The animal body (including human beings) consists of various blood components. It has Red Blood cells (RBCs), White Blood cells (WBCs), Platelets, and Plasma. The four are distinct and have a diversified impact on our lives.
The plasma cell membrane is filled with proteins, salts, water, fats, and sugar from this. It has lysosomes, which help clean our cells and the blood.
Cytoplasm and protoplasm are inherent in plasma. But both differ as the first is in fluid form, and the second is in colloidal semi-fluid.
Key Takeaways
- Cytoplasm refers to the entire contents of a cell, including the organelles, while protoplasm refers to the living substance within a cell, excluding the cell wall.
- Protoplasm is essential for life, as it contains all the cell’s vital functions, while cytoplasm provides a medium for the protoplasm to function.
- While protoplasm is found in all living cells, cytoplasm varies in composition and function depending on the cell type.
Cytoplasm vs Protoplasm
Cytoplasm refers to the jelly-like substance that fills the cell, surrounds and is responsible for supporting the organelles. Protoplasm is the living substance found in all living cells, including bacteria and plant and animal cells, and comprises the nucleus, the cytoplasm, and the cell membrane.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Cytoplasm | Protoplasm |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The cytoplasm consists of all of the biological portions in the cell enveloped by the plasma cell membrane, excluding the part of the cell nucleoplasm. | A plasma cell membrane encircles an animal cell’s biological portion. That portion is called a Protoplasm. |
| History | The term ‘Cytoplasm’ was originated by Rudolf Von Kolliker in 1863. | The term ‘Protoplasm’ was debated by Thomas Huxley against calling it a ‘Cell’ or protoplasm. After fairly discussing it sorted out in the year 1860s, as it is now called. |
