Pulse pressure and blood pressure are vital body measurements taken to understand the efficiency and circulating capacity of the blood-pumping system.
Both the pressure values have a range between which the vitals can be considered normal or not an emergency sign.
Having an overlapping value for the two pressures is rare as the normal range varies for both. The measuring goal for both is different as they both indicate two different body signs.
Key Takeaways
- Pulse is the rhythmic expansion and contraction of blood vessels due to the heart’s pumping action, while blood pressure is the force exerted by blood against the walls of blood vessels.
- Pulse rate measures the number of heartbeats per minute, whereas blood pressure is measured as systolic pressure over diastolic pressure.
- A healthy pulse rate varies depending on age and fitness level, while normal blood pressure is around 120/80 mm Hg.
Pulse vs Blood Pressure
Pulse refers to the rhythmic expansion and contraction of the arteries that occurs with each heartbeat. Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps blood throughout the body. It is measured using a blood pressure cuff placed around the arm.

Many other synonyms in the medical fraternity define pulse pressure. The most commonly used term is the heart rate which is the number of times the heart contracts and relaxes to release blood into the vessels.
Pulse pressure depends on many external factors of the patient, including their lifestyle and eating habits.
If there are slight variations in the normal value, it need not be taken seriously as it might also be an indication of a healthy individual. But this is only if the pressure value is below the normal range and not above.
Blood pressure originally gives the pumping efficiency of the arteries and veins along with the minute capillaries.
Blood pressure is always measured with an upper limit and a lower limit which are both just values indicating the pressure sustained by the vessels at different times, such as when the heart is contracting or even relaxing.
Frequent variations in both the upper and lower limit of blood pressure range are serious indicators of a health crisis.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Pulse Pressure | Blood Pressure |
|---|---|---|
| Symptoms Shown Due to Variations | Breathlessness, fatigue, nausea, etc. | Barely shows any symptoms at the time of reading variation |
| Is it fatal at the Time of Variation | Not always | Is called a silent killer |
| Lower Value Indicates | Could be signs of a healthy lifestyle | It’s better to be in the normal range |
| Devices Used to Measure | Heart rate monitor | Sphygmomanometer |
| Numbers in Reading | A single numerical value | Two numerical separated by “slash” |
What is Pulse Pressure?
Pulse pressure is the same as heart rate became they both technically give the heart contractions and relaxations in a given minute.
