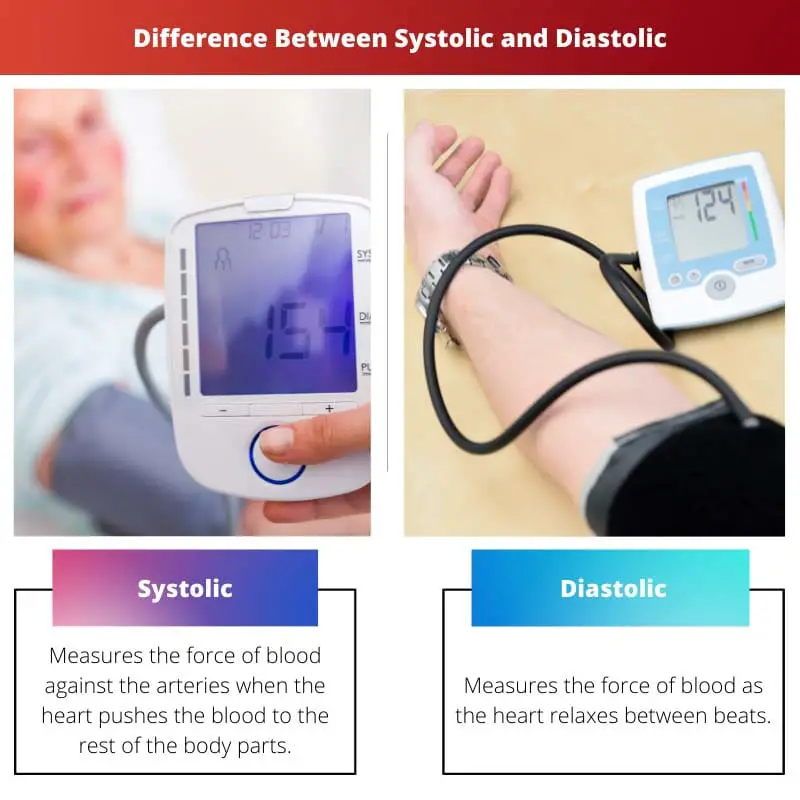
Systolic blood pressure represents the maximum force exerted on artery walls during heart contraction. In contrast, diastolic pressure denotes the minimum pressure during the heart’s relaxation phase, collectively providing a comprehensive measure of cardiovascular health. The systolic-diastolic difference, known as pulse pressure, reflects the dynamic changes in blood vessel elasticity and is a key indicator of cardiovascular function.
Key Takeaways
- Systolic blood pressure represents the highest pressure in the arteries when the heart contracts, pumping blood into the arteries.
- Diastolic blood pressure is the lowest pressure in the arteries when the heart relaxes between beats, allowing the heart to refill with blood.
- The main difference between systolic and diastolic blood pressure is their measurement points in the cardiac cycle, with systolic pressure occurring during heart contraction and diastolic pressure during heart relaxation.
Systolic vs Diastolic
Systolic blood pressure is the pressure exerted when blood is ejected into arteries. Normal systolic blood pressure is 120 mmhg or below. While Diastolic blood pressure is the pressure blood exerts within arteries between heart beats. Normal diastolic blood pressure is 80 mmhg or below.

However, the above is not the only difference. A comparison between both the terms on specific parameters can shed light on subtle aspects:
Comparison Table
| Feature | Systolic Pressure | Diastolic Pressure |
|---|---|---|
| Phase of Heartbeat | Contraction (pumping) | Relaxation (filling) |
| Measurement | Force exerted by the heart against the arterial walls during contraction | Pressure in the arteries when the heart is at rest and filling |
| Normal Range | 120-140 mmHg | 80-90mmHg |
| Significance | Indicates the pumping strength of the heart | Reflects the resistance of the blood vessels |
| Impact on Health | High systolic pressure can increase risk of heart attack, stroke, and kidney disease | Low diastolic pressure can be a sign of dehydration, shock, or heart failure |
| Factors influencing | Age, activity level, stress, diet, medications | Same as systolic, but also influenced by arterial stiffness |
| Monitoring | Regular blood pressure monitoring is crucial for managing cardiovascular health | Can be monitored alongside systolic pressure to provide a complete picture of heart health |
What is Systolic?
