There are many critical differences between a covalent and a hydrocarbon bond. Chemistry, the study of substances – elements and compounds, starts with the basics of bonds between two atoms and molecules.
This article will explain the differences between hydrogen and covalent bonds and how they are formed. We’ll look at the two types of chemical bonds. The interaction type makes a covalent molecule different from a hydrocarbon molecule.
Key Takeaways
- Hydrogen bonds form between molecules when a hydrogen atom bonds to a highly electronegative atom; covalent bonds share electrons between atoms within a molecule.
- Hydrogen bonds are weaker than covalent bonds, providing temporary and reversible interactions.
- Hydrogen bonds contribute to the structure and function of biological molecules; covalent bonds form the basis of molecular structures.
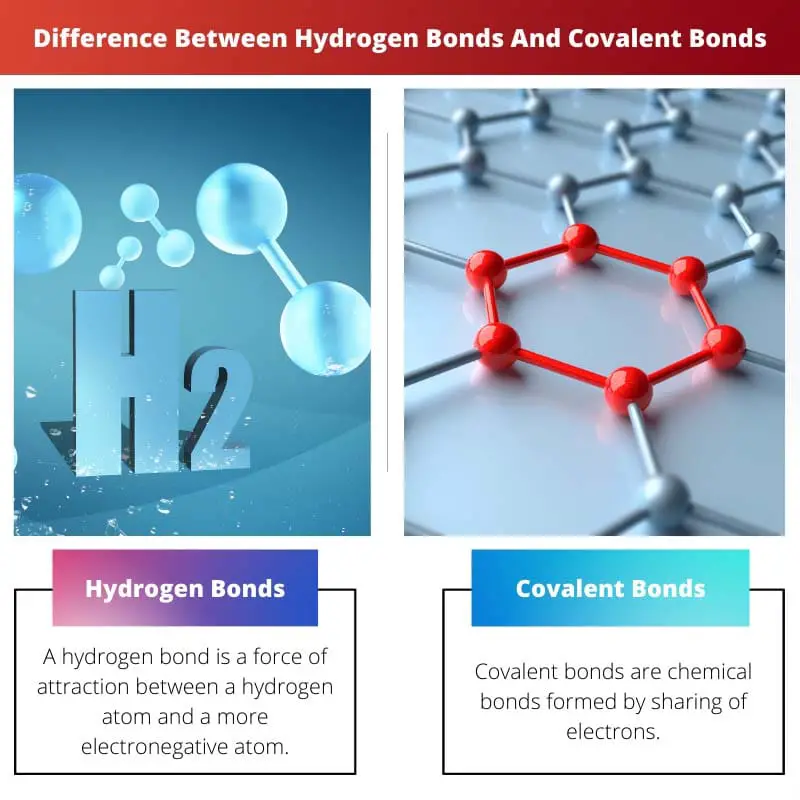
Hydrogen Bond vs Covalent Bond
Hydrogen bonds arise when a positively charged hydrogen atom interacts with an electronegative atom, creating a relatively weaker bond than covalent bonds that involve electron sharing. These bonds are essential for water’s unique properties. Covalent bonds form the foundation of most molecules.
A hydrogen bond can be either intramolecular or intermolecular. The energy associated with a hydrogen bond varies depending on the geometry and the atoms’ environment.
It is a weaker bond than the van der Waals interaction, occurring in organic and inorganic molecules. Some hydrogen bond examples are Salicylic acid, H2O (Water), Methyl alcohol, sugar, etc.
Covalent bonds are forms of intermolecular forces. They are formed when two or more atoms share their electrons to fill their outermost electron shells. Covalent bonds are much stronger than hydrogen bonds and have high stability.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Hydrogen Bond | Covalent Bond |
|---|---|---|
| What are they? | A hydrogen bond is a force of attraction between a hydrogen atom and a more electronegative atom. | Covalent bonds are chemical bonds formed by sharing of electrons. |
| Forces | Intermolecular and Intramolecular forces. | Intermolecular forces. |
| Strength | It is formed between two atoms. | Covalent bonds are much stronger as compared to hydrogen bonds. |
| Formed between | A hydrogen bond is formed between two atoms of two different molecules. | Formed between two atoms. |
| Examples | Salicylic acid, Water, Glucose, etc. | Methane, carbon monoxide, etc. |
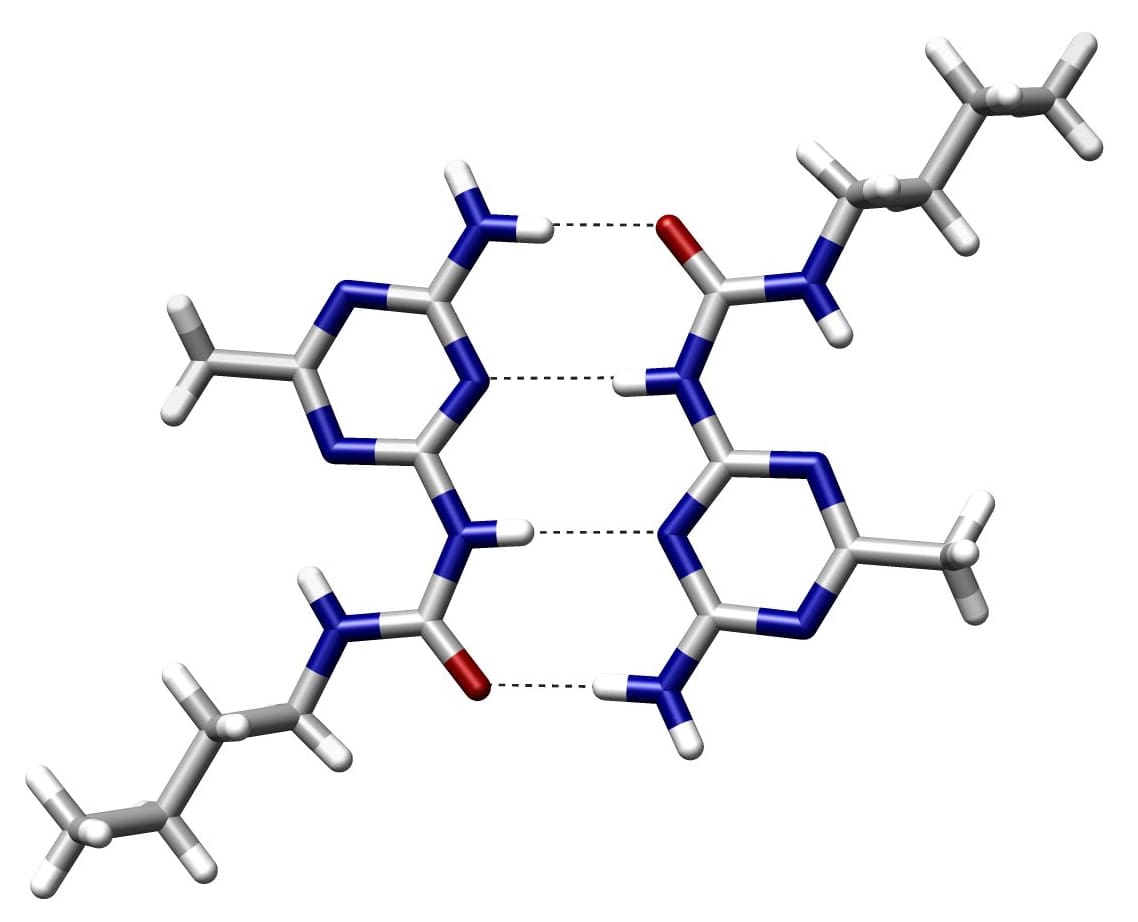
What is a Hydrogen Bond?
A hydrogen bond is an electric force of attraction between two atoms. It is created when a hydrogen atom covalently bonds with another more electronegative bit, such as an octet or a group.
