There are varieties of fats available in the market. Health depends on the fats you choose to include in your diet. The most widely used fats are Oils and butter.
Choosing the right fats in your daily life is important to stay fit and healthy in today’s world.
Key Takeaways
- Oil is a liquid fat extracted from plants, such as olive, canola, or sunflower, while butter is a solid fat made from churning cream.
- Butter contains saturated fats, cholesterol, and milk solids, whereas oil is cholesterol-free and consists of monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats.
- Oils have higher smoke points, making them suitable for high-temperature cooking, while butter adds rich flavor and texture to baked goods and sauces.
Oil vs Butter
Oil is a fat in liquid form at room temperature, extracted from plants or animals, used widely in cooking for frying, baking, and as a salad dressing. Butter, on the other hand, is a solid dairy product made by churning cream, used as a spread and in baking and cooking.

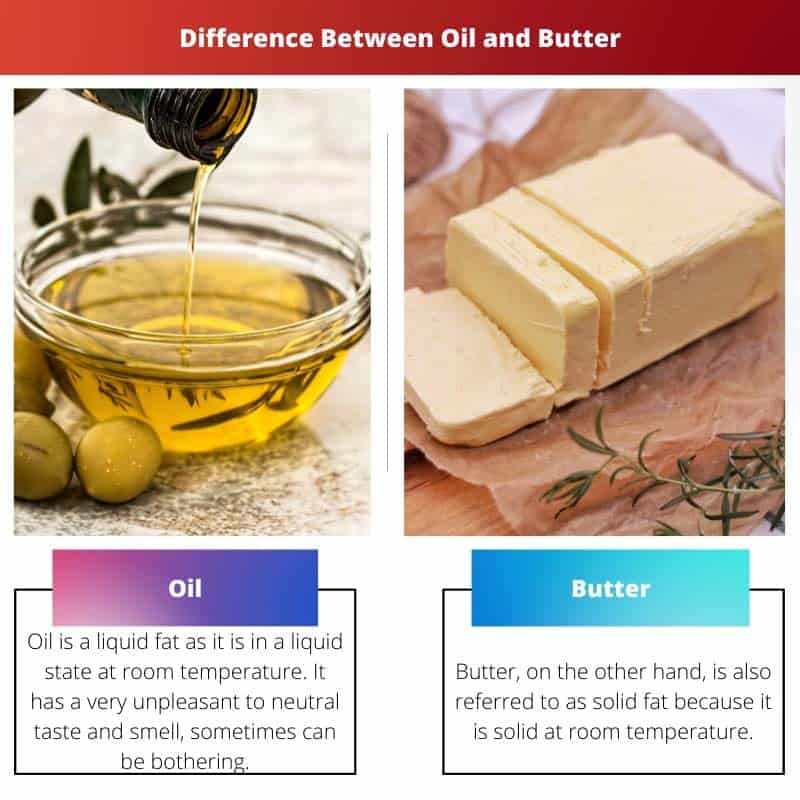
Oil is a liquid fat in a liquid state at room temperature. It has a very unpleasant to neutral taste and smell, and sometimes can be bothering.
However, it can be instrumental in cooking to maximize a particular flavour as the oil does not interfere with other flavours.
On the other hand, butter is also referred to as solid fat because it is solid at room temperature. It is a thick condensed form of a dairy product that is consumed day to day and also used for a variety of various reasons.
Butter is rich in saturated fatty acid;; therefore, it can be taken daily with the meal to gain weight.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Oil | Butter |
|---|---|---|
| Consistency | Liquid at room temperature | Thicker/solid at room temperature |
| Colour | Yellow to colourless (Sometimes depends on the composition or rancidity state of oil) | Yellow to pale yellow |
| Composition | Unsaturated fatty acids | Saturated fatty acids |
| Effect of heat | Food, Cooking, medicinal and dermatological, manufacturing of lubricants, paints, aromatherapy, calming, pain reliever, etc. | The rise in temperature results in melting |
| Use | Food, Cooking, medicinal and dermatological, manufacturing of lubricant, paints, aromatherapy, calming, pain reliever, etc. | Food and sometimes body care |
| Source | Plants, seeds, mineral sources, animals, marine sources, etc. | Milk |
What is Oil?
Oil is made up of unsaturated fatty acids. It is a nonpolar chemical entity that is composed mainly of hydrocarbons.
It has both hydrophobic and lipophilic,,, i.e. it does not mix with water but quickly gets mixed with other oils, oily substances, lipids, and fats.
Oils are combustible; thus, they easily catches flame and it has surface-active property. Most of the oils are unsaturated lipids in a liquid state at room temperature.
Oils can be obtained from plants, seeds, animals, vegetables, or petrochemicals.
They can be either volatile (quickly turns into a gaseous state when kept open at room temperature) or non-volatile (does not quickly turn into another form of matter at room temperature).
It can be used for food, fuel, medicinal purposes, dermatological use, traditional skincare, body care and hair care products, lubrication, pain relief, manufacturing of plastics, paints, and other materials and in religious ceremonies/rituals.
Based on different classifications, criteria oils are classified as natural, mineral, essential, purifying, cooking, volatile, solvents, etc.
It mainly comprises two components which are oleic acid and linoleic acid. Based on the presence and percentage of either one of these oils are classified for their medical and dermatological use.
Some oils have the properties of calming, relaxing, pain reliever, aromatherapy, intense body and hair treatments, etc.

What is Butter?
Butter is a dairy product. It is in the form of a solid to semi-solid state, which is 70-80% fat and 20-25% water produced from the protein and fat components of the churned cream. It consists almost of approximately 80% butterfat.
It is obtained as an inversion of the cream,, i.e. water in an oil type of emulsion,, resulting from the separation of salt and water from the buttermilk and its condensation into a solid form.
Here the protein present in the milk, which is most likely to be casein, acts as an emulsifier, i.e. it is responsible for binding the water and fatty substance together in the butter.
Temperature rise can lead to the breakage of the bond, giving a liquid state of butter.
At room temperature, it is used as a spread over bread, rotis, parathas and other similar food, added as a topping over curries to add extra flavour and creaminess, baking, melted as a condiment, and used as an ingredient in pan-frying, sauce making and another cooking process.
Butter has also proved to be excellent body care and hair care product. When applied topically over the body, they act as an emollient to protect the skin from excessive dryness and promote faster healing.
Its application on hair as a mask for at least 30 minutes helps deal with frizz and restores shine to the follicles.

Main Differences Between Oil and Butter
- Oils are in a liquid state at room temperature,, while butter is in a solid to semi-solid state at room temperature.
- Oil is mostly colourless and neutral to unpleasant taste (except for a few in which the composition of the source of origin has any typical colour or taste to it), while, butter is yellow to pale yellow with a salty or pleasing taste.
- Oils have a wider area of use, whereas, butter is mostly used as food or sometimes for body care.
- Oils are composed of unsaturated fats, therefore, do not add much to obesity, while butter contains saturated fats that can cause weight gain.
- Oils are sometimes combustible and volatile, whereas butter is non-combustible and non-volatile.