The human body has so many processes going on inside the body, and it is very complex. There are so many diseases that can be caused only by Women. Such two Uterine tumours, Polyps and Fibroids, cause health issues in women.
Polyps and Fibroids are both uterine outgrowths and are very similar to recognize but have certain differences in their nature and symptoms.
Key Takeaways
- Polyps are abnormal tissue growths that can develop on the lining of organs, while fibroids are noncancerous tumors that grow in or on the uterus.
- Polyps can occur in various organs, such as the colon or nose, whereas fibroids are specific to the uterus.
- Treatment options for polyps and fibroids may vary, but both conditions can cause symptoms that require medical attention.
Polyp vs Fibroid
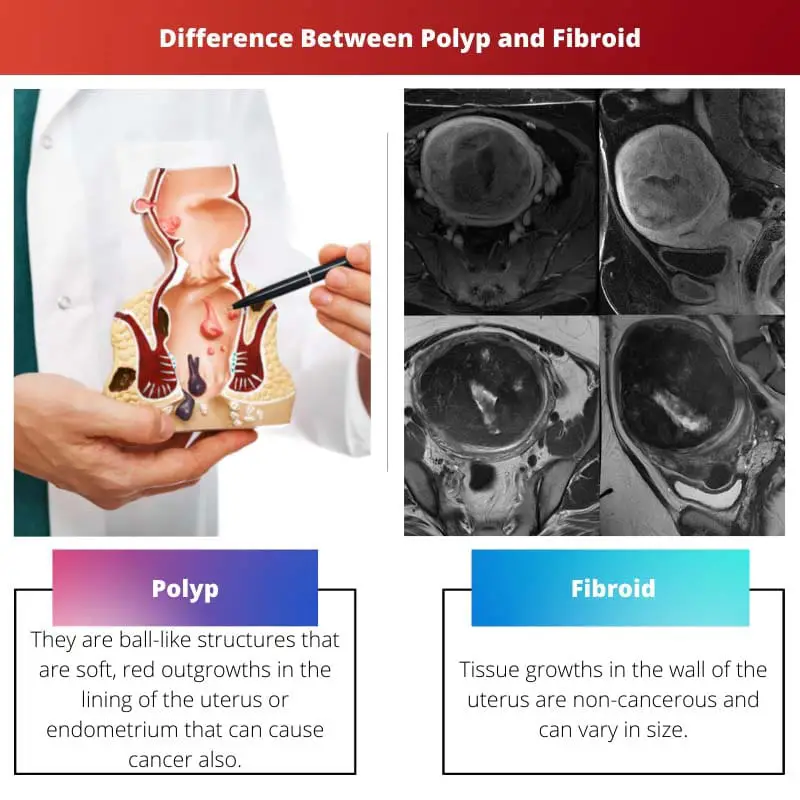
Polyps are life-threatening, cancerous growths that form ball-like structures in the lining of the uterus. They can cause vaginal bleeding, bladder issues and irregular menstruation. Fibroids are thick muscle tissues that grow on the walls of the uterus. They are non-cancerous and may cause lower back pain, pelvic pain or heavy bleeding during menstruation.
Polyps are more dangerous and are ball-like outgrowths that grow in the walls of the uterus. They need serious medical attention and can escalate if not properly treated.
They have risk factors such as diabetes, genetics, PCOS, and ovarian cancer. They happen to women between the ages of 40 to 50.
Fibroids are outgrowth tissues in the wall of the uterus which are not considered very dangerous and life-threatening.
Estimated to happen 1 in every 5 women, Fibroids are found in women who are aged over 30, and sometimes they are asymptotic. They can, however, likely cause miscarriage and infertility.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Polyp | Fibroid |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | They are ball-like structures that are soft, red outgrowths in the lining of the uterus or endometrium that can cause cancer also. | Tissue growths in the wall of the uterus are non-cancerous and can vary in size. |
| Composition | They are made up of endometrial tissues that are the lining of the uterus. | They are made of muscle tissues that are thick. |
| Treatments | Polyps need immediate medical attention, and medical treatments are required for them but not a long-term solution. Surgery is a long-term option to remove polyps. | Fibroids are not a very serious issue and need treatments such as hysterectomy that is a non-surgical treatment, and Uterine fibroid embolization (UFE) treatment. |
| Effect | They are more dangerous and cause serious health issues such as bladder issues, abnormal menstrual cycles, vaginal bleeding, etc. | They are not life-threatening diseases, and they cause health issues such as lower back pain, heavy bleeding during periods, pelvic pain, etc. |
| Risks | Major risks include Genetics, high fat diet, Diabetes, Ovarian cancer, PCOS, etc. | Major risks include Genetics, obesity, vitamin D deficiency, low consumption of vegetables, etc. |
What is Polyp?
Polyps are made up of endometrial tissues and are most common in females belonging to the age group over the age of 20. They are rare for females who don’t menstruate.
They are considered dangerous and life-threatening as they can cause cancer. They can be one or several in the woman’s body.
They can cause many health issues, such as bladder issues, cancer, abnormal periods, vaginal bleeding, etc.
It is not yet certain the reasons behind it, but they can be developed due to increased estrogen levels or by certain medications. They need a surgical operation to get it removed as a long-term result.
What is Fibroid?
The fibroid is a tumour that is made from thick muscle tissues as soft, red outgrowths within the uterus wall. They extend into the uterus cavity and sometimes on the surface of the uterus.
Three kinds of Fibroids are Submuscosal, Subserosal, and Intramural. Also referred to as Leiomyomas, myomas, and tumours, fibroids are non-cancerous.
1 in 5 women of childbearing age have uterine fibroids. It is found mostly in women over 30 years of age and rarely happens in the age group under 20.
They are not life-threatening diseases but can cause infertility and miscarriage for women who sometimes don’t know their symptoms.
They cause issues like bleeding, discomfort, pelvic pain, etc. They don’t need surgical treatment to remove or treat them.
Main Differences Between Polyp and Fibroid
- Polyps are more dangerous and can cause cancer in the uterus, whereas Fibroid is not life-threatening and does not cause cancer.
- Polyps are softer, ball-like outgrowths in the lining of the womb or cervix, whereas Fibroid is tissue outgrowths in the walls of the uterus.
- Risk factors for Polyps are genetics, high-fat diets, diabetes, PCOS, etc., whereas risk factors for Fibroids include obesity, low vegetable consumption, Vitamin D deficiency, etc.
- Polyps can cause serious health issues such as cancer, bladder issues, vaginal bleeding, pain, etc., whereas Fibroid can result in less serious health issues such as lower back pain, heavy bleeding, and pelvic pain.
- Polyps are more serious and dangerous, thus need immediate medical attention, and can be treated by doing surgery for a long-term solution, whereas Fibroids are less dangerous and sometimes asymptotic. They can be treated using non-surgical options.
- Polyps are made from endometrial tissues, whereas Fibroids are made up of thick muscle tissues.