Foot ulcers have become common in today’s life. People spend their entire day in formally busy with their office chores. Thus, moisture, dirt, and germs remain captured in the feet. In addition to that, the lack of a healthy lifestyle leads to diseases such as diabetes which deteriorate the body slowly.
Lack of proper foot care and these common diseases sometimes lead to ulcers. However, it’s important to know to identify the type and kind of ulcers. The most common ulcers seen in the foot region include diabetic ulcers and pressure ulcers.
Key Takeaways
- Diabetic ulcers occur due to complications from diabetes, while pressure ulcers result from prolonged pressure on the skin.
- Diabetic ulcers commonly develop on the feet, while pressure ulcers can occur in any area with reduced blood circulation.
- Prevention and treatment strategies differ, with diabetic ulcers requiring blood sugar management and pressure ulcers needing pressure relief.
Diabetic Ulcer vs Pressure Ulcer
Diabetic ulcers and pressure ulcers are both types of skin ulcers. Diabetic ulcers occur on the feet and are caused by poor circulation due to diabetes. Pressure ulcers, also known as bedsores, are caused by prolonged pressure on an area of skin.
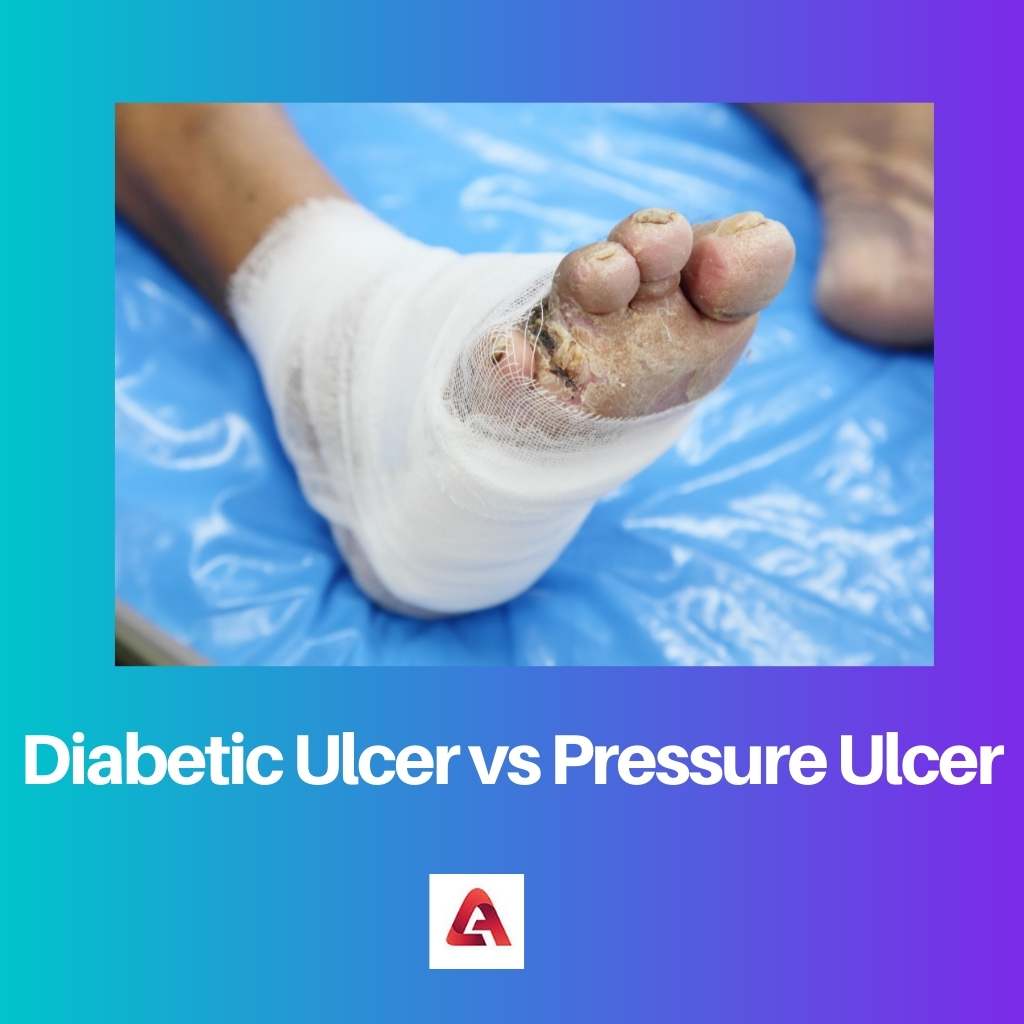
Diabetic ulcers are seen in diabetes patients where the nerves get weakened, leading to neuropathy. The black discolouration of some regions of one or both feet, followed by swelling and odorous discharge, are the symptoms of diabetic ulcers.
