In 800 CE, feudalism was established in Europe, but it existed in Japan only in the 1100s when Kamakura Shongute came into power. Japanese feudalism existed and was retained till 1868. With the rise of stronger political parties, European feudalism fell off.
Key Takeaways
- In Japanese feudalism, samurais were the dominant class, while in European feudalism, the nobles were the dominant class.
- Japanese feudalism was characterized by the concept of Bushido, while the chivalric code characterized European feudalism.
- Japanese feudalism had a more centralized power structure, with the emperor at the top, while European feudalism had a more decentralized power structure, with various nobles holding power.
Japanese vs European Feudalism
Japanese feudalism developed during the 12th century and lasted until the mid-19th century. It was characterized by a system of lords, vassals, and serfs. European feudalism developed during the 9th and 10th centuries and lasted until the 15th century. It was characterized by a similar system of lords, vassals, and serfs, but with the monarch at the top of the hierarchy.

Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Japanese Feudalism | European Feudalism |
|---|---|---|
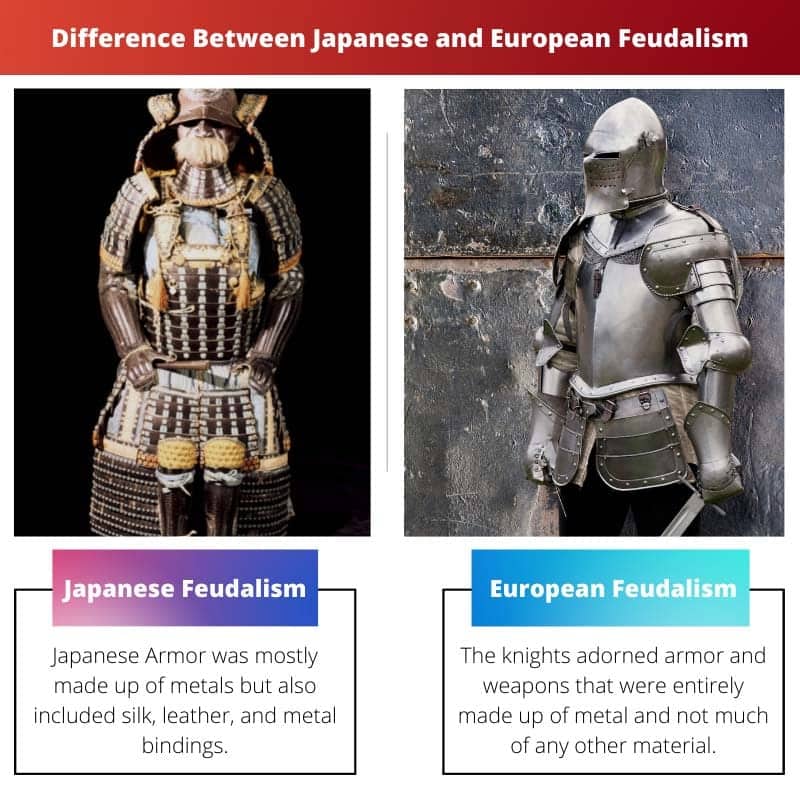
| Armor | Japanese Armor was mainly made of metals but included silk, leather, and metal bindings. | The knights adorned armor and weapons entirely made of metal and not much other material. |
| Influence | The ideas and philosophies of Confucius, a Chinese philosopher, influenced Japanese feudalism. | Roman imperial laws and theories were the inspiration for the customs and rules of European feudalism. |
| Land Ownership | The samurai were not privileged to earn any land and were paid for rice or grains. | The knights were paid in assets and land for their service. |
| Women’s Role | Like men, Samurai women were also considered too powerful, gallant, and brave. | The Europeans considered the females weak, fragile, and always needed to be taken care of. |
| Literacy | Samurai were stressed to have cultural values and develop artistic skills like poetry, music, and calligraphy. | European knights weren’t literate and did not know much about the cultures and values since they were not educated. |
What is Japenese Feudalism?
In Japanese feudalism, being a part of it or being a warrior was quite challenging. It was their lifestyle rather than their job.
The warriors of the samurai were supposed to be completely dedicated and were expected to commit to it and would put their lives at stake. The warriors were supposed to kill themselves if they crossed their lines of loyalty, honesty, commitment, and honor.
The warriors are to be committed, and in return, they receive financial provisions, shelter, protection, and all the necessities to live a comfortable life.
From Europe, the warriors came to London during the rule of Nobunaga. It was a significant advantage for the warriors, and it was convenient for them to establish and take charge.
Nobunaga was a dedicated and religious follower of Buddhism. As a result, he set fire to all of the monasteries and monks and established Jesuit monasteries with their roots in Portugal and Spain.

What is European Feudalism?
According to European feudalism, all the lands were owned by the king. The emperor was the ruler, and the hierarchy below him consisted of nobles.
The vassal and the suzerain are the two parties involved in the land ownership system. The vassal is the higher authority who is the recipient of the land.
The vassal takes position and power through a ceremony called the fief, in which the vassal takes an oath of allegiance to express his faith and promise they will be committed to their services and acts.
The ceremony occurs every time the vassal dies and a new person is about to take charge. The nobility was a class of military people or warriors with armor and weapons led by the knight.

Main Differences Between Japanese and European Feudalism
- Japanese Samurai wore silk, leather, and metal as their armor, whereas the European knight used only metals.
- Japanese laws were influenced by the Chinese, whereas the Romans influenced European feudalism.