Our body is made up of many complex things.
Just like plants have a root system and shoot system, animals also have a digestive system, respiratory system, heart, lymphatic system, nervous system, bone, reproductive system, integument, etc., which keeps our body moving and balanced.
Our respiratory system helps us inhale and exhale. Amphibians, like frogs, breathe through their skin, and fish breathe through their gills, similar to mammals have respiratory systems.
Our respiratory system comprises many things like the nose, mouth, pharynx, trachea, lungs, etc.
Key Takeaways
- Alveoli are tiny, balloon-like air sacs in the lungs responsible for gas exchange between the air and the bloodstream.
- Alveolar sacs are clusters of alveoli connected by shared openings, facilitating efficient gas exchange.
- Both structures play crucial roles in the respiratory process, with alveoli performing the actual gas exchange and alveolar sacs providing a supportive structure.
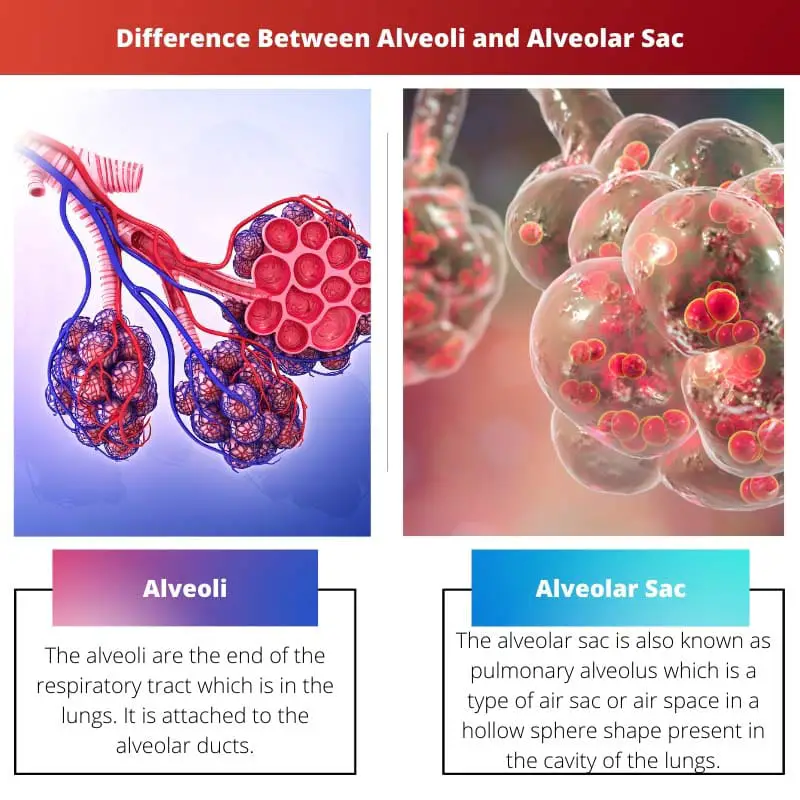
Alveoli vs Alveolar Sac
Alveoli are small sacs found within the lungs where gas exchange takes place between the air we breathe and the bloodstream. Alveolar sacs are clusters of alveoli connected to each other. They play a crucial role in facilitating the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide during respiration.
The alveoli are the end of the respiratory tract in the lungs. It is attached to the alveolar ducts. It is like a thin-walled sphere where gas exchange takes place in the highest percentage.
At least 700 million alveoli are present in each human lung. The surface area generated by the alveoli used for surface diffusion is about 80 m2, which is 42 times larger than the entire human surface area.
The alveolar sac is, also known as pulmonary alveolus, a type of air sac or air space in a hollow sphere shape present in the cavity of the lungs.