Timely treatment involving proper foot care, hygiene, and blood sugar levels is essential for faster healing and fewer inflexions.
Pressure ulcers develop when some parts or regions of the body get pressurized, leading to an insufficient blood supply. In such cases, the nerves may even die.
Besides pressure, deposition of moisture and friction between feet and toes are common reasons for pressure ulcers. Although these ulcers appear similar to diabetic ulcers, they are different from those in symptoms.
Thus, the diagnosis and treatment of pressure ulcers are also different. If left untreated, these ulcers will eat away the skin, thereby exposing the bones of the affected region.
Comparison Table
| Parameters Of Comparison | Diabetic Ulcer | Pressure Ulcer |
|---|---|---|
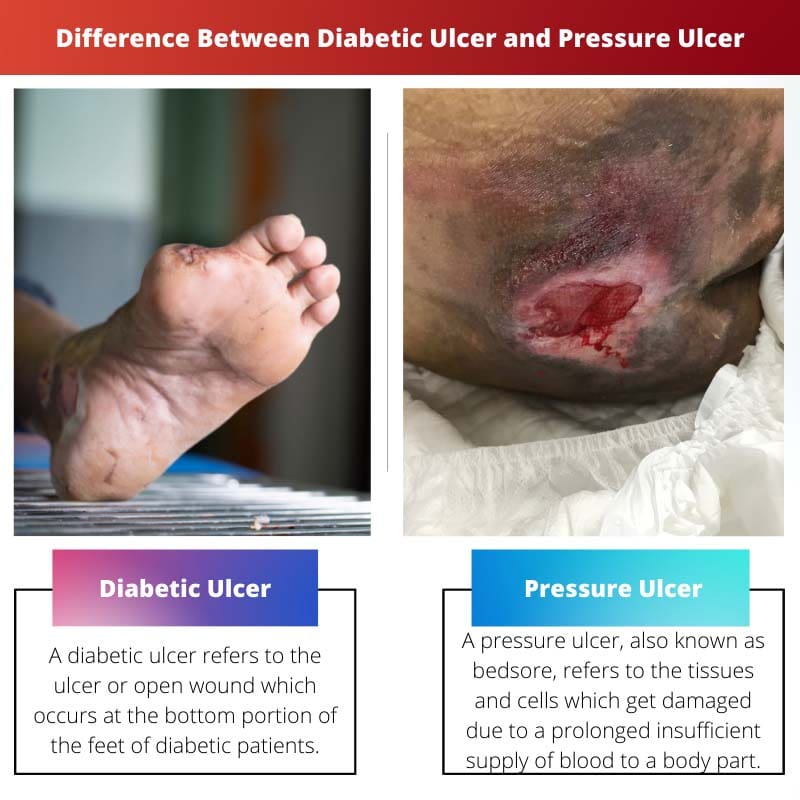
| Definition | A diabetic ulcer refers to the ulcer or open wound which occurs at the bottom portion of the feet of diabetic patients. | A pressure ulcer, also known as bedsore, refers to the tissues and cells which get damaged due to a prolonged insufficient supply of blood to a body part. |
| Affected organ | Diabetic ulcers are mainly noticed in the foot region. | Pressure ulcers can be found on any part of the body where bony projections are present such as hips. |
| Symptoms | The symptoms of diabetic ulcers include:Black discoloration of the skin of the affected region.Swelling, pain, irritation, numbness, and odorous discharge around the affected region. | The symptoms of pressure ulcers include:Reddish coloration and warmth around the affected region.Formation of blistersErosion of the skin in extreme layers leads to the visibility of bones. |
| Causes | The causes of diabetic ulcers include:Poor blood circulationHigh levels of blood sugar, i.e., hyperglycemiaWounds or irritation in feet.Nerve damage | The causes of pressure ulcers include:External pressure on the foot.Friction between blood vessels.Shear and tear of the skin.Deposition of moisture in the intricate regions. |
| Risk factors | The risk factors for patients with diabetes include:Usage of low-quality shoes.Maintenance of poor hygiene.Increase in consumption of alcoholObesity and other underlying health problems such as health and kidney problems. | The factors which increase the chances of pressure ulcers include:Elderly and aged people.Underlying health problems where the person is bedridden. |
What is Diabetic Ulcer?
Open wounds and sores, most commonly found in the feet of diabetic patients, are known as diabetic ulcers. These ulcers can further lead to infections. When left untreated, complicated situations involving amputation of the affected feet may also arise.