The major variations seen in pulse pressure are when an individual undergoes major stress-inducing situations or while exercising.
In both these cases, the pulse pressure reduces and might even go above the upper limit of the normal range.
While sleeping or even while digesting ingested food, there is a decrease in the pulse pressure of the body.
During sickness or maybe an intra-body infection, or when an individual faints, there are high chances of reduced pulse pressure.
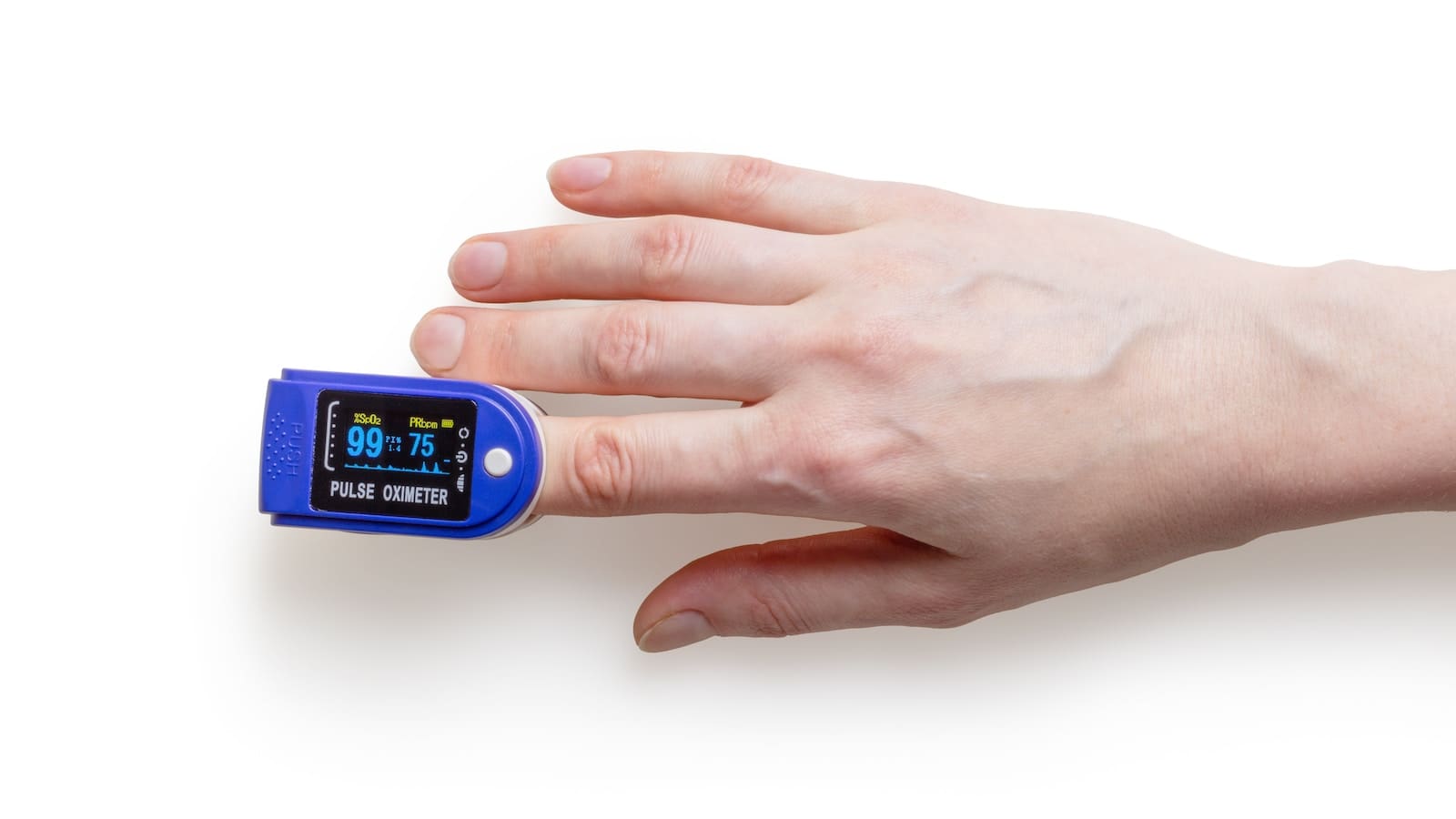
The normal pulse pressure for an adult individual at rest is 60-100 per minute.
If the measured pulse pressure turns out to be abnormal, it can be an indicator of diseases that might concern heart functioning.
The medical term for such heart functional irregularities is arrhythmia. There are different forms of arrhythmia.
One of the most commonly seen arrhythmic conditions is atrial fibrillation which affects the atrial functioning over ventricular activities.
Atrial fibrillation increases the pulse rate of an adult at rest to such a high value that there might be risks of stroke.
On the other hand, the pulse rate could also be slow or lower than normal. This could also, on certain occasions, be a cause of concern.
The slow pulse rate can be termed a heart block.
The reason for a heart block is a failure of the electrical circuits that regulate rhythmic heart action.
The circuit failures may not affect all the electrical control centres of the heart. Just a few.
Lack of all the circuits working together as a unit causes a reduction in the heart pumping efficiency.
It can also mean the heart missing out on a few heartbeats at an interval. Murmurs of the heart seen in newborn infants are also a result of heart block.
The symptoms of heart block are tiredness, fatigue, and collapsing tendencies.
But more than not, a lower pulse pressure shows that an individual is healthy and engaged in certain activities.
They might be in better shape and have regular exercises with a pulse pressure of 40-60 per minute.
What is Blood Pressure?
The technical meaning of blood pressure is the blood-carrying efficiency of the blood vessels, the arteries and veins.
There could also be variations in blood pressure depending on the external life factors of the individual under consideration.
During exercise exertion or when stressed, the blood pressure tends to rise above the normal limit.
At total rest, especially while asleep or digesting food, the blood pressure need not be high and lowers below the normal range.
The blood pressure reduces at times of infection or even in a sickly situation in life.
The natural reduction and increase of BP in the above-mentioned cases can be considered normal because no major external factors take make much difference in them.
