Gooseberries and Tomatillos (all in the Physalis family) are delicious and decorative substitutes to gardens cape gooseberries, having their fruit developing in protected lantern-like calyxes that keep the animals and insects at bay.
All three kinds should be grown in the springtime & treated in the same way as tomatoes.
Key Takeaways
- Tomatillos are part of the nightshade family and are native to Mexico, while gooseberries belong to the Ribes family and are native to Europe, Asia, and North America.
- Tomatillos have a papery husk surrounding their fruit, which is green and tart, commonly used in Mexican cuisine. In contrast, gooseberries are round and small and come in different colors, such as green, yellow, and red, with a sweet-tart taste.
- Tomatillos are commonly used in dishes such as salsa verde, while gooseberries are used in pies, jams, and other desserts.
Tomatillo vs GooseBerry
Tomatillos are a type of berry native to Mexico, are part of the nightshade family, and are green, round, and covered with a papery husk. Gooseberries are a type of small, tart berry that belongs to the Grossulariaceae family, are smaller than tomatillos and have a similar green color.

Tomatillos have such a bright, tangy flavour with citrus nuances and are used in a variety of Mexican green recipes. If a person ever tries Enchiladas Suizas or Salsa Verde, they’re certainly acquainted with tomatillos’ flavour. Purchase those with taut green skin inside, though.
They are past their peak if they are pallid or squishy.
The appetizing fruit produced by gooseberry plants is known as gooseberries. The European gooseberry, as well as the American gooseberry, are also the main sources of such berries.
They weren’t to be mistaken with several other fruits named “gooseberry,” such as cape or Chinese gooseberries, which do not fit underneath the horticulture categorization of real berries.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Tomatillo | Gooseberry |
|---|---|---|
