Gastric ulcers and duodenal ulcers are both common types of ulcers. They may also be called peptic ulcers or stomach ulcers.
More than four different types of ulcers can affect the stomach, but gastric and duodenal are the most common.
Key Takeaways
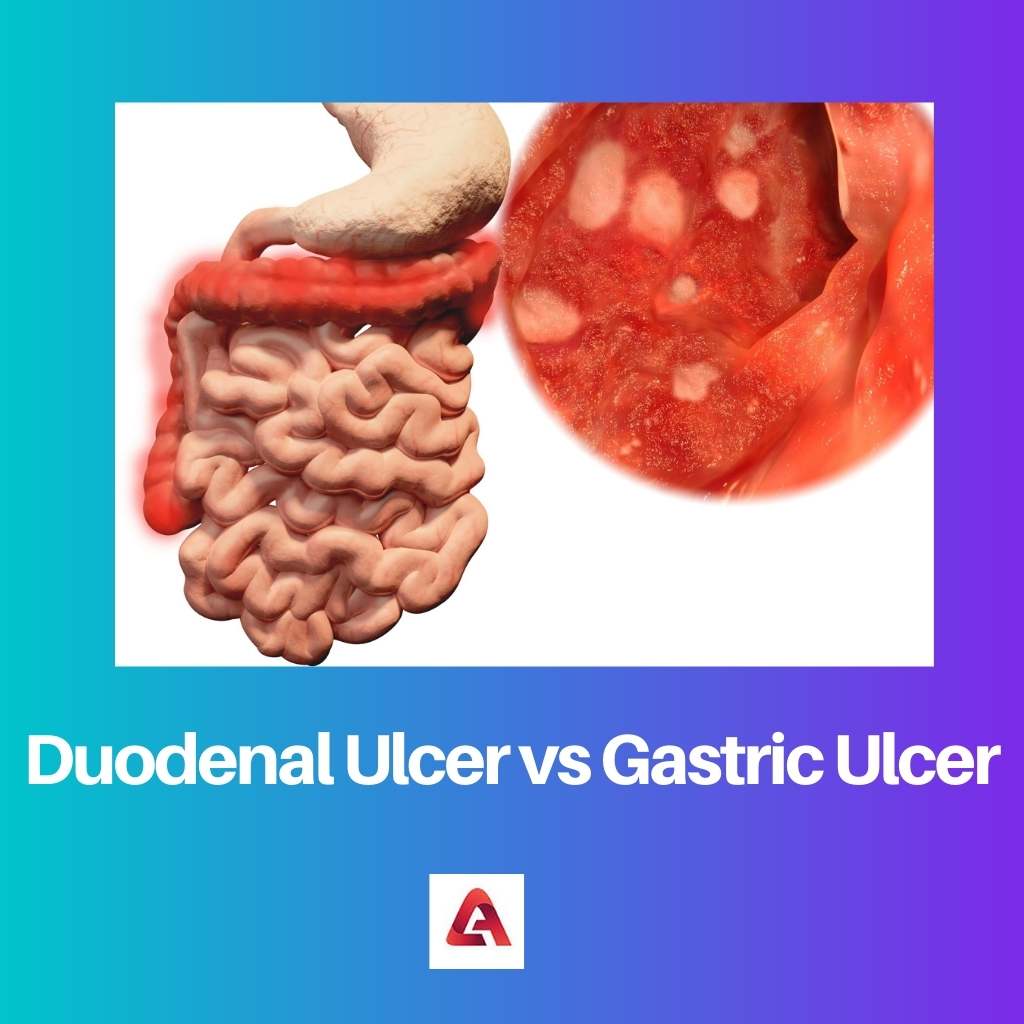
- Duodenal ulcers occur in the duodenum, the first part of the small intestine, while gastric ulcers develop in the stomach lining.
- Duodenal ulcers are more common than gastric ulcers and are associated with Helicobacter pylori infection.
- Pain from duodenal ulcers may decrease after eating, whereas gastric ulcer pain can worsen with food intake.
Duodenal Ulcer vs Gastric Ulcer
Helicobacter pylori cause duodenal ulcers and can be caused by long-term use of NSAIDs, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption. Gastric ulcers are peptic ulcers caused by an infection with Helicobacter pylori. Other factors can increase the risk of developing a gastric ulcer.
Duodenal ulcers are also called “pancreatic” ulcers. This type of ulcer is in the duodenum or the first part of the small intestine.
Duodenal ulcers are caused by low stomach acid levels, which may be due to taking acid-blocking medication. They can also result from chronic illnesses such as diabetes and Crohn’s disease.
Gastric ulcers are in your stomach, although they may be in any part of the stomach lining that is exposed to gastric juices.