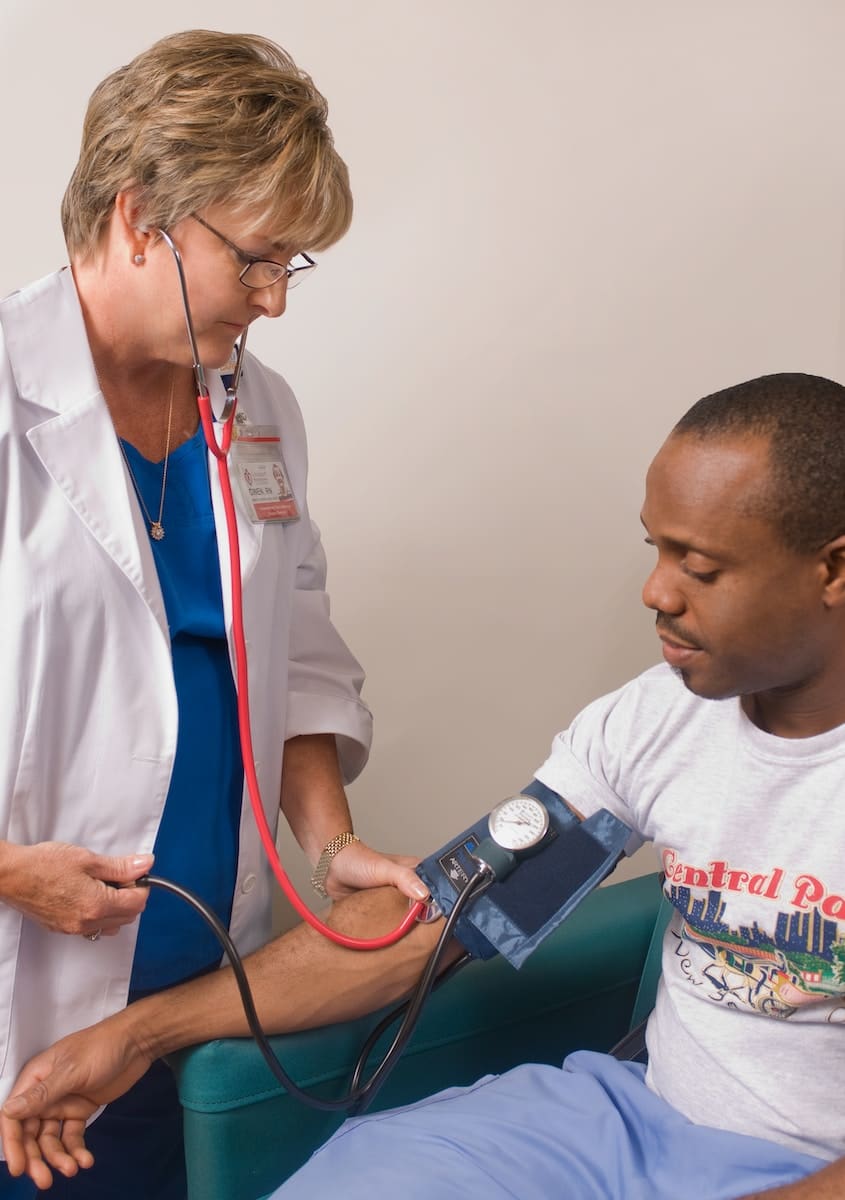
Blood pressure can’t be measured manually by placing the hand over a certain neural point. A certain device is needed to measure the BP.
A device like a blood pressure cuff that is wrapped around the hand is used to calculate the blood pressure.
They are also called a sphygmomanometer. But owing to the big word, it’s always referred to as the BP cuff.
There are both manual and electrical cuffs by which blood pressure can be calculated.
The manual cuff requires the user to pump in air to inflate the cuffed part of the hand.
On the other hand, the electrical cuff inflates with the push of a button.
The release of air pressure from the cuffed part enables the user to read the pressure value.
Blood pressure is always presented by a two-number system.
The first of the two numbers is always the higher value and shows the systolic pressure.
This is the pressure in the blood vessel as the heart pumps out blood. This is the heart contraction pressure.
The second number is a lower value and is called the diastolic pressure.
This pressure measures the pressure released by the heart while it is in a relaxed state.
By this, the normal blood pressure can be given as 120/80 mmHg. The mmHg is the measuring unit.
High BP values can be considered the silent killer due to their lack of showing symptoms.
Main Differences Between Pulse and Blood Pressure
- While pulse pressure gives the number of times the heart beats in a minute, blood pressure gives a different value measuring the strength and efficiency of the blood vessels in pumping the blood.
- While blood pressure is difficult to measure, pulse pressure is easier, with many checking points spread all over the body.
- The device used to measure blood pressure is called a sphygmomanometer, while pulse pressure can be calculated by a device called a heart rate monitor.
- Pulse pressure has only a single numeric value giving the normal range, whereas blood pressure has two numerical values for a single reading.
- Higher values of blood pressure can be a killer or fatal, whereas it is otherwise for pulse pressure and not necessarily fatal.




