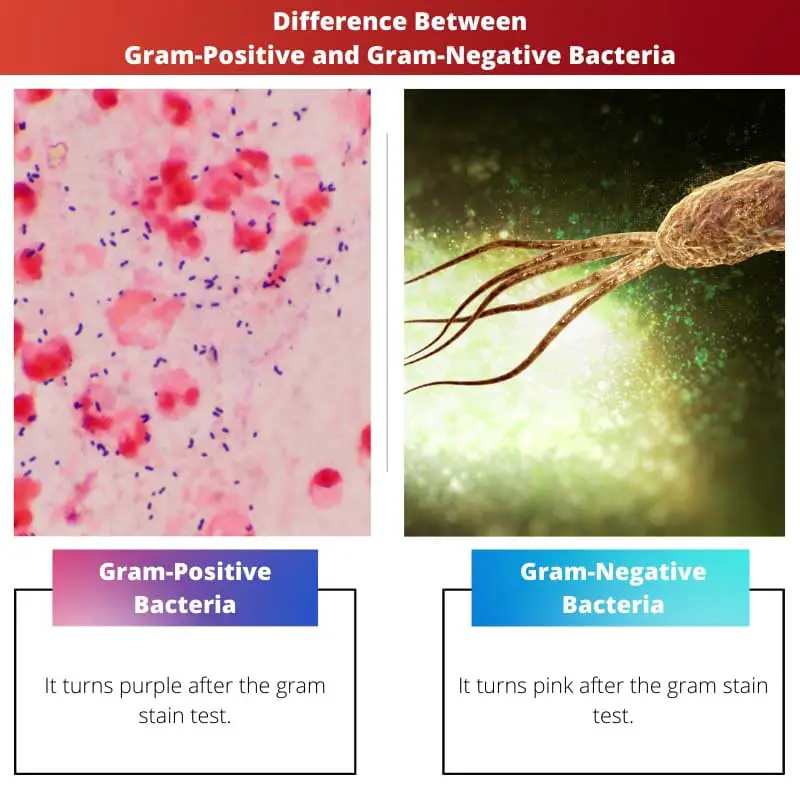
Bacteria, being one of the smallest microorganisms on the planet, are found in 2 major tapes, GRAM-POSITIVE and GRAM-NEGATIVE. Scientists have developed various methods such as genome sequencing, mass spectrometry, and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) techniques to differentiate between these teeny-tiny bacteria.
Key Takeaways
- Gram-positive bacteria have a thick peptidoglycan layer in their cell wall, while gram-negative bacteria have a thin layer and an additional outer membrane.
- Gram-positive bacteria stain purple during the Gram stain test, while gram-negative bacteria appear pink or red.
- Gram-negative bacteria tend to be more antibiotic-resistant due to their outer membrane, making them harder to treat.
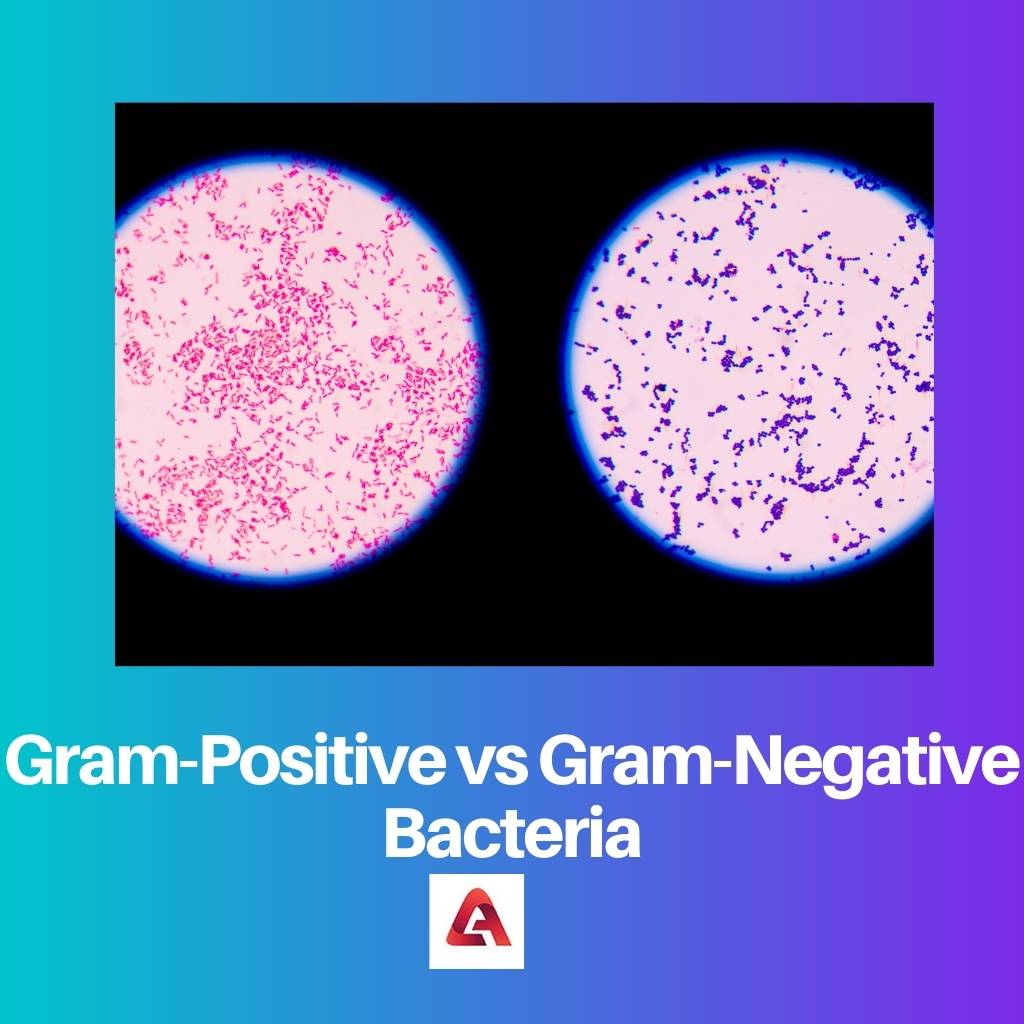
Gram-Positive vs Gram-Negative Bacteria
The difference between gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria sees the presence or absence of cell membranes as a parameter of differentiating. It is the presence of this cell membrane in gram-positive bacteria which makes it different from the gram-negative ones. Lipid is absent in gram-negative bacteria but is present in gram-positive ones.