Diabetes patients who are regularly dependent on insulin, or are overweight, or have any other heart, kidney, or serious disease are at more risk of developing diabetic ulcers.
Besides these, diabetes patients who are addicted to alcohol and tobacco may also develop diabetic ulcers. Improper blood circulation to the feet, underlying foot deformities, and lack of proper foot care and hygiene lead to diabetic ulcers in the foot.
People affected with diabetes for a long time have neuropathy due to improper supply of blood to the affected region. These conditions also trigger the chances of diabetic ulcers.
These diabetic ulcers should be immediately treated with proper podiatric medical care on the diagnosis. The proper treatment would involve faster healing which implies fewer chances of infection.
During the treatment, the patient should avoid overloading the affected region. Moreover, keeping the affected region clean by regular dressing is essential.
Moreover, the patient should also manage his blood sugar levels well. With the proper treatment of diabetic ulcers, the chances of amputations and further infection decrease.
What is Pressure Ulcer?
Regions of cells and tissues that get damaged due to prolonged pressing of skin over bone for a significantly longer time are known as pressure ulcers.
Pressure ulcers, also known as bedsores and decubitus ulcers, are seen mostly in bedridden patients. Patients who are on bed rest or sit in a wheelchair for long periods have an insufficient distribution of blood to some parts of the body.
This leads to the development of pressure ulcers. In the initial stages, these pressure ulcers only affect the topmost covering layers of the skin, with symptoms including pain and itching.
These ulcers even attack ligaments, tissues, and muscles in extreme cases when the sores are too big and deep. In such severe cases, the reddish coloration of the skin, followed by erosion of skin layers, is also noticed.
Sometimes, the muscles and skin covering the affected region get eroded, leading to the visibility of bones.
Persons above the age of 70 years with dry skin, unhealthy lifestyles, low BMI, physical restraints, smoking, and drinking habits are at higher risk of developing pressure ulcers.
The treatment involves debridement of the ulcer along with dead tissues. Furthermore, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics to stop the growth of the infection. In some severe cases, the doctor may also prescribe special footwear.
Main Differences Between Diabetic Ulcer and Pressure Ulcer
- Diabetic ulcers refer to the ulcers or open wounds which occur at the bottom portion of the feet of diabetic patients. On the other hand, pressure ulcers, also known as bedsores, refer to the tissues and cells which get damaged due to a prolonged insufficient supply of blood to a body part.
- Diabetic ulcers are mainly noticed in the foot region. In contrast, pressure ulcers can be found on any body part where bony projections are present such as hips.
- The symptoms of diabetic ulcers include black discoloration of the skin of the affected region, swelling, pain, irritation, numbness, and odorous discharge around the affected region. On the other hand, The symptoms of pressure ulcers include reddish coloration and warmth around the affected region, blisters formation, and skin erosion in extreme layers leading to the visibility of bones.
- The causes of diabetic ulcers include poor blood circulation, high blood sugar levels, i.e., hyperglycemia, wounds or irritation in feet, and nerve damage. Whereas, The causes of pressure ulcers include external pressure on the foot, friction between blood vessels, shear and tear of the skin, and deposition of moisture in the intricate regions.
- The risk factors for patients with diabetes include the usage of low-quality shoes, maintenance of poor hygiene, increase in consumption of alcohol, obesity, and other underlying health problems such as health and kidney problems. But, The factors which increase the chances of pressure ulcers include elderly and aged people and underlying health problems where the person is bedridden.
- https://aacnjournals.org/ajcconline/article-abstract/4/5/361/6110
- https://journals.lww.com/aswcjournal/fulltext/2007/01000/certification_and_education__do_they_affect.12.aspx

The comparison table is really helpful. It summarizes the differences between diabetic ulcers and pressure ulcers in a clear way, making it easier to understand.
The article provides a comprehensive understanding of diabetic and pressure ulcers, shedding light on both the causes and treatment options. A very informative read.
The symptoms and risk factors described for diabetic and pressure ulcers are very insightful. It’s important for people to understand the warning signs and take necessary actions for their foot health.
I agree, the details about risk factors and symptoms are crucial for early detection and effective management of foot ulcers.
Absolutely, the article provides valuable information on how to identify the symptoms and prevent the development of these ulcers.
It’s alarming to see how factors like lack of proper foot care, poor blood circulation, and prolonged pressure contribute to foot ulcers. This article is very informative and raises awareness about foot health.
The article seems a bit biased towards foot ulcers occurring in diabetes patients. It would have been beneficial to see more information on pressure ulcers and their prevention and treatment.
The article clearly distinguishes between diabetic ulcers and pressure ulcers, providing detailed information on their differences and symptoms.