Azithromycin and clarithromycin belong to a class of antibiotics called Macrolide. They are derivatives of an older antibiotic of the same class called erythromycin.
Both are effective medications that are useful for the treatment of various infections, including those of the respiratory tract, soft tissue, skin, and other mycobacterial infections.
Key Takeaways
- Both azithromycin and clarithromycin are antibiotics belonging to the macrolide family and are effective against a wide range of bacterial infections.
- Azithromycin has a longer half-life and requires fewer doses, while clarithromycin requires a shorter half-life and more frequent dosing.
- Azithromycin is better tolerated, with fewer gastrointestinal side effects than clarithromycin.
Azithromycin vs Clarithromycin
Azithromycin is an antibiotic that is effective against bacterial infections, like respiratory tract infections, skin infections, and sexually transmitted infections. Clarithromycin is an antibiotics is used to treat respiratory tract infections, such as pneumonia, bronchitis, and skin infections.

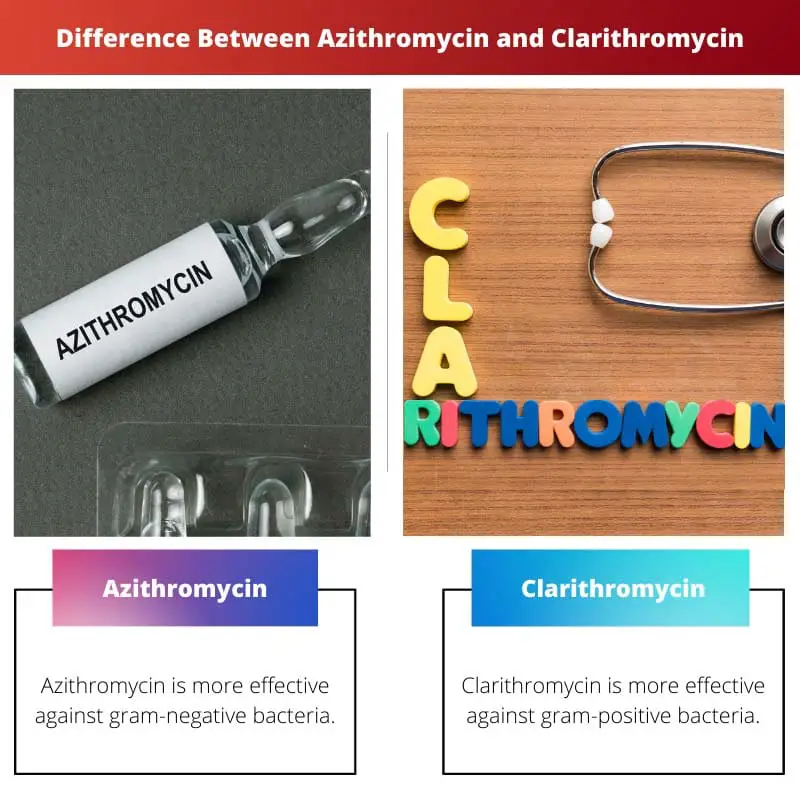
Gram-negative bacteria possess a thin layer of cell wall which is less than 10 nanometres in width. Because of this, such bacteria respond only to certain antibiotics, out of which azithromycin is the most effective.
The function of this medication is to decrease the production of protein in the cells, which leads to a halt in bacterial growth.
Gram-positive bacteria have a relatively thicker cell wall which ranges from 20 to 80 nanometers. Such bacteria respond very well to clarithromycin, which works even better than erythromycin in this case.
Just like azithromycin, clarithromycin stops the production of protein in cells, but it is less sensitive and works more vigorously than the former.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Azithromycin | Clarithromycin |
|---|---|---|
| Potency | Azithromycin is not as potent as clarithromycin. | Clarithromycin is more potent than azithromycin and even erythromycin. |
| Bacteria | Azithromycin is more effective against gram-negative bacteria. | Clarithromycin is more effective against gram-positive bacteria. |
| Coverage | Azithromycin has less coverage against H Influenza and MSSA. | Clarithromycin has better H Influenza and MSSA coverage. |
| Intravenous Form | The medication azithromycin is available in intravenous form. | The medication clarithromycin is not available in intravenous form. |
| Drug Interactions | Azithromycin does not have any recorded drug interactions. | Clarithromycin has drug interactions with other medications such as Aspirin, Benadryl and even fish oil. |
| Safety | Azithromycin is safer to use even during pregnancy. | Clarithromycin may cause harm if used by pregnant women. |
What is Azithromycin?
Azithromycin is an antibiotic medication that is sold under the trade names of Zithromax, Azithrocin, Sumamed and others.
It is effective for the treatment of several bacterial infections, including that of the middle ear, strep throat, and Intestine. It is also used for the treatment of pneumonia and traveller’s diarrhoea.
Many medical professionals prescribe it along with other drugs for Malaria. It can be expended orally or injected through the veins.
Azithromycin is safe to use. However, some common side effects may occur, such as nausea, vomiting, stomach upset, or diarrhoea.
Prolonged medication use may cause increased bacterial resistance in isolates or potentially result in hearing impairments. It may even cause allergic reactions, although such cases are rare.
Because of this, azithromycin is available to patients only through prescriptions.
The drug was discovered in 1980 by a Croatian pharmaceutical company called Pliva. However, it was only approved for medical use in the year 1988. The World Health Organization categorizes it as one of the most important drugs for human medicine.
It even made it to the WHO’s List of Essential Medicines. It was prescribed more than 17 million times in the United States in 2018, making it the 46th most prescribed.
What is Clarithromycin?
Clarithromycin is an antibiotic that is sold under the brand name of Biaxin, among others. It is used for the treatment of strep throat infection, skin infections, pneumonia, H. pylori infection, Lyme disease and much more.
The medication is a derivative of Erythromycin, while its parent drug is azithromycin. It is available as a generic medicine and is chemically known as 6-O-methyl erythromycin.
It is available for use in tablet or liquid form. Unlike azithromycin, clarithromycin cannot be taken intravenously.
Clarithromycin is much more potent than its parent drug and works more vigorously against protein formation in cells. Some of the common side effects of the medication include nausea, headaches, vomiting and diarrhoea.
Allergic reactions and liver problems are possible but rare. The drug is not safe to take during pregnancy.
The medication was discovered in 1980 but was approved for medical use only in the year 1990. It was claimed to be one of the safest and most effective medicines to exist in the entire health system.
Like azithromycin, clarithromycin also made it to WHO’s List of Essential Medicines. However, despite having better potential and more strength, it was not prescribed as much as the former for atypical infections.