Gastric ulcers are most associated with chronic Helicobacter pylori infection, an overactive parietal cell, or a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Duodenal ulcer | Gastric ulcer |
|---|---|---|
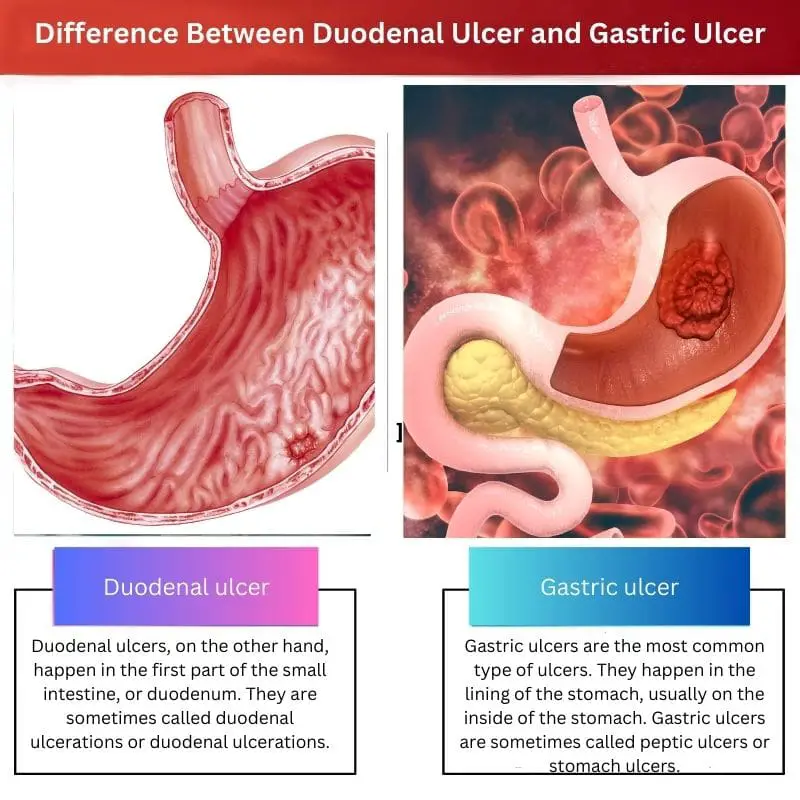
| Meaning | Duodenal ulcers, on the other hand, happen in the first part of the small intestine, or duodenum. They are sometimes called duodenal ulcerations or duodenal ulcerations. | Gastric ulcers are the most common type of ulcers. They happen in the lining of the stomach, on the inside of the stomach. Gastric ulcers are sometimes called peptic ulcers or stomach ulcers. |
| Site | Affects the first part of the small intestine, or duodenum. | Occurs in the lining of the stomach |
| Symptoms | Duodenal ulcers cause a burning sensation that can be relieved by eating or drinking a cold drink. They may also cause nausea, vomiting, pain in the upper abdomen, and a loss of appetite. | Gastric ulcerations can cause nausea, vomiting, heartburn (a burning sensation in the esophagus), appetite loss, and weight loss. |
| Treatment | Treatment for duodenal ulcers include medications to decrease acid production, promote healing, and suppress stomach acid | Treated with over-the-counter medications like antacids, H2 blockers, or proton pump inhibitors. If these don’t work, they can be treated with more serious medications like proton pump inhibitors or gastric acid reducers. |
| Mostly Affects | more common in the elderly and develop slowly | common in the young and middle-aged |
What is a Duodenal Ulcer?
Duodenal ulcers are also called “pancreatic” ulcers. This type of ulcer is in the duodenum or the first part of the small intestine.
Duodenal ulcers are caused by low stomach acid levels, which may be due to taking acid-blocking medication. They can also result from chronic illnesses such as diabetes and Crohn’s disease.
Gastric ulcers are in your stomach, although they may be in any part of the stomach lining that is exposed to gastric juices.
Gastric ulcers are most associated with chronic Helicobacter pylori infection, an overactive parietal cell, or a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID).
Duodenal ulcers are treated with drugs that increase stomach acid levels, which include proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) or H2 receptor blockers.
They also may be treated with other medications, such as antibiotics, if the ulcer is caused by Helicobacter pylori infection.
Gastric ulcers are treated with drugs that decrease stomach acid levels, such as Antac.
What is a Gastric Ulcer?
A gastric ulcer is a type of ulcer caused by stomach acid. Gastric ulcers can occur anywhere in the stomach but are most located in the lower part of the stomach.
Most people with a gastric ulcer have a chronic Helicobacter pylori infection, an overactive parietal cell, or a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory.
Duodenal ulcers, on the other hand, are located in the duodenum or the first part of the small intestine.
They may be caused by low stomach acid levels, which may be due to taking acid-blocking medication. Duodenal ulcers can also result from chronic illnesses such as diabetes and Crohn’s disease.
Duodenal ulcers are also called “pancreatic” ulcers.
Duodenal ulcers are more common in the elderly and develop slowly. While they can cause discomfort, they seldom cause severe pain or bleeding.
Main Differences Between Gastric Ulcers and Duodenal Ulcers
- Different factors cause gastric ulcers and duodenal ulcers. Gastric ulcers are due to taking over-the-counter NSAIDs such as aspirin or ibuprofen.
- Duodenal ulcers may be due to low stomach acid levels, which may be due to taking acid-blocking medication or to chronic illnesses such as diabetes and Crohn’s disease.
- It is important to distinguish between the two different types of ulcers. They require different treatments. For instance, over-the-counter medications can treat duodenal ulcers, while gastric ulcers may require prescription medications. Your doctor needs to determine which type of ulcer you have before prescribed a treatment.
- The main difference between these two is their location in the digestive system. A gastric ulcer occurs in the lining of the stomach, while a duodenal ulcer affects the first part of the small intestine or duodenum.
- Duodenal ulcers cause a burning sensation that can be relieved by eating or drinking a cold drink, whereas Gastric ulcers cause severe pain, vomiting, and bleeding.