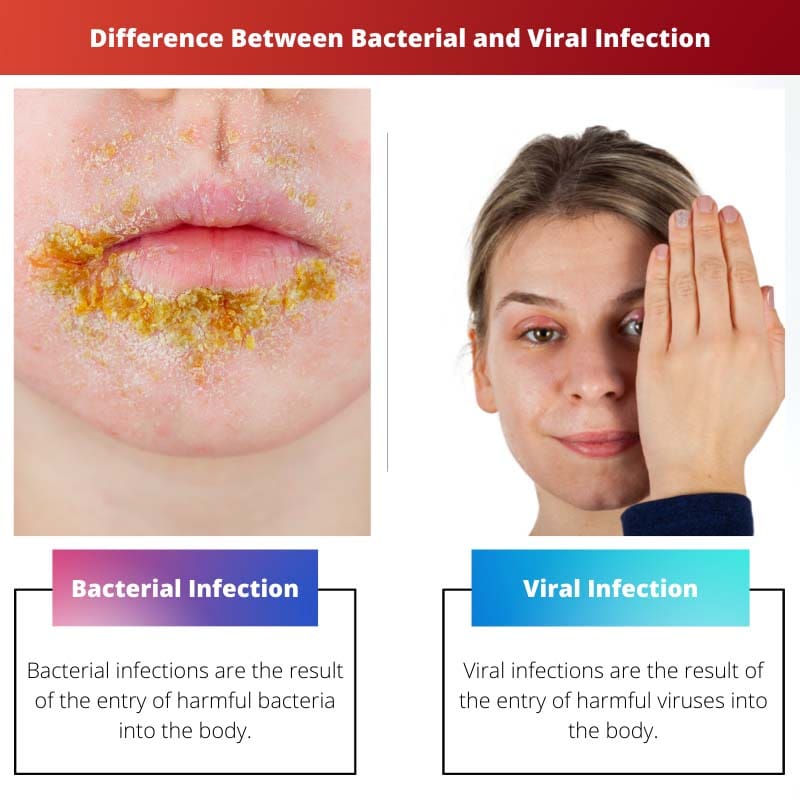
CDC (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention) has reported about 15.5 million infections and 3.7 million emergency cases yearly. Infections occur due to the entry of harmful organisms into the body.
Infections are classified into various types depending on the organism involved. These conditions are viral infections, bacterial infections, fungal infections, parasitic infections, prion infections, etc.
The two most common types of infections are bacterial and viral infections.
Key Takeaways
- Bacterial infections result from harmful bacteria entering the body, while viral infections occur due to viruses invading the body.
- Antibiotics effectively treat bacterial infections but do not work against viral infections, requiring antiviral medications or symptom management.
- Bacterial infections can sometimes be prevented through proper hygiene and vaccinations, while viral infections are prevented through vaccinations, hygiene, and avoiding close contact with infected individuals.
Bacterial vs Viral Infection
The difference between bacterial and viral infection is that bacterial infection is caused due to harmful bacteria, whereas viral infection is caused due to deadly viruses. While bacterial infection persists in the body for two weeks, the viral infection persists for one week. While antibiotics can treat bacterial infections, viral infections can be treated with antiviral medicines.

When harmful bacteria enter the body, it causes bacterial infection. These infections result from contact (direct or indirect) with the bacteria. The transmission of these infections takes place through faeces, food, and sharing of personal items.
These infections also pass from mother to child. Examples of bacterial infections include strep throat, UTI (urinary tract infections), bacterial vaginosis, etc.
A viral infection occurs when a harmful virus intrudes into the body. These infections are transmitted through direct touch, sexual contact, saliva, and sharing of needles.
