Mobile networks and communication have evolved technology over the past years to the point that it is now an everyday commodity.
The demand for high-speed internet and data has increased too, which has led mobile broadband services to provide higher-quality networks. The LTE network has been around for a while now, and its evolved network is called 5G.
Key Takeaways
- 5G offers faster data speeds and lower latency than LTE.
- 5G supports more connected devices per square kilometer than LTE.
- 5G requires a higher density of cell towers than LTE to provide coverage.
5G vs LTE
LTE is the current standard for 4G mobile networks, offering high-speed data transfer with low latency. It uses a flat IP network architecture to manage and optimize network resources. 5G promises faster data transfer speeds, lower latency, and increased capacity, with a more complex network architecture.
5G (fifth generation) refers to the next wave of wireless communication advances designed to improve the speed and reliability of wireless networks.
The 5G system intends to improve performance parameters such as coverage, peak rate, spectral efficiency, and latency. Multiple radio access technologies are projected to be supported by the 5G network (RATs).
LTE is an important enabler for providing mobile broadband. In less than 20 years, the number of users grew from zero to over one billion.
3GPP (Third Generation Partnership Project), a global organization comprised of seven regional and national SDOs that maintain cellular standards, develops LTE technical specifications.
LTE employs Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing (OFDM) as the underlying modulation and multi-access technology.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | 5G | LTE |
|---|---|---|
| Generation | Fifth-generation | Fourth generation |
| Radio Frequency | 30 GHz to 300 GHz | Up to 6 GHz |
| Download Speeds | Speed of around 1 to 20 Gbps | Range of 50 to 100 Mbps |
| Bandwidth | Around 30 GHz | Around 20 MHz |
| Latency | Less than 10 milliseconds | Around 50 milliseconds |
| Data Rate | About 10 Gbps | Downlink of 300 Mbps, Uplink of 75 Mbps |
| No. of Connected Devices | It can support 1 million devices per square kilometre. | It can support 250 devices per sector. |
What is 5G?
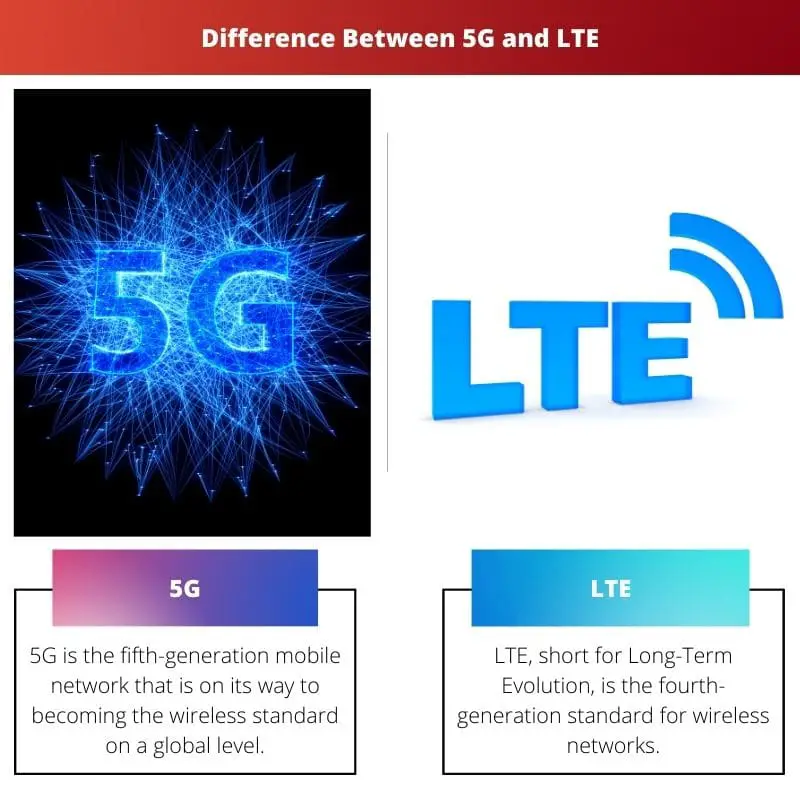
5G is the fifth-generation mobile network that is on its way to becoming the wireless standard on a global level. It has been designed to connect everyone and every device virtually.