Systolic blood pressure is a key component of measurements, representing the higher of the two numbers commonly used to express blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force exerted by circulating blood against the walls of the arteries. It is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and is conveyed as a ratio of two values: systolic over diastolic pressure.
1. Definition and Measurement: Systolic blood pressure is the higher value in a blood pressure reading and is associated with the contraction of the heart’s left ventricle, which pumps blood into the arteries. During this phase, the pressure in the arteries increases as blood is pushed into the circulatory system. Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury, and a typical blood pressure reading is expressed as systolic over diastolic pressure (e.g., 120/80 mmHg).
2. Significance in Blood Pressure Readings: The systolic value is crucial for assessing the force exerted on the arterial walls when the heart contracts. It is called the “top” number in a blood pressure reading. For example, in a blood pressure reading of 120/80 mmHg, 120 represents the systolic pressure. Elevated systolic blood pressure is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular diseases and other health complications.
3. Relationship with Diastolic Pressure: The diastolic pressure, represented by the lower number in a blood pressure reading, reflects the arterial pressure during the heart’s relaxation phase between beats. The combination of systolic and diastolic pressures provides a comprehensive understanding of an individual’s cardiovascular health.
4. Health Implications: High systolic blood pressure, especially when consistently elevated, can lead to a range of health issues, including an increased risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular problems. Maintaining a healthy blood pressure range is vital for overall cardiovascular well-being, and healthcare professionals use blood pressure readings to assess an individual’s risk and recommend appropriate interventions or lifestyle modifications.
What is Diastolic?
Diastolic blood pressure is one of the two components used to measure blood pressure, the other being systolic blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force exerted by circulating blood on the walls of blood vessels, and it is expressed in millimeters of mercury (mmHg). Diastolic blood pressure specifically refers to the pressure in the arteries when the heart is at rest between beats, during the diastolic phase of the cardiac cycle.
Understanding the Cardiac Cycle
The cardiac cycle consists of two main phases: systole and diastole. During systole, the heart contracts to pump blood into the arteries, leading to an increase in blood pressure known as systolic pressure. Diastole, on the other hand, represents the resting phase of the heart when it refills with blood, and the pressure in the arteries decreases, reaching its lowest point, which is the diastolic blood pressure.
Measurement and Interpretation
Diastolic blood pressure is expressed as the second number in a blood pressure reading, for example, in the format 120/80 mmHg. In this reading, 120 represents the systolic pressure, and 80 represents the diastolic pressure. A normal blood pressure reading is around 120/80 mmHg. Elevated diastolic pressure, when consistently higher than the normal range, may indicate hypertension or other cardiovascular issues.
Clinical Significance
Diastolic blood pressure is crucial for assessing overall cardiovascular health. While systolic pressure is emphasized in discussions about hypertension, an elevated diastolic pressure can also be a significant health concern. Consistently high diastolic blood pressure may contribute to conditions such as heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular problems. Healthcare professionals use blood pressure readings, including diastolic values, to evaluate the risk of these health issues and to guide interventions for maintaining or improving cardiovascular health.
Factors Influencing Diastolic Blood Pressure
Various factors can influence diastolic blood pressure, including age, lifestyle, genetics, and underlying health conditions. As individuals age, there is a natural tendency for diastolic blood pressure to increase. Unhealthy lifestyle choices, such as a poor diet, lack of physical activity, and smoking, can contribute to elevated blood pressure. Additionally, conditions like diabetes and kidney disease can impact diastolic blood pressure regulation.
Main Differences Between Systolic and Diastolic
- Definition:
- Systolic Blood Pressure (SBP): This is the higher of the two numbers in a blood pressure reading. It represents the pressure in the arteries when the heart contracts or beats, pumping blood into the circulation.
- Diastolic Blood Pressure (DBP): This is the lower of the two numbers in a blood pressure reading. It represents the pressure in the arteries when the heart is at rest between beats, or during the relaxation phase.
- Measurement Values:
- Systolic Blood Pressure (SBP): It is the maximum pressure exerted on the arterial walls during the heart muscle contraction.
- Diastolic Blood Pressure (DBP): It is the minimum pressure in the arteries when the heart is at rest or between beats.
- Phases of the Cardiac Cycle:
- Systolic Blood Pressure (SBP): Corresponds to the systolic phase of the cardiac cycle when the heart is contracting.