Sometimes, insects also act as vectors and result in the transmission of diseases. Intake of contaminated food also results in information. Viral infections tend to be highly contagious.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Bacterial Infection | Viral Infection |
|---|---|---|
| Causing Agent | Viral infections result from the entry of harmful viruses into the body. | The symptoms of bacterial infection are: HeadacheSwollen lymph nodesFeverDiarrheaSorenessFever and Chills |
| Transmission Methods | Bacterial infections spread from one person to another through direct contact, vectors, airborne methods, droplets, and vehicular means. | Viral infections spread through direct contact, saliva, sharing of needles, vectors, and contaminated food. |
| Symptoms | The tests for detecting bacterial infections are: Urine testSwab sample test (complete blood count) testImaging tests such as X-ray | The tests for detecting bacterial infections are: Urine testSwab sample testCBC (complete blood count) testImaging tests such as X-ray |
| Diagnosis | The methods of detecting viral infections are Direct detection methods such as Microscopy and StainingVirus isolation methods such as PCRSerology methods such as antibodies. | The methods of detecting viral infections are:Direct detection methods such as Microscopy and StainingVirus isolation methods such as PCRSerology methods such as antibodies. |
| Treatment | The antibiotics for treating bacterial infections include ciprofloxacin, amoxicillin, and erythromycin. | Antiviral drugs and medicines are used for the treatment of viral infections. |
What is Bacterial Infection?
Shaped like balls, spirals, and rolls, bacteria refers to living creatures with a single cell. Various kinds of bacteria will have varying effects on the body.
The intrusion into the body, thereby leading to chemical reactions and various imbalances, is known as bacterial infection.
When a bacterium enters the body, it multiplies itself and then triggers the destruction in our body. The intrusion of bacteria into the body can even occur through the skin.
The diseases caused due to bacteria may range from minor ones, such as ear infections, to serious ones, such as meningitis.
Common infections include Salmonella, Tuberculosis, etc. Salmonella, much like food poisoning, is caused due to intake of uncooked poultry.
The bacteria in the GI of various poultry animals enter the body, showing symptoms such as diarrhoea, vomiting, abdominal pain, stomach upset, etc. Tuberculosis is a lung infection caused due to the bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Clostridium difficile refers to the excellent and harmless bacteria in our gastrointestinal tracts. If a person has a weak immune system or uses antibiotics, these bacteria get multiplied in numbers, leading to infections in the gastrointestinal tract.
The symptoms of these infections are constant diarrhoea and inflammation of the colon. Various bacteria lead to various diseases, which in turn have varying symptoms.
What is Viral Infection?
Viruses refer to organisms with a protein coat surrounded by RNA/DNA as their genetic material. These organisms can’t reproduce all by themselves. They are dependent on their host for their food and survival.
However, it’s still unsure whether these organisms are alive or not. Some scientists consider them alive as they reproduce and take energy from the host’s body.
On the contrary, some scientists consider them dead because they lack cella and the ability to reproduce by themselves.
Viruses are both harmful and helpful. Viral infections occur due to the intrusion of a deadly virus into the human body. On entering the host’s body, they transfer their genetic material into the cell body of the host.
As a result, they keep multiplying themselves, thereby hijacking the cell’s internal machinery. Further, these multiplied viruses lead to their multiplication in the host’s body, thereby harming the concerned body part.
The most common viral infections affecting the respiratory tract include Rhinovirus, Seasonal influenza, RSV (Respiratory Syncytial Virus), etc.
The most common viral infections infecting the skin include Molluscum contagiosum, VZV (Varicella-zoster virus), etc. The most common viral infections affecting the stomach include Hepatitis A, Norovirus, Rotavirus, etc.

Main Differences Between Bacterial and Viral Infection
- Bacterial infection is not always contagious. However, viral infections are most infectious.
- While antibiotics help treat bacterial infections, viral infections can’t be treated with antibiotics. Antibiotics do not affect viruses and are thus, valueless.
- While the bacterial infection is localized, the viral infection affects the whole body.
- In bacterial infections, the symptoms last in the body for up to 2 weeks. But, in viral infections, the symptoms last in the body for no less than 1 week.
- Bacterial infections include whooping cough, ear infection, strep throat, UTIs. On the other hand, examples of viral infections include flu, common cold, bronchitis, HIV/AIDS, coughs, chickenpox, etc.