When the terms Glucose and Sucrose are placed in front of someone, they automatically think of sugar and chemistry. Both the words are very common for people in the chemists, food analysts department and also for someone who checks the beneficial content of sugar-related goods.
Sucrose is quite familiar for people who love to eat chocolates or any candies which are sold in any market. Because these words are related to sugar, not everyone knows the major difference between them.
Key Takeaways
- Glucose is a monosaccharide sugar, while sucrose is a disaccharide sugar composed of glucose and fructose.
- Glucose is the primary energy source for cells, while sucrose is a common sweetener used in various food products.
- Glucose is absorbed directly into the bloodstream, whereas sucrose must be broken down into glucose and fructose before absorption.
Glucose vs Sucrose
Glucose is a simple sugar that cannot be further broken down into smaller sugars. It is an important source of energy for the body’s cells and is the primary source of fuel for the brain. Sucrose is a type of table sugar made up of two simple sugars, glucose and fructose, joined together.
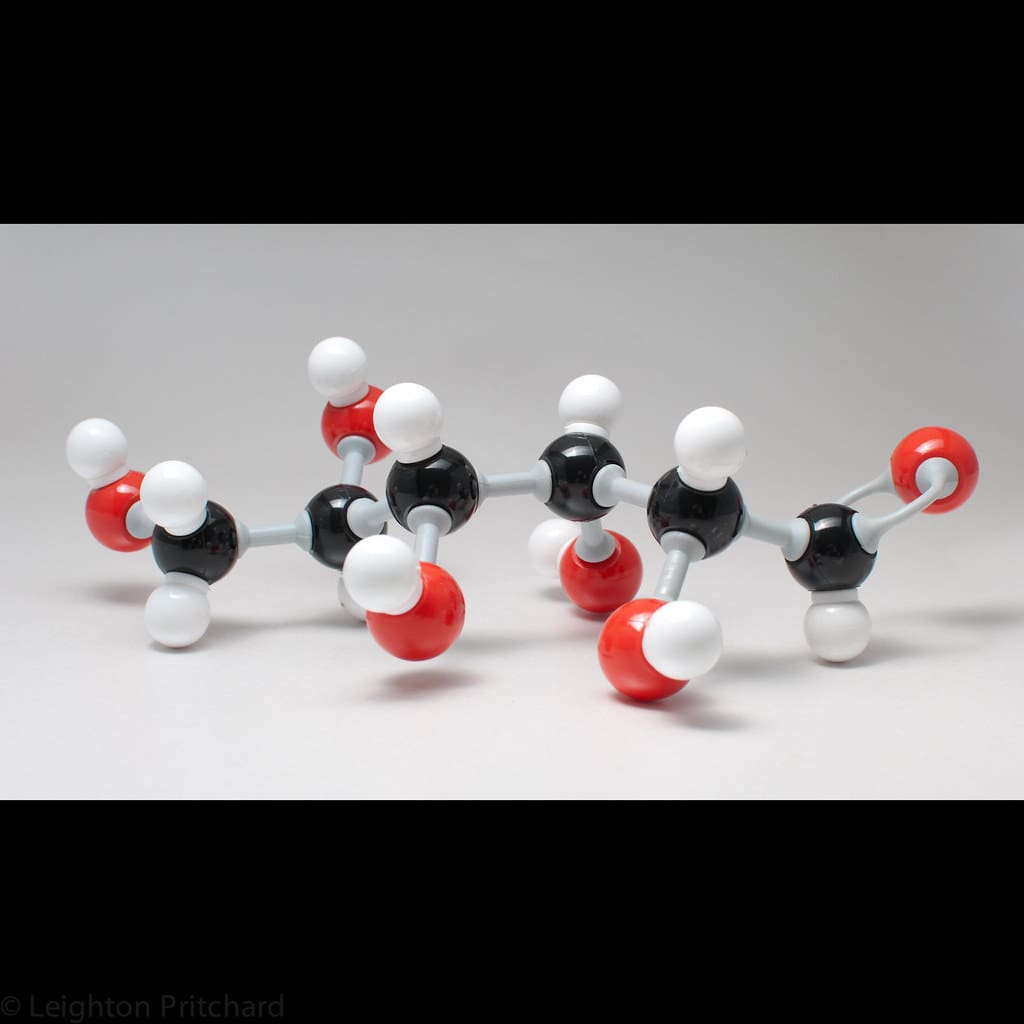
Glucose is a type of simple sugar that has C6H12O6 as its chemical formula. Glucose is a monosaccharide that plays a vital role in forming disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Glucose has a molar mass of 180 g/mol and appears like a powder in white color. According to the chemical structure of the molecule, the melting point of glucose varies between 140°C to 150°C.