Main Differences Between Azithromycin and Clarithromycin
- Azithromycin has excellent potential against infections, but clarithromycin has more potential than the former.
- Azithromycin is more effective against gram-negative bacteria, whereas clarithromycin is more effective against gram-positive bacteria.
- Azithromycin has less coverage against H Influenza and MSSA, whereas clarithromycin has more coverage against the two.
- Azithromycin is available for use in intravenous form, whereas clarithromycin is available only in tablet and liquid form.
- Azithromycin does not have any recorded drug interactions, whereas clarithromycin interacts with other drugs such as Aspirin and Benadryl.
- Azithromycin is safe to use during pregnancy, whereas clarithromycin is not.
- https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/infection-control-and-hospital-epidemiology/article/azithromycin-and-clarithromycin-overview-and-comparison-with-erythromycin/3BDBD9E4044B8E570197939153EE53C1
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0025619611641402

Is this post supposed to be funny? The author can be quite sarcastic about medicines, can’t he?
Extremely insightful article, as always. Both antibiotics’ mechanisms of action are explained splendidly.
This article fails to mention some serious side-effects of the two drugs, which is a letdown.
Article is filled with insightful and very informative content
The author has done a great job with this article
This is disappointing. The writer has failed to explain how these drugs work in a simple language.
The comparison table is the most helpful part of this post. Kudos to the author.
I’ve learned a lot from this article, and I believe that professionals would find it very informative.