Infections of the lungs can develop into serious complications. Vector germs and organisms cause most infections of the lungs.
There are several types and levels of severity depending upon the cause of the infections. The two main types of lung infections are pneumonia and atypical pneumonia.
Key Takeaways
- Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. In contrast, atypical pneumonia is caused by certain bacteria not associated with pneumonia.
- Pneumonia presents with symptoms such as cough, fever, and difficulty breathing, while atypical pneumonia may present with milder symptoms such as headache, sore throat, and fatigue.
- Pneumonia can be treated with antibiotics, while atypical pneumonia may require a different type of antibiotic or antiviral medication.
Pneumonia and Atypical Pneumonia
Pneumonia is a common respiratory infection that can be caused by various types of bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Atypical pneumonia, also known as walking pneumonia, is a milder form of pneumonia that is caused by a specific group of bacteria, such as Mycoplasma pneumoniae or Chlamydophila pneumoniae.

Pneumonia is an infection caused by several vector germs, such as viruses, bacteria, and fungi. The infection mainly affects the air sacs of the kings and causes inflammation in one or both of the lungs.
The symptoms of pneumonia are similar to cold and flu.
On the other hand, atypical pneumonia is also called walking pneumonia. It is an infection caused by vector bacteria of many kinds.
The symptoms of atypical pneumonia are mild. Sometimes there are no distinct symptoms in atypical pneumonia. The patients recover quickly.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Pneumonia | Atypical Pneumonia |
|---|---|---|
| Cause | Caused by numerous vector organisms like viruses, bacteria, fungi | Caused by three major bacteria called Mycoplasma pneumonia, Chlamydophila pneumonia, and Legionella pneumophila and rarely by the bacteria Chlamydophila psittaci |
| Symptoms | Chest pain, fatigue, cough and fever, confusion, nausea, diarrhoea, vomiting | Persistent cough, fever, cold sweats, chills, headache, difficulty in breathing, aches and pains in the muscles and joints |
| Diagnosis | Blood tests, chest X-ray, pulse oximetry, a test to check sputum, arterial blood gas tests, bronchoscopy, CT scan, and a pleural fluid culture | Previous medical history, a physical exam of pulse, breathing rate, and oxygen levels. Some cases even require CT scans and blood tests. |
| Treatment | Prescription of antibiotics, oxygen therapy, fluids, or breathing treatments by a doctor based on the condition | Antibiotics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and other medications, depending on the condition |
| Prevention | Taking regular vaccination for pneumonia and whooping cough. Leading a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet, withdrawing from drugs and addiction, and maintaining distance from other patients. | Maintaining distance from people with pneumonia, regular washing of hands, cleanliness and sanitization in the surrounding, and intake of a healthy diet with plenty of fluids |
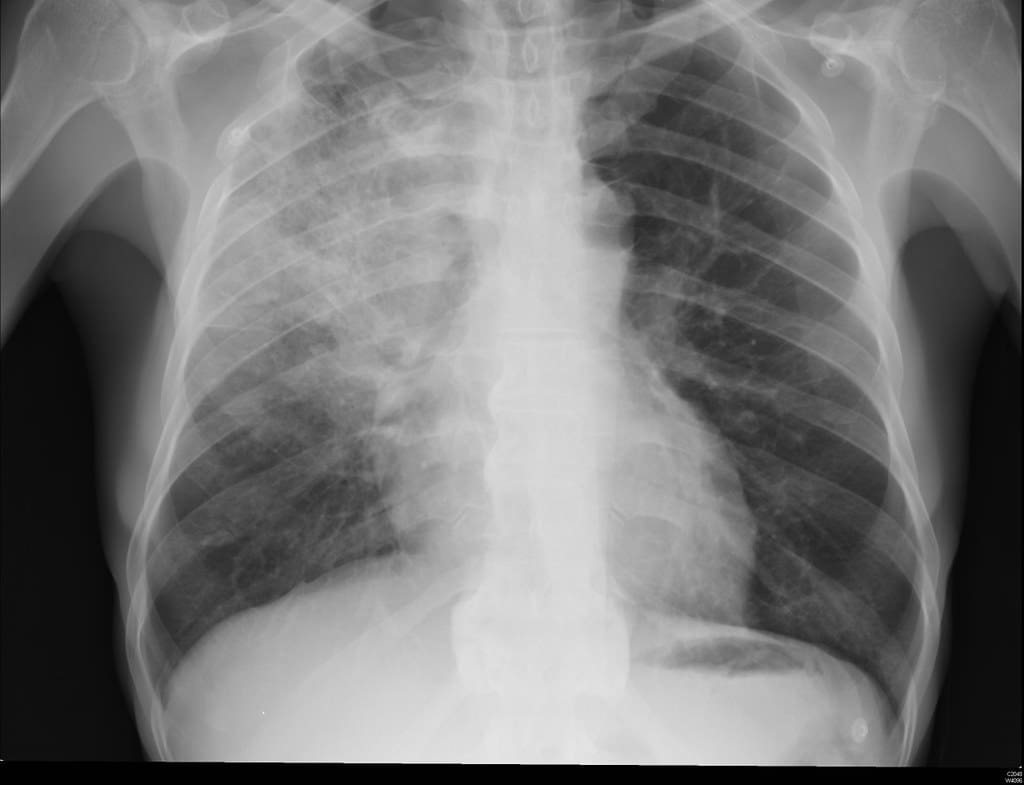
What is Pneumonia?
