granules of the body, while Stereocilia are present in the inner ear and the male reproductive parts: Vas deferens and Epididymis.
- The functions of these particular projections are also different. The main function of Cilia is to sweep the mucus in a particular direction, while the function of Stereocilia is to increase the cell’s surface area, allowing greater absorption.
- Cilia is a cytoplasmic process, and Stereocilia is a protoplasmic process, meaning that it arises from the plasma membrane.
- A Cilium has a 9+2 ultra-structure, meaning it has 9 pairs of fused microtubules and 2 pairs of unfused microtubules, while Stereocilia has no ultrastructure.