| Growth Habitat | Tomatillo plants reach a height of 3 to 4 feet and a width of 3 to 4 feet. These plants can be grown from seeds with ease. | Cape gooseberries grow to be 2 to 3 feet in height and 3 to 4 feet broad, with several spreading stems. |
| Fruit | The 1 to 2 mm thickness tomatillo fruits grow to a green, yellow-green, or purple colour. | When fully mature, the Cape gooseberry fruits become golden or pale yellow and have a melon-like flavor. The husks dry out, open, and the 3/4-inch fruits fell to the floor. |
| Uses | Gazpacho, guacamole, and salsas, particularly salsa verde, contain tomatillos. | Raw cape gooseberries are being used in appetizers and therefore are nicer. |
| Size | Tomatillo are larger is size. | Whereas, Gooseberry is similar but smaller in size. |
| Plant Genus | Although they both are from the same plant genus, Tomatillo is a fruit. | On the other hand, gooseberry seeds turn into a berry after ripening. |
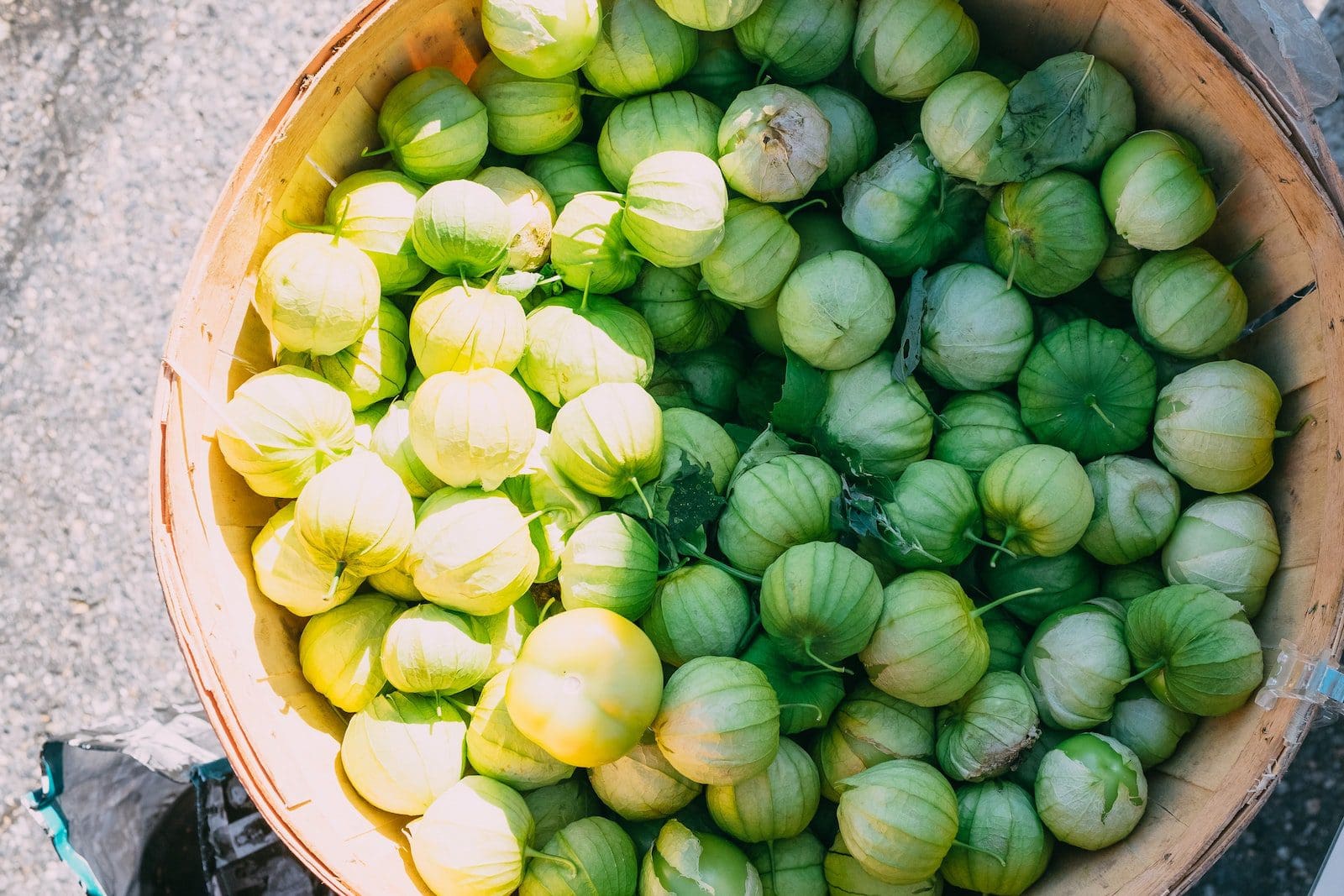
What is Tomatillo?
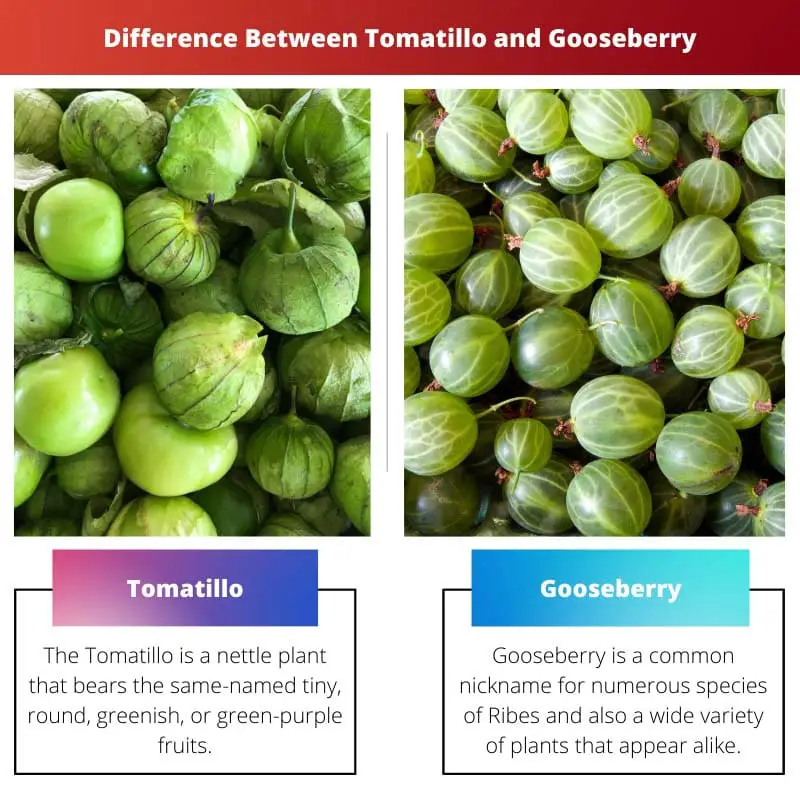
The Tomatillo, known as the Mexican husks tomato, is a nettle plant that bears the same-named tiny, round, greenish, or green-purple fruits. Tomatillos were first planted in Mexico during the pre-Columbian period.
They are a mainstay of Mexican food and can be eaten or consumed raw in a range of ingredients, including salsa verde.
The term Tomatillo is derived from the French word tomatillo, which means “small tomato.” This fruit is used in a variety of cuisines, most notably in Mexican food, stews, salsas, and chutneys. The shrub is mainly cultivated in Mexico, followed by the United States.
The plant’s appearance resembles that of an underdeveloped tomato. It can also be consumed both raw and cooked. Tomatillo has a low caloric intake, making it a great choice for those on dieting.
These plants cannot be cultivated independently and require pollination from at least two or three different varieties of the same vegetation. The fruits are also known by some other names, such as Mexican green tomato, huge Tomatillo, Mexican ground Cherry, miltomate, and many others.
| # | Preview | Product | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |

