A human is exposed to various biological and mechanical processes involving different body parts. Some of these processes are respiratory, digestive, excretion, etc.
The digestive process is one of the most complex processes in the human body.
In the digestive process, the body parts, such as the mouth, esophagus, intestines, stomach, etc., are involved, and the product obtained after processing food in each part Is different.
Bolus and chyme are products obtained after processing food in the mouth and stomach, respectively, but they are confused.
The bolus is a product obtained in the initial stage of the digestive process just after chewing the food, and chyme is the product obtained when food is mixed with gastric juices. Both of these products undergo chemical and mechanical digestion.
Key Takeaways
- Bolus is a mass of food that has been chewed and mixed with saliva in the mouth, while the chyme is a mixture of partially digested food and digestive juices in the stomach.
- Bolus is formed during the oral phase of digestion, while the chyme is formed during the gastric phase.
- Bolus is relatively solid and easy to swallow, while the chyme is more liquid and is gradually released into the small intestine.
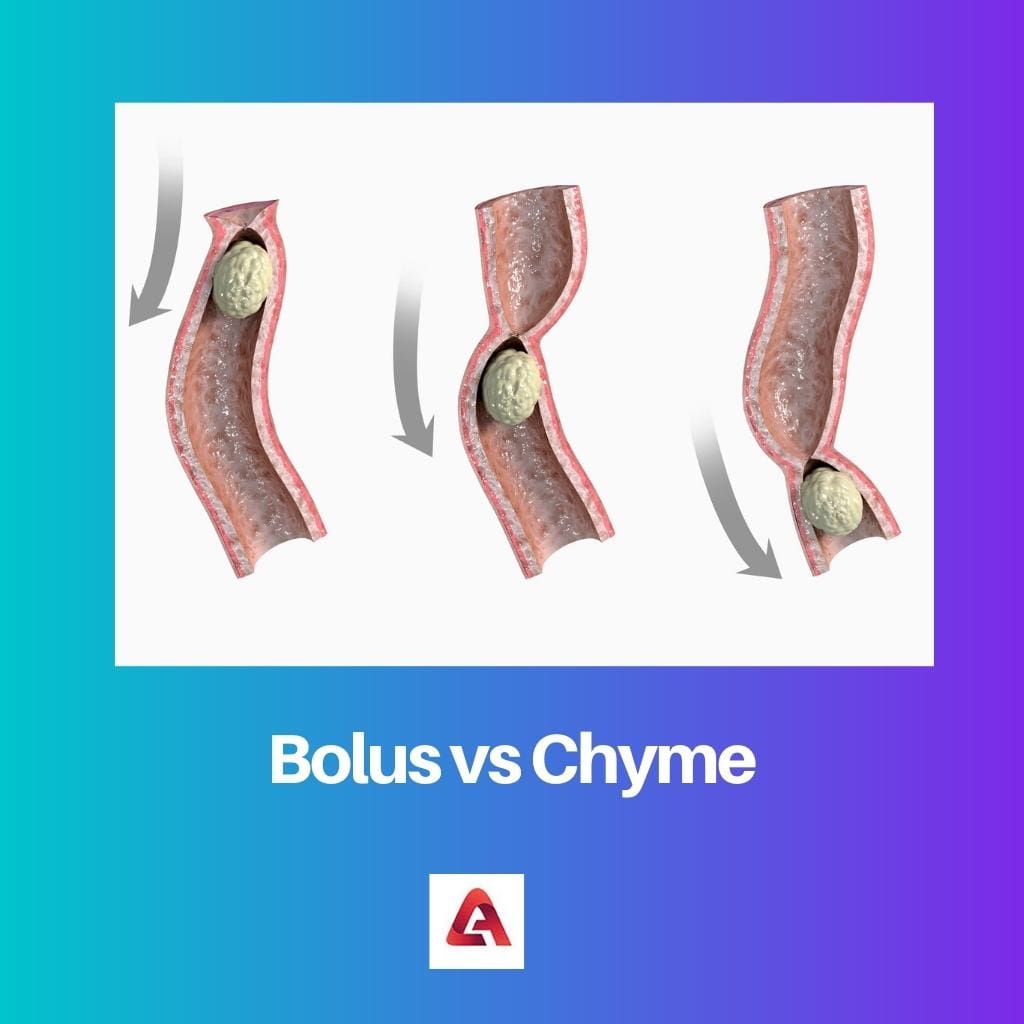
Bolus vs Chyme
Bolus is a mass of food formed in the mouth while chewing and mixing with saliva, making it easy to swallow and can pass through the esophagus. Chyme is a semi-liquid mixture of partially digested food, digestive juices, and enzymes that are produced in the stomach.