The main function of these air spaces is to provide space for the process of exchange of gas in the highest percentage. These gases are mainly carbon dioxide and oxygen. The pulmonary alveolus is a Latin name for the alveolar sac.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of comparison | Alveoli | Alveolar Sac |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The alveoli are the last end of the tract of our respiratory system, which is connected to the alveolar tubes. | The alveolar sac is, also known as pulmonary alveolus, a type of air sac or air space in a hollow sphere shape present in the cavity of the lungs. |
| Number | The number of alveoli present in the lungs is approx. 700 million. | The number of alveolar sacs is approx. 5-6 into which cluster of alveoli open. |
| Function | The alveoli mainly perform the gas exchange function, where they carry carbon dioxide from the blood to the lungs and allow the oxygen in the blood to reach the body’s cells. | The primary function of these air spaces is to provide space for the process of exchange of gas in the highest percentage. These gases are mainly carbon dioxide and oxygen. |
| Composed of | The alveoli are mainly composed of epithelial layers and the extracellular matrix of capillaries. | The alveolar sac is a type of space that forms the distal end of the alveolar ducts. |
| Biological name | The biological name of the alveoli is pulmonary alveolus. | The biological name of alveolar sacs is Sacculi Alveolares. |
What are Alveoli?
The alveoli are the end of the respiratory tract in the lungs. It is attached to the alveolar ducts. It is like a thin-walled sphere where gas exchange takes place in the highest percentage.
At least 700 million alveoli are present in each human lung. The surface area generated by the alveoli used for surface diffusion is about 80 m2, which is 42 times larger than the entire human surface area.
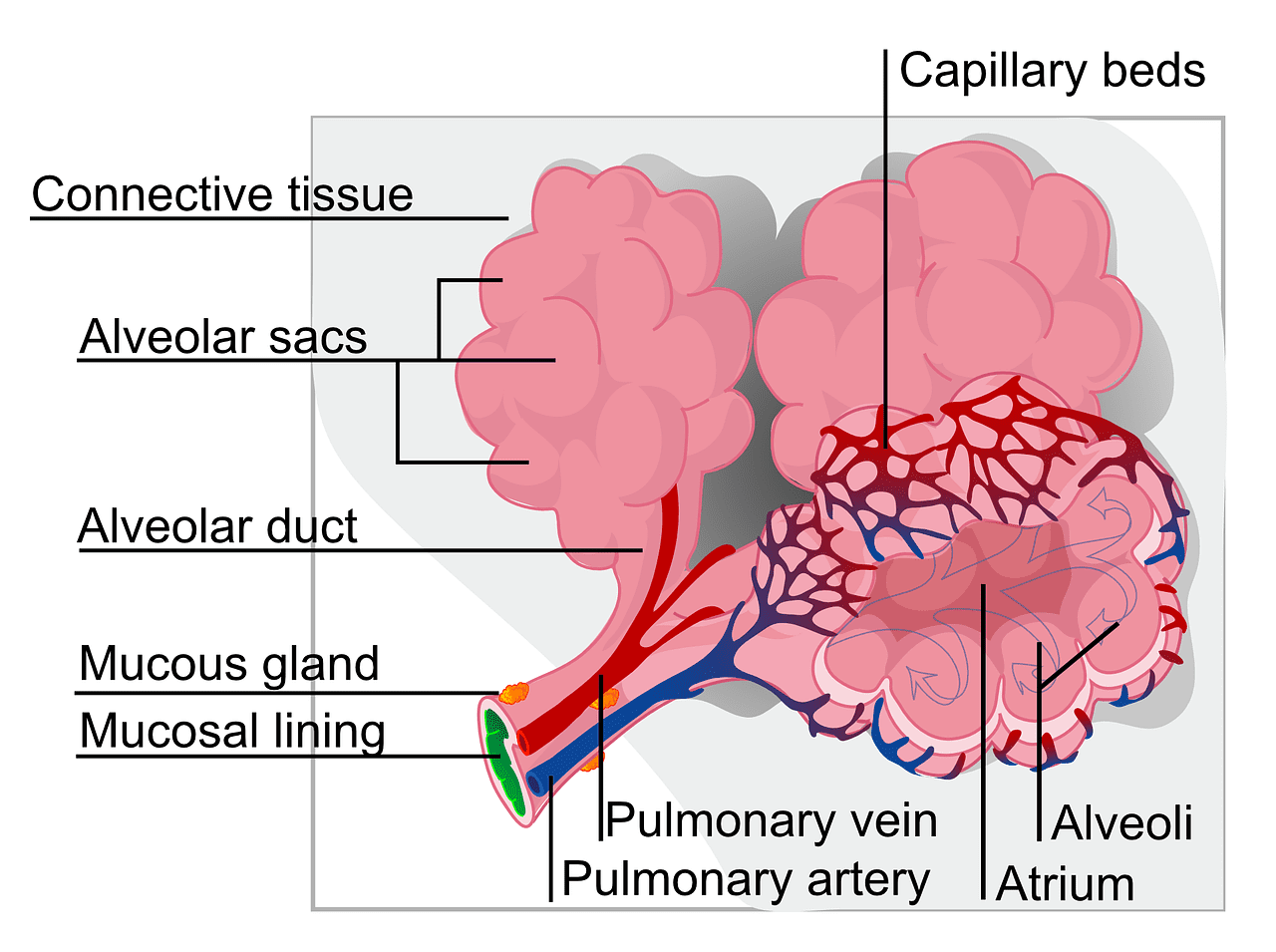
The space of air where two or more alveoli open is called the alveolar sac. Each alveolus is separated by a common wall called the interalveolar septum. This wall is made up of many cells and connective tissue, which is a network of reticular fibres.
This wall mainly provides space for gas exchange, which is a type 1 alveolar cell (simple squamous epithelium). In addition, it includes other things such as type II alveolar cells (septal cells), fibroblasts, and alveolar macrophages, etc.