- Diastolic Blood Pressure (DBP): Corresponds to the diastolic phase of the cardiac cycle when the heart is relaxing and refilling with blood.
- Representation in Blood Pressure Reading:
- Blood Pressure Reading (mm Hg): Blood pressure is expressed as two numbers, with the systolic pressure over the diastolic pressure. For example, a blood pressure reading might be written as 120/80 mm Hg, where 120 is the systolic pressure, and 80 is the diastolic pressure.
- Clinical Significance:
- Systolic Blood Pressure (SBP): Elevated systolic blood pressure is associated with increased risk of cardiovascular events, especially in older adults.
- Diastolic Blood Pressure (DBP): Elevated diastolic blood pressure is considered a risk factor for cardiovascular disease, but it tends to be more relevant in younger individuals.
- Blood Pressure Pulse Pressure:
- Pulse Pressure: The numerical difference between the systolic and diastolic blood pressure values. A wider pulse pressure may indicate stiffer arteries.
- https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/articlepdf/195749/JOC21616.pdf
- https://www.nature.com/articles/nm1394
- https://journals.lww.com/jgpt/00004872-200208000-00001.fulltext

The article’s in-depth analysis of systolic and diastolic blood pressure is insightful and educative. It is an essential read for individuals seeking to gain a comprehensive understanding of cardiovascular health.
The article effectively captures the essence of systolic and diastolic blood pressure, underscoring their relevance in evaluating cardiovascular function and the associated health risks.
Absolutely, the article’s focus on the significance of pulse pressure and the implications of high systolic and low diastolic pressure is valuable for promoting awareness of cardiovascular health.
An insightful and informative article, shedding light on the critical parameters that differentiate systolic and diastolic blood pressure and their implications for overall health.
Indeed, the article’s emphasis on the significance of monitoring and managing blood pressure for cardiovascular well-being is commendable and educative.
The detailed comparison between systolic and diastolic blood pressure along with the explanation of their significance is enlightening. It provides a clear understanding of these vital physiological measures.
Agreed, this article effectively breaks down the complex concepts of blood pressure and its health implications, making it accessible to a wide audience.
The meticulous analysis of systolic and diastolic blood pressure in this article offers valuable insights for individuals seeking to monitor and manage their cardiovascular health.
A well-researched and articulated article, shedding light on the dynamic changes in blood vessel elasticity and their significance in assessing cardiovascular function.
The clarity and depth of information in this article on systolic and diastolic blood pressure are commendable. It serves as an educational tool for readers seeking to enhance their knowledge of cardiovascular health.
Absolutely, the article’s comparison and detailed explanations contribute to a greater understanding of key indicators of cardiovascular function.
The article exemplifies a comprehensive analysis of systolic and diastolic blood pressure, offering a detailed understanding of these vital measures and their role in assessing cardiovascular health.
The article’s detailed comparison table provides a comprehensive breakdown of systolic and diastolic blood pressure, enhancing readers’ knowledge of the impact of these measures on cardiovascular health.
Absolutely, the article’s elucidation of the differences in blood pressure measurements is valuable for individuals seeking to monitor and manage their cardiovascular well-being.
I found the article on systolic and diastolic blood pressure to be highly informative and insightful. It effectively presents the nuances of these measurements and their implications for health.
The detailed comparison table and explanations in the article serve as a significant resource for understanding the dynamics of blood pressure and its impact on overall health.
Indeed, the article provides a well-structured overview of systolic and diastolic blood pressure, offering valuable knowledge for readers interested in cardiovascular well-being.
The article provides a comprehensive explanation of systolic and diastolic blood pressure and their significance in cardiovascular health. It sheds light on the difference between the two measures and their implications for overall well-being.
I agree, it’s important to understand these measures, especially for those with cardiovascular conditions or those looking to maintain good heart health.
This article is a valuable resource for understanding the intricacies of blood pressure and its impact on health. It’s well-documented and informative.
This article offers a meticulous breakdown of systolic and diastolic blood pressure, providing valuable insights into the significance of blood pressure readings for overall health assessment.
The article effectively elucidates the complexities of blood pressure measurements, helping readers grasp the critical factors influencing cardiovascular health and the associated risk factors.
Indeed, the article’s portrayal of the health implications associated with high systolic and low diastolic pressure contributes to better understanding and awareness of cardiovascular well-being.