Comparison Table
| Parameter of Comparison | Bolus | Chyme |
|---|---|---|
| What does it mean? | The bolus is defined as the ball-like structure obtained by mixing food and saliva in the mouth at the initial stage of the digestive process. | Chyme is a semi-liquid or paste-like substance formed in the stomach due to mixing food and gastric juices. |
| Formation process | The bolus is a result or product of the chewing process in which the food is mixed with saliva at the initial stage of digestion. | The chyme results from churning the food and gastric juices in the stomach. |
| Composition and nature | The bolus is a mixture of food and saliva and is alkaline. | The chyme is the product formed after the food is mixed with the gastric juices and is more acidic. |
| Function | The function of the bolus is to break down the food so that the further action of enzymes can take place. | The most important function of chyme is to increase the surface area of food to ease the digestive processes. |
| Degree of digestion, texture and colour | The bolus is formed at the beginning of the digestion process, it has a ball-like texture, and the colour is similar to that of the food. | The chyme is a partly finished product of digestion; it is a semi-liquid creamy paste with natural food colour. |
What is Bolus?
In the digestive process, the bolus is a ball-like soft structure of food when saliva is mixed with it formed in the mouth just after food intake and chewing it. It makes its way from the mouth to the stomach.
Teeth and saliva convert the food into a bolus. The bolus is alkaline in nature due to the nature of salivary enzymes. It has a colour that is similar to the colour of the food. It is always obtained in the initial stage of the process since it is the result of chewing food.
The main function of the bolus is to break down the food into small pieces, increasing the surface area of food upon which enzymes act.
What is Chyme?
In the digestive process, the chyme, also termed chymus, is a semi-liquid or paste-like product of food obtained when the food is mixed with the gastric juices in the stomach. It is digested in the stomach.
In other words, chyme results from further mechanical processing of the bolus. The gastric juices in the stomach are responsible for the formation of the chyme.
The chyme is more acidic because gastric juices are acidic. It had the colour of natural food.
The main function of the chyme is to increase the surface area of food to ease the digestive process.
Main Differences Between Bolus and Chyme
- The bolus is a term used to refer to the soft spherical of food obtained when saliva is mixed with food, while chyme refers to the semi-liquid product obtained when gastric juices are mixed with food.
- In other words, it can be said that bolus is food mixed with saliva, and chyme is food mixed with gastric juices.
- The bolus is obtained in the mouth and goes to the stomach, whereas the chyme goes from the stomach to the small intestine.
- The bolus is converted to chyme in further stages of digestion, whereas the chyme is digested in the stomach.
- The bolus results from a chewing process in the mouth, and chyme results from churning food and gastric juices.
- The bolus is alkaline; on the other hand, chyme is acidic.
- The bolus is soft and spherical, whereas the chyme has a semi-liquid or paste-like texture.
- The colour of the bolus is similar to that of the food, whereas chyme has the colour of natural food.
- The bolus is obtained at the beginning of the digestive process, whereas chyme is obtained in the later stages of the process.
- The main function of the bolus is breaking down food, whereas the main function of chyme is increasing the surface area of food to ease the digestive process.



