Both AED and defibrillator work the same by producing an electrical shock to the heart and resuming a normal heartbeat. Although both are used for the same purpose, yet there are subtle differences between them.
Key Takeaways
- An AED (Automated External Defibrillator) is a portable device that can detect abnormal heart rhythms and deliver electric shocks. At the same time, a defibrillator refers to a broader category of devices, including implantable and manual types.
- AEDs are user-friendly and designed for non-medical personnel, whereas manual defibrillators require training and are used mainly by healthcare professionals.
- AEDs play a crucial role in public spaces and emergencies, increasing the chances of survival after sudden cardiac arrest.
AED vs Defibrillator
AEDs work by analyzing the heart’s electrical activity and delivering a shock to restore normal rhythm and prevent SCA. They provide step-by-step instructions and only deliver a shock if needed. Defibrillators are used to treat cardiac conditions and are operated by trained healthcare professionals.
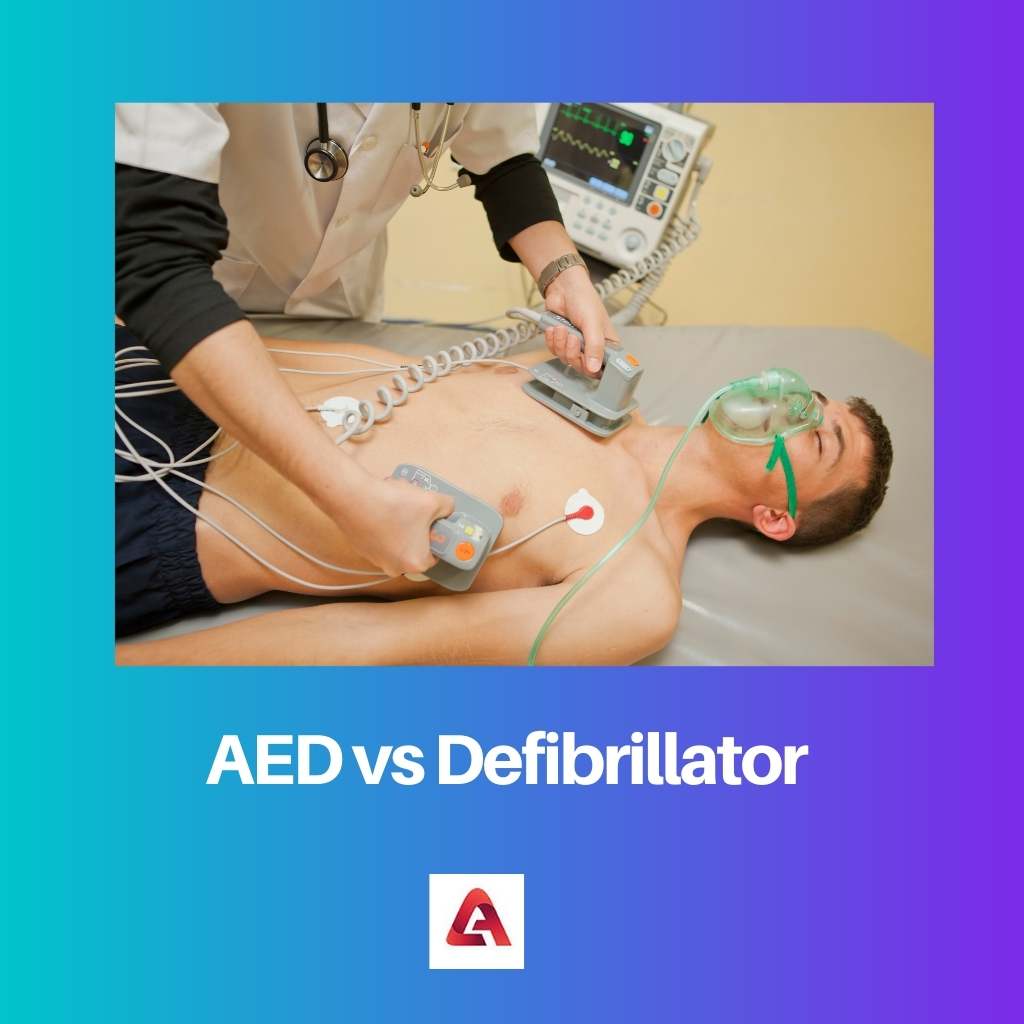
Moreover, the principle of the device is to administer abnormal heart rhythms by sending an electric shock that halts the abnormal heart rhythm. As halts ultimately revert the rhythm to an orderly and efficient rhythm.
A defibrillator is a device used for cardiac patients in emergency rooms as well as medical centres. It is used for defibrillation, heart arrhythmias, ventricular tachycardia, and ventricular fibrillation.