It delivers a higher multi-Gbps peak data speed, more reliability, increased availability, etc., which makes it the more attractive option for networks.
5G also gives you access to Virtual Reality and AR with more uniform and faster data rates. 5G is capable of achieving a peak data rate of around 10 Gbps. It also provides an option to expand into new spectrums like mmWave.
It has a bandwidth of around 20 GHz. It can support around 1 million connected devices per square kilometre. It also has ultra-low latency, less than 10 milliseconds. It has a massive network capacity and offers a minimum speed of around 1 to 20 Gbps.
It also has a 10-year battery life for low-power devices. 5G offers 100% area coverage for every device. 5G networks enable better ultra-low latency applications to be executed via multi-access computing (MEC).
Researchers discovered that the full economic impact of 5G will likely be realized globally by 2035, benefiting many companies and potentially facilitating up to $13.1 trillion in products and services.
What is LTE?
LTE, short for Long-Term Evolution, is the fourth-generation standard for wireless networks. It offers an increased network capacity and data speed for devices when compared to their previous generations.
LTE played a significant role in the creation of the current 5G standard, known as 5G New Radio. To manage 5G data sessions, early 5G networks, known as non-standalone 5G, require a 4G LTE control plane.
LTE was developed by the third-generation partnership project and is very marketed as 4G LTE. Its download speed can range from 50 to 100 Mbps. Its data rate is also great considering its 4-generation. It offers a downlink of 300 Mbps and an uplink of 75 Mbps.
For its downlink signal, an LTE network uses a multiuser form of the orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) modulation system known as orthogonal frequency-division multiple access (OFDMA).
The uplink signal is transmitted using single-carrier FDMA, which decreases the transmit power required by the mobile terminal.
It can support around 750 devices per base station and an average of 250 devices per sector. Its radio frequency is up to 6 GHz. It has a bandwidth of around 20 MHz. Its latency is longer than 5G, coming in at around 50 milliseconds.
Main Differences Between 5G and LTE
- 5G has a radio frequency ranging from 30 GHz to 300 GHz, whereas LTE has a radio frequency of up to 6 GHz.
- 5G is of the fifth generation, whereas LTE is of the fourth generation.
- 5G offers a speed of around 1 Gbps to 20 Gbps, and LTW offers a speed of 50 Mbps to 100 Mbps.
- The bandwidth of 5G is around 30 GHz, and that of LTE is around 20 MHz
- The latency of 5G is extremely low as it’s less than 10 milliseconds, whereas the latency of LTE is slightly longer, coming in at around 50 milliseconds.
- The data rate of 5G is about 10 Gbps overall, and LTE offers a downlink of 300 Mbps and an uplink of about 75 Mbps.
- 5G can connect to 1 million devices per square Kilometer, and LTE can connect to 750 devices per base station and around 250 devices per sector.
- https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8485317/
- https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/7876975

The increased capacity and lower latency of 5G will undoubtedly pave the way for a new generation of applications and services that rely on ultra-low latency connections.
The development of 5G is a significant technological advancement, offering faster speeds, lower latency, and a higher capacity to connect devices.
LTE has played a pivotal role in the evolution towards 5G networks, with its improved network capacity and data speed characteristics.
The main differences between 5G and LTE are striking, particularly when it comes to their associated features such as speed, bandwidth, and latency.
The prospect of a wireless standard that can deliver higher multi-Gbps data speeds, greater reliability, and massive network capacity, as seen in 5G, has the potential to change how we integrate technology in our daily lives.
The advancements in technology to achieve lower latency, such as those exhibited by 5G, will likely revolutionize various industries and applications across the globe.
The key differences between 5G and LTE are apparent, especially in terms of data speed, bandwidth, and the number of connected devices each technology can support.
5G’s ability to support a massive number of connected devices per square kilometer is a testament to its advancement over LTE.