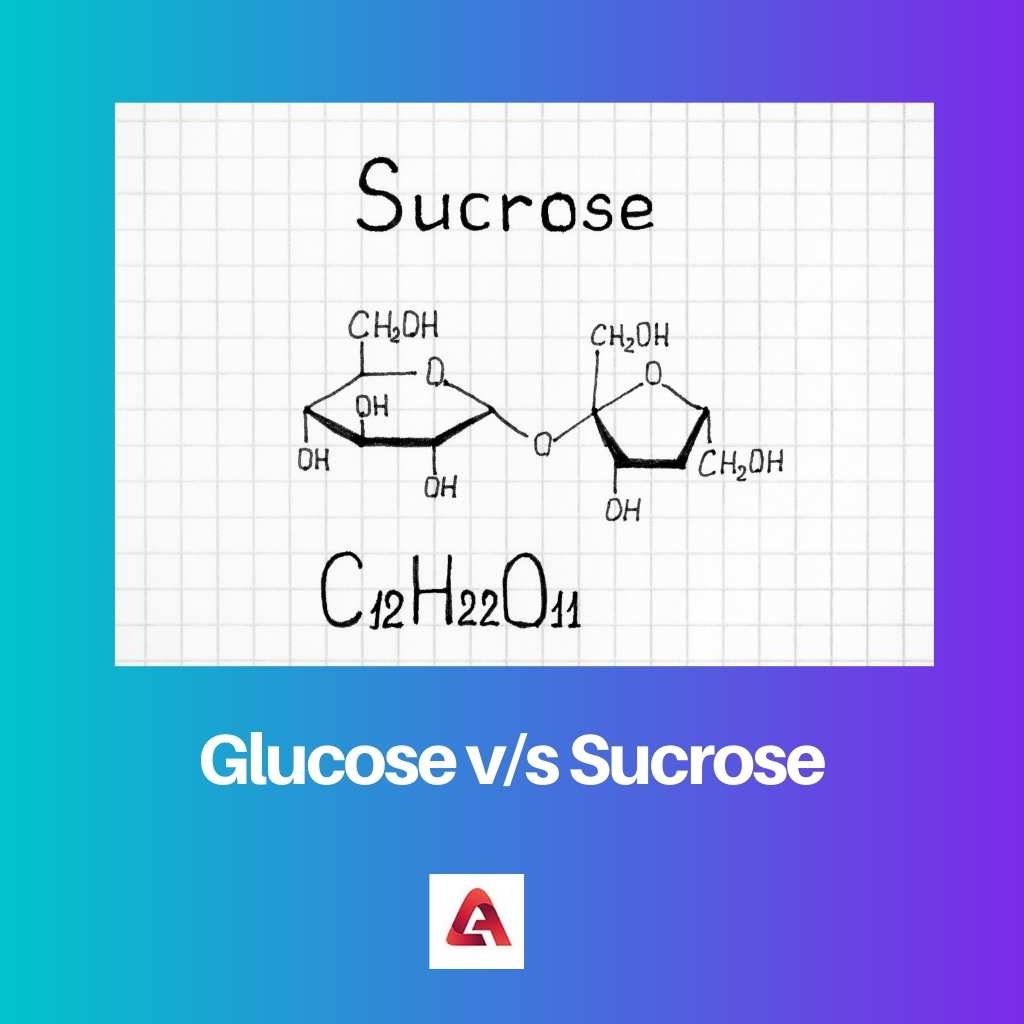
Sucrose is also a type of sugar that is a disaccharide in nature with the chemical formula C12H22O11. Sucrose was created by mixing two monosaccharide molecules which were glucose and fructose.