| Nucleus | It does not include the nucleus. | It does include the nucleus. |
| Constituents | The cytoplasm comprises the compound of inclusions, cytosol, organelles, etc. | Protoplasm comprises the compound of amino acids, water, ions, and monosaccharides, such as micro molecules and proteins, polysaccharides, lipids, nucleic acids, and macromolecules. |
| Correlation | The cytoplasm is a part of the Protoplasm. | The protoplasm includes cytoplasm. |
| Forms | It has been found to exist and appear in sol-gel, glass, or sometimes unconventional shapes. | It has been found to exist and appear in the two forms, such as jelly-like gel form or liquified sol shape. |
| Equilibrium | The fluid is in equilibrium into it. | The colloidal semi-fluid is equilibrium into it. |
| Structure | Its structure comprises mitochondria, lysosomes, Golgi body, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, etc., except the nucleoplasm. | Its structure is made up of cytoplasm and nucleoplasm together. |
| Other Terms | It is also known as Protoplasm as it is a part of it. | It is also known as protoplasma, metaplasm, primordialschlauch, bioplasm, etc. |
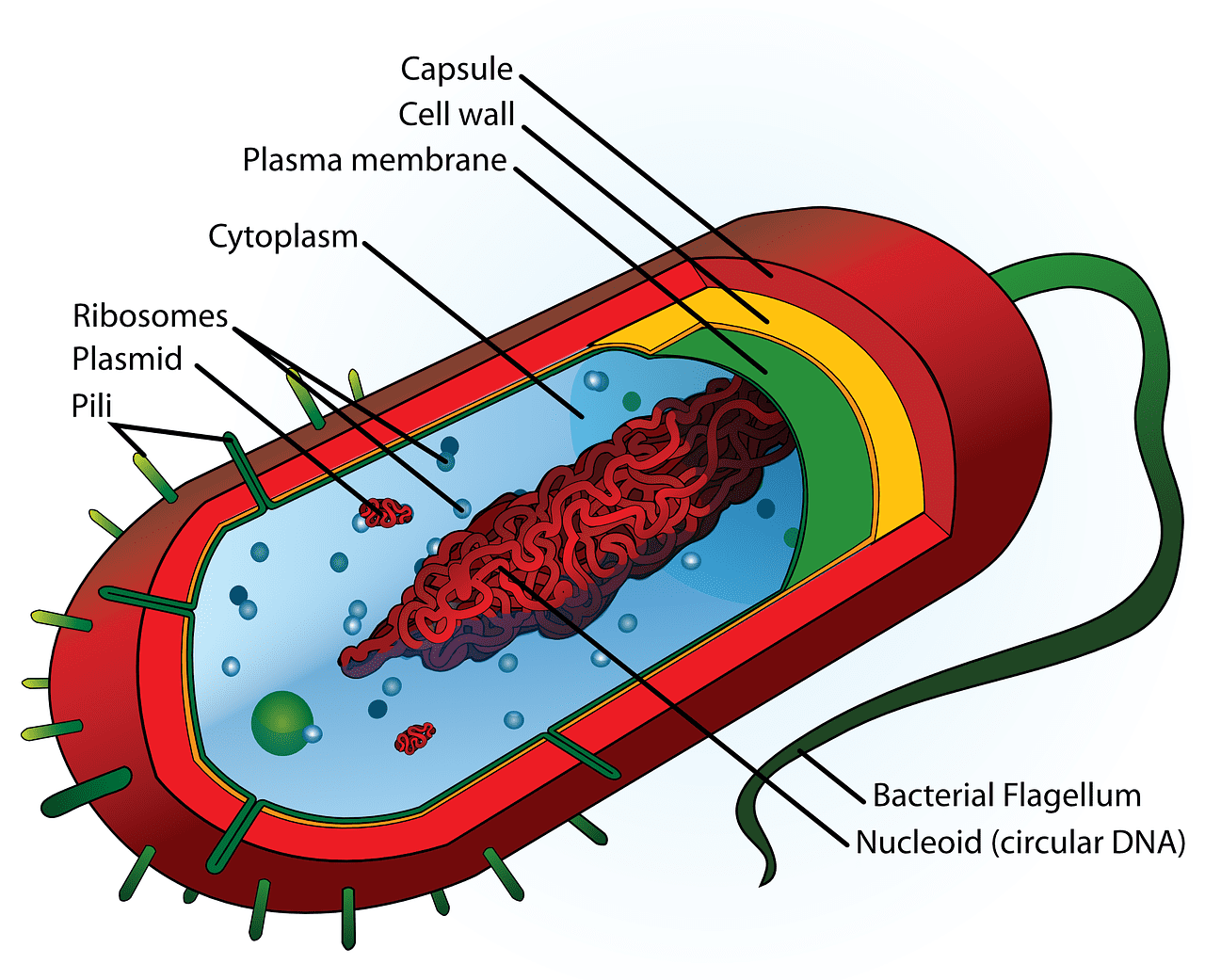
What is Cytoplasm?
All of the biological portions in the cell are enveloped by the plasma cell membrane, excluding the part of cell nucleoplasm that makes the ‘Cytoplasm.’ It was coined by Rudolf Von Kolliker in 1863.
The cell comprises the compound of inclusions, cytosol, organelles, etc. Its structure comprises mitochondria, lysosomes, Golgi body, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, etc.
It has been found to exist and appear in sol-gel, glass, or sometimes unconventional shapes. It is part of the Protoplasm, also known as Protoplasm. But the difference is it does not include the nucleus.