Mostly, the electronegative molecules are either oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine. In most cases, a more electronegative atom with a lone pair of electrons is called the acceptor.
Hydrogen bonds are strong attractions between partially positive and positively charged atoms. They are the strongest of all the known types of bonds. These bonds are found in many covalent compounds but are weaker than the covalent ones.
The electronegative nature of the hydrogen atom bonds the two molecules together. Water can therefore move between the particles and form stable chemical compounds. For example, when wet paper sheets stick together.
Hydrogen bonds occur between two molecules containing the same type of hydrogen.
C-H bonds are formed when two carbon atoms become electronegativity bound.
In a donor/acceptor bond, the proton donor is the electronegative atom, and the proton acceptor is the one that is not covalently bound with hydrogen. The hydrogen atoms in the base pair are held together by hydrogen bonding.
What is a Covalent Bond?
Two atoms share electron pairs to form a covalent bond. These electron pairs are called bonding pairs. Covalent bonds are created through a balance of attractive and repulsive forces.
Here are some examples. To illustrate, here is a chemical equation. Read on to discover the science behind them. The simplest example of covalent bonding is sharing a pair of electrons.
The bonding process involves sharing electrons between two different atoms. Because electrons share energy, they can have lower energy than the other atoms. They become entangled when the centres attract one another.
“The shared electrons decrease the energy of the other atom. This is called”equilibrium”. This phenomenon is common and can be used to track progress and identify essential lessons.”The shared electrons decrease the energy of the other atom. This is called “equilibrium”. This phenomenon is common and can be used to track progress and identify essential lessons.
The process of sharing electrons results in a decrease in energy. The electron that shares an atom with another electron will lose power. It is in this state that the covalent bond forms.
An electron between two attracting centres has lower energy than an electron between two neutral ones. The power of a single atom increases in a molecule if it is shared with a bit with a higher energy level.
Main Differences Between a Hydrogen Bond and Covalent Bond
- A hydrogen bond is only 1/10 times stronger than a covalent bond.
- Hydrogen Bonds are intramolecular and intermolecular bonds. On the other hand, covalent bonds are Intermolecular chemical bonds.
- Hydrogen bonds are formed between two atoms of two different molecules. Covalent bonds are formed between two atoms.
- Hydrogen bonds are attraction forces. Covalent bonds are chemical bonds.
- Hydrogen bonds have low stability as compared to covalent bonds.