The bond that links these two monosaccharides is known as a glycosidic bond. Sucrose is found in white and odorless solid compounds which is in a crystalline state.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Glucose | Sucrose |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | It is a monosaccharide. | It is a disaccharide. |
| Molar mass | 180 g/mol. | 342.29 g/mol. |
| Sugar | It is a reducing sugar. | It is a non-reducing sugar. |
| Bonds | It has no glycosidic bond. | It has glycosidic bonds between Fructose and Glucose. |
| Glycemic index | The glycemic index is high. | The glycemic index is low. |
What is Glucose?
Glucose is the simplest compound in the list of carbohydrates which makes it a monosaccharide that has one sugar. It is the key element that keeps the body’s mechanism working in order.
When the glucose level in the body is normal, it gets unnoticed, but when the level fluctuates, it can cause health issues that can go unnoticed and affect you with some permanent and serious health problems.
It is also one of the most preferred sources of fuel that a body wants to function properly. One can get glucose from many common food items like bread, veggies, fruits, and dairy products.
Whenever we eat something, our body starts to process glucose and this processing occurs multiple times a day. With the help of the pancreas, enzymes begin the process of breakdown.
Insulin produced by the pancreas is an important part that helps our body deal with glucose.
When food passes to our system, the pancreas gets an indication to release insulin, which will help in maintaining the sugar level in the blood. A person with diabetes is required to include the testing of glucose levels in their regular check-up routine.
The testing of glucose levels is very easy and can be done at home by simply pricking a finger with a small needle called Lancet. The blood drop then is smeared on a test strip that is placed into a meter which tests the level of sugar in the blood.
In just 20 seconds, this device can give you the readings.

What is Sucrose?
Sucrose is a type of naturally occurring sugar that is found in several plants of fruits, nuts, and vegetables. Sucrose is extracted from sugarcane and sugar beets for commercial purposes.
It can be used as a natural sugar or added sugar depending on its source. Generally, sucrose is considered as a natural sugar when it is consumed directly from its natural source, while it is considered as an added sugar when it is present in packaged foods and beverages.
When sucrose is consumed, it breaks down equally into glucose and fructose. Glucose is absorbed by our cells because of insulin, whereas the liver deals with fructose without insulin.
Irrespective of its source, any type of sucrose gives out four calories per gram and our bodies are made to process it similarly. The nutritional benefits that various nutrients provide differ from source to source, which can affect the way we metabolize sucrose.
Fiber is one of such nutrients that slows down the process of digestion. Other than adding flavor and sweetness to food and drinks sucrose is also used in various pharmaceutical products.
It also acts as a chemical intermediate for numerous compound agents and as a food stabilizer. When sucrose is incorporated in food products like jams and jellies, it extends their shelf life of them along with adding sweetness to them.

Main Differences Between Glucose and Sucrose
- Glucose is a sugar compound that is a monosaccharide in nature, whereas sucrose is also a type of sugar that is a disaccharide in nature.
- The other name used to refer to Glucose is blood sugar, whereas the other name for sucrose is table sugar.
- Glucose is termed a monosaccharide because it can’t be broken down by using hydrolysis, whereas sucrose is termed a disaccharide as it is made by combining glucose and fructose in equal quantities.
- Glucose is mainly used for treating patients with diabetes, whereas sucrose is mainly used as a sweetener in food and drinks.
- Glucose does not have a glycosidic bond as it is a monosaccharide, whereas sucrose has a glycosidic bond as it is made by linking two monosaccharides through a bond.