Pneumonia is an infection that can inflame the air sacs of the lungs. It is a common infection.
The sacs fill with pus or fluid, called purulent material, which can cause cough, fever, difficulty in breathing, and chills.
Numerous vector organisms like viruses, bacteria, fungi, and other such organisms can cause pneumonia.
The symptoms of pneumonia are mild at the beginning which can later end up being serious and life-threatening if not diagnosed at the right stage.
The common symptoms are chest pain, fatigue, cough and fever, confusion, nausea, diarrhoea, vomiting, and other symptoms similar to cold and flu.
Pneumonia mainly affects the age of groups of infants and young children or senior citizens over the age of 65. Any individual with a weakened immune system is susceptible to pneumonia.
Pneumonia is contagious if the organisms from the host body affect another healthy body. However, pneumonia caused by fungi is not contagious.
People with a history of other diseases, chemotherapy, transplant of organs, or other neurological conditions can get severely affected by pneumonia.
Lifestyle habits or addiction to cigarettes or alcohol also can increase the risk of pneumonia.
Pneumonia can lead to several complications like bacteremia, trouble breathing, fluid build-up, or even lung abscess.
A professional or a doctor can determine the cause and then prescribe antibiotics, oxygen therapy, fluids, or breathing treatments based on the cause of pneumonia.
The recovery time depends on the severity of the condition.
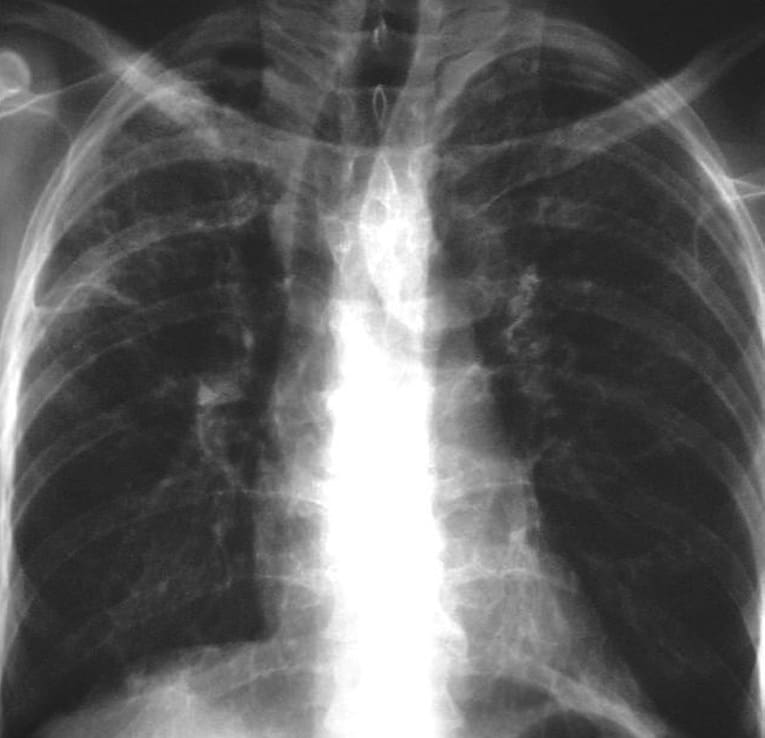
What is Atypical Pneumonia?
Atypical pneumonia is also commonly known as walking pneumonia. It is also an infection of the respiratory system. Atypical pneumonia affects the lower respiratory tract.
Bacteria can cause atypical pneumonia. The most common bacterial atypical pneumonia is Mycoplasma, with common severity and condition as ear and sinus infections.
Atypical pneumonia is a milder version of actual pneumonia. Some people do not even develop any distinct differential symptoms and carry out their daily tasks with little or no difficulty.
Some patients do develop mild symptoms like a low-grade fever, sore throat, headache, and even earache.
Infants, senior citizens, patients with a chronic respiratory condition, weak immunity, and addicts of drugs, cigarettes, or alcohol are most susceptible to atypical pneumonia.
Atypical pneumonia outbreaks can occur, which has the potential to affect a large mass at a given period. The symptoms appear at a slow pace than pneumonia.
Atypical pneumonia can even cause complications like Legionnaire’s disease. Some patients have even developed rashes and ear infections after developing atypical pneumonia.
Visiting the doctor or professional in the slightest appearance of symptoms is essential to diagnose the infection.
The doctor prescribes antibiotics and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Intake of plenty of fluids such as water or herbal tea provides relief.
Adequate sleep and rest work wonders in the recovery period.
Main Differences Between Pneumonia and Atypical Pneumonia
- Pneumonia is an infection caused by germs and vector organisms like viruses, bacteria, and fungi, while atypical pneumonia is an infection caused by different types of bacteria.
- The symptoms of pneumonia are severe, while the symptoms of atypical pneumonia are mild.
- Patients with or after pneumonia feel extreme fatigue, while patients with atypical pneumonia do not feel extreme weakness and fatigue.
- Most cases of pneumonia require hospitalization, while cases of atypical pneumonia do not require hospitalization.
- Pneumonia can cause serious complications like bacteremia, trouble breathing, fluid build-up, or even lung abscesses while atypical pneumonia does not cause many serious complications and resolve faster.