Gram-positive bacteria possess thick cell walls, but the cell membrane (also known as the outer membrane) is absent in them. Substances can easily penetrate through gram-positive bacteria because of the absence of a cell membrane.
Gram-negative bacteria, on the other hand, possess a thin cell wall. However, a cell membrane (also known as the outer membrane) is also present in them. Substances cannot penetrate it because of the lipid present in the cell membrane.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of comparison | Gram-positive bacteria | Gram-negative bacteria |
|---|---|---|
| Gram stain color | It turns purple after the gram stain test | It turns pink after the gram stain test |
| Cell membrane | The cell membrane is absent in these. | The cell membrane is present in these. |
| Cell wall thickness | The thick, smooth cell wall of 20-80 nanometer thickness | The thin uneven cell wall of 8-10 nanometer thickness |
| Penetrating capacity | Can be easily penetrated through. | It is difficult to be penetrated through. |
| Presence of lipid | Lipid is absent | Lipid is present in the cell membrane. |
What Is Gram-Positive Bacteria?
Gram-positive bacteria are those which have a thick, smooth, and even cell wall of thickness ranging from 20-80 nanometers. The cell membrane (also known as the outer membrane) is absent in these.
These bacteria can be easily penetrated by foreign substances due to the absence of cell membranes and are thus easily destroyed. During the Gram Stain Test, where a sample is placed under a slide and treated with gram stain, it turns purple, which is observed through a microscope.
It mostly contains exotoxins which are unstable and intolerant to heat, thus, they diffuse into the surrounding medium. These bacteria might cause minor gum diseases, diphtheria, acne, leprosy, and various bacterial skin infections and inflammations.
Various examples of these types of bacteria include – Staphylococcus Aureus, Streptococcus Pneumoniac, Enterococcus Faecalis, Hay Bacillus, Bacillus Cereus, Anthrax bacterium, Mycoplasma Hominis, Milky spore, Ureaplasma Parvum, and Mycobacterium large.
What Is Gram-Negative Bacteria?
Gram-negative bacteria have many of their characteristics opposite to those of gram-positive bacteria. It has a thin, uneven, multilayered cell wall of thickness ranging from 8-10 nanometers.
These bacteria cannot be easily penetrated by foreign substances because of the presence of lipid-filled cell membranes. These are thus harder to be destroyed.
It contains both Exotoxins, which are proteins that aren’t heat resistant. And Endotoxins, which are heat-resistant lipopolysaccharide (LPs) proteins that only diffuse after the death of bacteria. It contains many types of amino acids.
Examples of gram-negative bacteria include E. Colli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Meningococcus, Proteus Vulgaris, Chlamydia Pneumoniae. Gram-negative bacteria can cause some harmful ailments such as low blood pressure, low oxygen levels, Cholera, and various infections.
Main Differences Between Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacteria
- During the gram stain test, gram-positive bacteria change their color to purple, whereas gram-negative bacteria turn pink.
- The cell membrane (also known as the outer membrane) is absent in gram-positive bacteria. But in the case of gram-negative bacteria, a cell membrane is present.
- The cell wall is thick, with a thickness of up to 20-80 nanometers, and smooth in gram-positive bacteria. In contrast, it is thin of the thickness of 8-10 nanometers and uneven in gram-negative bacteria.
- Gram-positive bacteria have a high penetrating capacity as the cell membrane is absent, and foreign substances penetrate it easily. However, gram-negative bacteria have a cell membrane which makes it difficult to be penetrated.
- Lipid layer on absent gram-positive bacteria. Whereas in gram-negative bacteria, the lipid layer is present, this lipid layer might undergo toxic reactions and cause diseases.