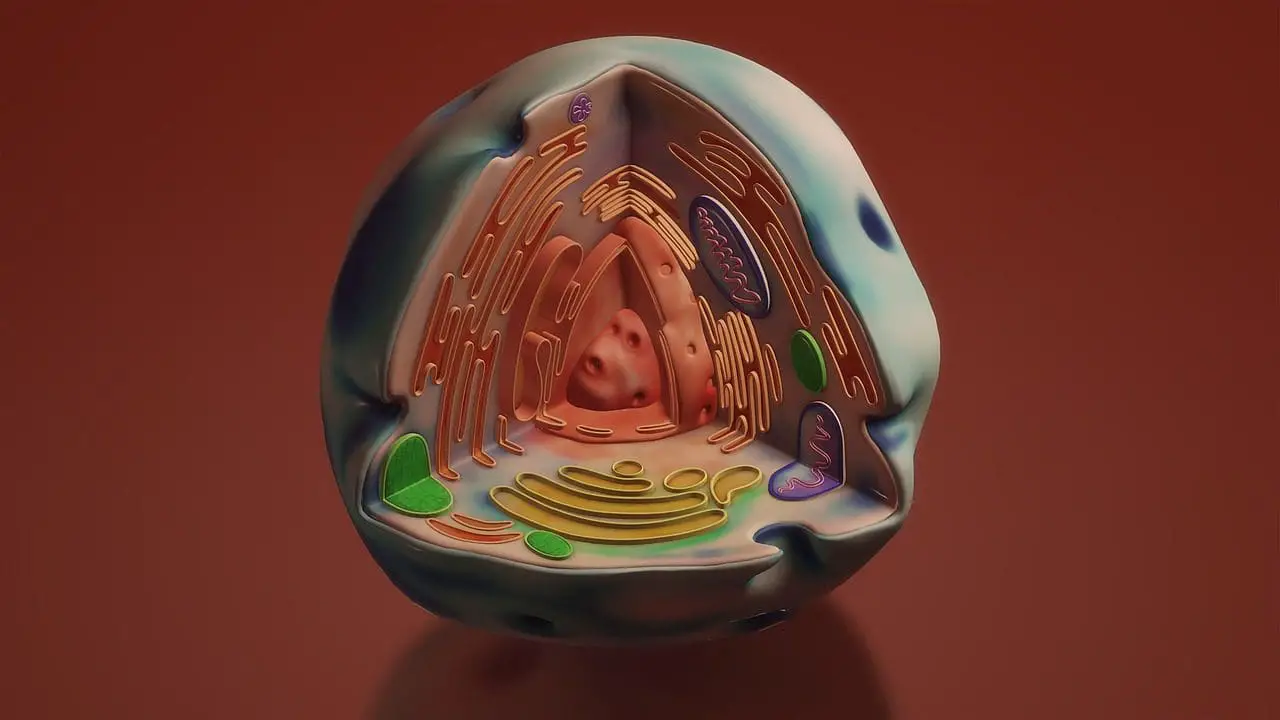
What is Protoplasm?
A protoplasm consists of a cell that is encircled by a membrane of the plasma cell, which is called a Protoplasm. It has been found to exist and appear in the two forms, such as jelly-like gel form or liquified sol shape.
The term was debated before it came to exist. It was supposed to be either a protoplasm or a cell. Around the 1860s, Thomas Huxley wrote a long-form debate about it and then fairly resolved and decided as protoplasm it is.
It comprises the compound of amino acids, water, ions, monosaccharides, micro molecules, proteins, polysaccharides, lipids, nucleic acids, and macromolecules.
It includes the cytoplasm as well as the nucleoplasm. Other terminologies for it are protoplasma, metaplasm, primordialschlauch, bioplasm, urschleim, sarcode, deutoplasm, paraplasm, idioplasm, kinoplasm, etc.

Main Differences Between Cytoplasm and Protoplasm
- All of the biological portions in the cell are enveloped by the plasma cell membrane, excluding the part of cell nucleoplasm, known as Cytoplasm. At the same time, Protoplasm consists of the biological portion of a cell encircled by a plasma cell membrane.
- The term ‘Cytoplasm’ was originated by Rudolf Von Kolliker in 1863. Conversely, the ‘Protoplasm’ term was debated by Huxley against calling it the Cell and sorted out in the 1860s.
- The cytoplasm does not include the nucleus, while the protoplasm does.
- The former comprises the compound of inclusions, cytosol, organelles, etc. On the other hand, the latter is of amino acids, water, ions, monosaccharides, micro molecules, proteins, polysaccharides, lipids, nucleic acids, and macromolecules.
- The protoplasm includes cytoplasm within itself.
- It has been found to exist and appear in the cytoplasm in the form of sol-gel, glass, or sometimes unconventional forms. On the contrary, the protoplasm in the two forms follows a jelly-like gel form or liquified sol shape.
- The structure of cytoplasms is made up of mitochondria, lysosomes, Golgi body, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, etc. At the same time, protoplasm is the cytoplasm, including nucleoplasm.
- The cytoplasm is also known as protoplasm, as it is a part of it. Although protoplasm, metaplasm, primordialschlauch, and bioplasm are some of the terminologies used for the latter.