| La Costeña Green Tomatillos (3-Pack) | Check Price on Amazon |
| 2 |

| La Costena Green Tomatillos, 28 oz | Check Price on Amazon |

What is Gooseberry?
Gooseberry is a common nickname for numerous species of Ribes (that also encompasses currants) and also a wide variety of plants that appear alike.
The berries of the species Ribes (also known as Grossularia) are delicious and come in a variety of colors, including green, red, magenta, yellowish, white, and black.
The gooseberry is native to much of Europe and western Asia, where it can be cultivated wild in alpine woodlands and rocky forests in the lower area between France east to the Himalayas & peninsular India.
It’s common in British copses and hedgerows, as well as around historic ruins. However, the gooseberry has indeed been farmed so extensively that it’s impossible to tell the difference between wild and feral plants and whether the gooseberry belongs through into the island’s original flora.
The gooseberry, as abundant as it is now on a few of the lower elevations of both the Piedmont and Savoy Alps, is unknown to the Romans, although it might be referenced in a vague section of Plautus.
Gooseberries are native to many regions of Europe, and Western humans grow them as insect homes or for the tasty fruits themselves. For both residential and business use, many varieties have been created.

Main Differences Between Tomatillo and Gooseberry
- Tomatillo plants reach a height of 3 to 4 feet and a width of 3 to 4 feet. These plants can be grown from seeds with ease. Cape gooseberries grow to be 2 to 3 feet in height and 3 to 4 feet broad, with several spreading stems.
- The 1 to 2 mm thickness tomatillo fruits grow to a green, yellow-green, or purple color. When fully mature, the Cape gooseberry fruits become golden or pale yellow and also have a melon-like flavour. The husks dry out and open, and the 3/4-inch fruits fall to the floor.
- Gazpacho, guacamole, and salsas, particularly salsa verde, contain tomatillos. Raw cape gooseberries are being used in appetizers and therefore are nicer.
- Tomatillo is larger in size. Whereas, Gooseberry is similar but smaller in size.
- Although they both are from the same plant genus, Tomatillo is a fruit. On the other hand, gooseberry seeds turn into a berry after ripening.
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4611412/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0023643807002745



The history and origin of tomatillos and gooseberries was fascinating to learn about. It provides a greater context for their significance.
I completely agree, understanding the origins of these fruits adds a deeper layer of appreciation for them.
Absolutely, this article has broadened my understanding of the cultural significance associated with tomatillos and gooseberries.
I appreciate the detailed comparison table. It makes it easy to understand the specific characteristics of tomatillos and gooseberries.
The growth habitat and uses section was particularly enlightening. I’ve learned a lot about these plants.
Agreed, having a clear, concise comparison table is very helpful in understanding the nuances within these fruits.
I had no idea that gooseberries have such a wide variety of colors. Learning about their native regions was also enlightening.
The diversity of gooseberry colors is truly fascinating. It’s wonderful to learn about horticulture in such detail.
Absolutely, the natural habitats of these fruits provide a deeper understanding of their cultural and geographical significance.
This article provided a wealth of knowledge about tomatillos and gooseberries. It’s always a pleasure to delve into the nuances of horticulture.
Absolutely, the depth of information in this article is truly commendable.
Thanks for this comparison. It’s very interesting to learn about the differences and similarities between tomatillos and gooseberries.
I agree, this was a very informative read. It’s always great to expand our knowledge in horticulture.
The details provided about the growth habitat and size of tomatillos and gooseberries was excellent. It’s great to learn about the intricacies of these plants.
I found the comparisons between tomatillos and gooseberries to be very educational. It’s always enriching to learn about different fruits and their uses.
I second that, the comprehensive nature of this comparison has expanded my understanding of horticulture.
Agreed, the depth of knowledge provided in this article is commendable.
I never knew that tomatillos were a mainstay in Mexican cuisine. This was an eye-opening article. Thank you.
Learning about the uses of tomatillos in Mexican cuisine and the various desserts made from gooseberries was extremely interesting.
I completely agree, the versatility of tomatillos and gooseberries presents a myriad of culinary possibilities.
Absolutely, the culinary applications of these fruits are vast and captivating.
The informative section about the growth habitat and uses of tomatillos and gooseberries was very insightful. Thank you for sharing this knowledge.
I couldn’t agree more. Understanding the specific characteristics of these fruits opens up new avenues for culinary exploration.