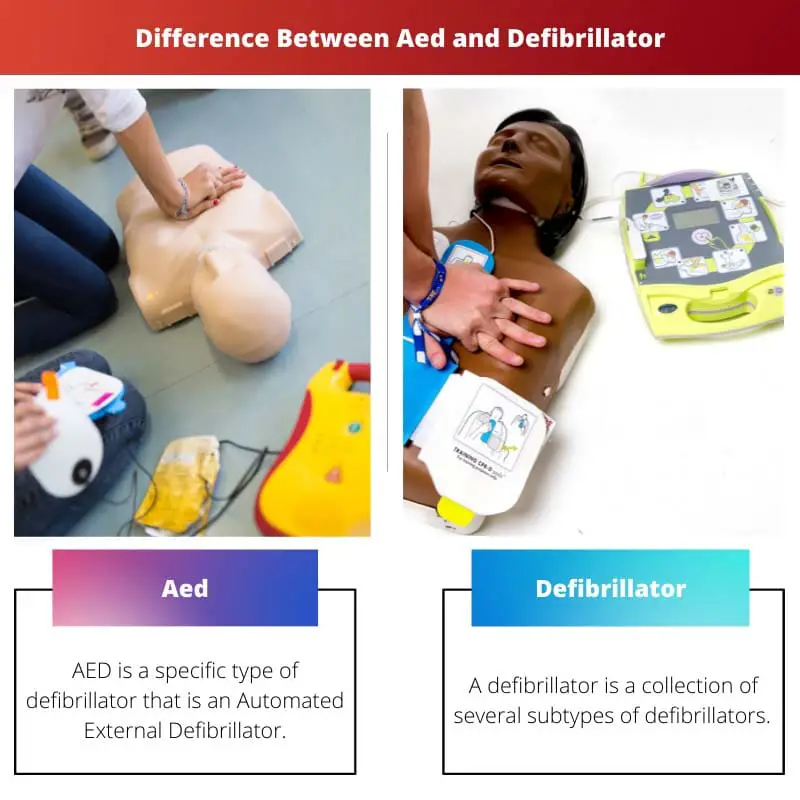
Comparison Table
| Parameters of comparison | AED | Defibrillator |
|---|---|---|
| New or Old | AED is the latest type of defibrillator. | The defibrillator has new and old types. |
| Type | AED is a specific type of defibrillator that is an Automated External Defibrillator. | A defibrillator is a collection of several subtypes of defibrillators. |
| Portable | AED is a handy device. | A defibrillator is not portable. |
| Simple and easy to use | AED can be used easily and has simple working. | A defibrillator has many technical portions. |
| Automatic | AED is automated, | A defibrillator can be automatic, semi-automatic, or manual. |
| Assessment of defibrillation’s need | AED can assess the need for defibrillation. | Some types of defibrillators cannot. |
| Use | AED can be used for defibrillation, diagnosing heart rhythm, and fatal cardiac arrhythmias. | A defibrillator is used in defibrillation, heart arrhythmias, ventricular tachycardia, and ventricular fibrillation. |
What is AED?
AED is a handy electronic device used for defibrillation diagnosing cardiac arrhythmias, and heart rhythm. It stands for Automated External Defibrillator.
Although it is portable, yet also does defibrillation. It is more efficient than a conventional defibrillator. However, it was built for easy use purpose. And, of course, it can be easily operated by anyone.
As for working, it works similarly to the conventional defibrillator. The principle of the device is to administer abnormal heart rhythms by sending an electric shock that halts the abnormal heart rhythm.
With simple training, a person without a medical background can operate AED. Simple defibrillation training provided in the first-aid training sessions, first responder classes, and BLS seminars will provide practical knowledge.
One of the plus points of AED is its simplicity and automated nature. Additionally, it asses the need for defibrillation on its own, which gives the upper hand in survival.