The function of fibroblasts is to produce reticular and elastic fibres. Type 2 alveolar cells secrete alveolar fluid that maintains the moisture of the respiratory surface. Macrophages block any foreign particles from entering and eliminate them there.
Alveoli are responsible for the filtration of air that we inhale. This mainly separates oxygen and carbon dioxide inside our lungs. The size of alveoli are very small, but they are present in large number.
What is Alveolar Sac?
Bronchioles are found in each lung, which is very numerous. A bronchiole divides into two or more respiratory bronchioles that divide with alveoli, and each of these alveolar ducts and more alveoli is attached to them.
Each alveolar duct is connected to a round of vacuoles in which alveoli and atria are already present. Each atrium is connected to 2-5 alveolar sacs attached to the periphery of the alveoli or air sac.
It is also known as Sacculi Alveolares which is a type of air sac or air space in a hollow sphere shape present in the cavity of the lungs. The main function of these air spaces is to exchange gas in the highest percentage.
These gases are mainly carbon dioxide and oxygen. The Sacculi Alveolares is a biological name for the alveolar sac.
The alveoli present in the lungs are in the form of pockets extending into the respiratory bronchioles, which are present in their lumen.
It is quite elongated, and the alveolar tubules become increasingly alveolar with branches, which are further lined with alveoli. Two to eleven tubules are present in each bronchiole.
Each duct opens into an alveolar sac which is a group of alveoli. The number of ducts is 5 to 6.
Main Differences Between Alveoli and Alveolar Sac
- The alveoli are mainly composed of epithelial layers and the extracellular matrix of capillaries, while the alveolar sac is a type of space that forms the distal end of the alveolar ducts.
- Alveoli are mainly a cluster of collagen and elastic fibres, whereas the alveolar sac is a group of alveoli where they communicate.
- The alveoli mainly perform the gas exchange function, carrying carbon dioxide from the blood to the lungs and allowing the oxygen in the blood to reach the body’s cells. Whereas the alveolar sac provides the space for this process to happen where this whole process is completed.
- The biological name of alveoli is pulmonary alveolus, while the biological name of alveolar sacs is Sacculi Alveolares.
- The number of alveoli present in the lungs is approx. 700 million while the number of alveolar sacs is approx 5-6 into which cluster of alveoli open.