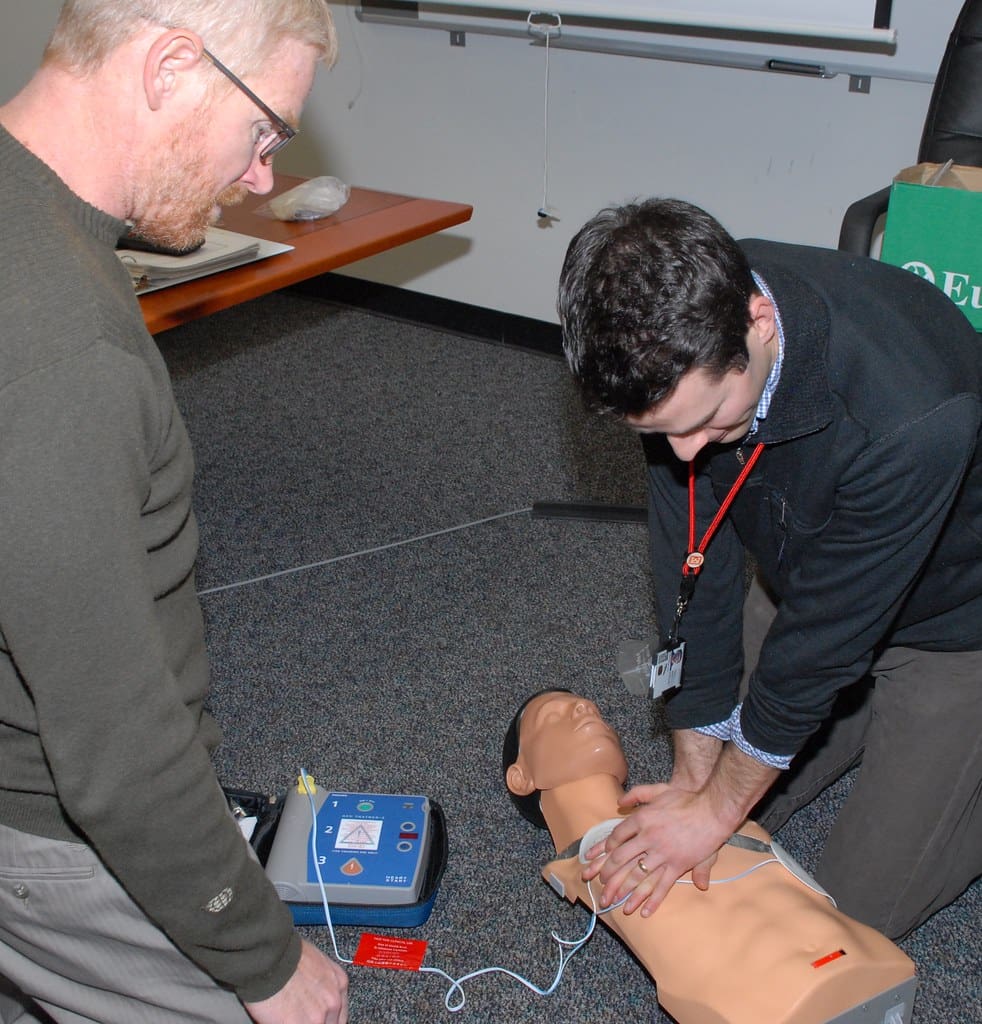
What is Defibrillator?
A defibrillator is an electric device used for defibrillation in cardiac patients, chiefly for those with heart arrhythmias, ventricular tachycardia, and ventricular fibrillation.
Over time, many types of defibrillators are developed. Some are manual defibrillators, semi-automated defibrillators, the ICD, wearable cardiac defibrillators, and AED. All are used based on the patient’s requirements.
Compared to AED, other defibrillators are not easy to use as usage is manual. Even if a person wants to educate himself to operate the defibrillator, it’ll take a lot of training.
As for the conventional defibrillator, they’re harder to use and manual or semi-automatic. Additionally, it cannot assess the need for defibrillation, unlike some types of defibrillators.

Main Differences Between AED and Defibrillators
Many electronic devices are used for the administration of patients. In cardiac patients, one of the devices used is an AED and Defibrillator. Although they seem pretty similar yet they have different configurations.
- AED can assess the need for defibrillation, while some types of defibrillators cannot.
- AED can be used for defibrillation, diagnosing heart rhythm, and fatal cardiac arrhythmias. In contrast, a defibrillator is used in defibrillation, heart arrhythmias, ventricular tachycardia, and ventricular fibrillation.

The distinction between AEDs and defibrillators is crucial for public awareness. The access to this information can truly make a difference in emergencies.
I appreciate the in-depth comparison between AEDs and defibrillators. It’s vital to understand the differences and how each device works in different scenarios.
The explanation of AED and defibrillators is clear and concise. It is very useful for non-medical professionals.
The references provided at the end of the article are an important addition to support the information presented. It’s great to see the credibility of the sources.
The detailed explanation of AED and defibrillators has increased my understanding of these life-saving devices. Thank you for this informative piece.
AED and automated defibrillators are important tools to save lives. It is important to educate the general public about their importance.
I agree. AEDs also provide step-by-step instructions, something else that can be beneficial for people who are not healthcare professionals.
The straightforward comparison table provided a simple way to distinguish between AEDs and defibrillators. This is incredibly helpful information.
The clear presentation of the main differences between AED and defibrillators was very enlightening. This article is a valuable resource.