Figs and dates are fruits eaten either raw, cooked, or dried by people worldwide. They are popular for their nutritional value and sweet taste, which makes them the perfect ingredients for healthy desserts.
Key Takeaways
- Figs are a sweet fruit with a soft, chewy texture grown on the Ficus tree; dates are also a sweet fruit with a dense, fibrous texture grown on the date palm tree.
- Figs are smaller and have a milder, honey-like flavor; dates are larger and have a distinct caramel-like taste.
- Figs are commonly eaten fresh or dried as a snack or ingredient in various dishes; dates are eaten dried as a sweet snack or ingredient in baking.
Figs vs. Dates
Figs have a soft, chewy texture and a sweet, honey-like flavor and are high in fiber, potassium, and other nutrients. Dates are popular in Middle Eastern cuisine due to their dense, chewy texture and sweet, caramel-like flavor. They are high in fiber, antioxidants, and other nutrients.

Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Figs | Dates |
|---|---|---|
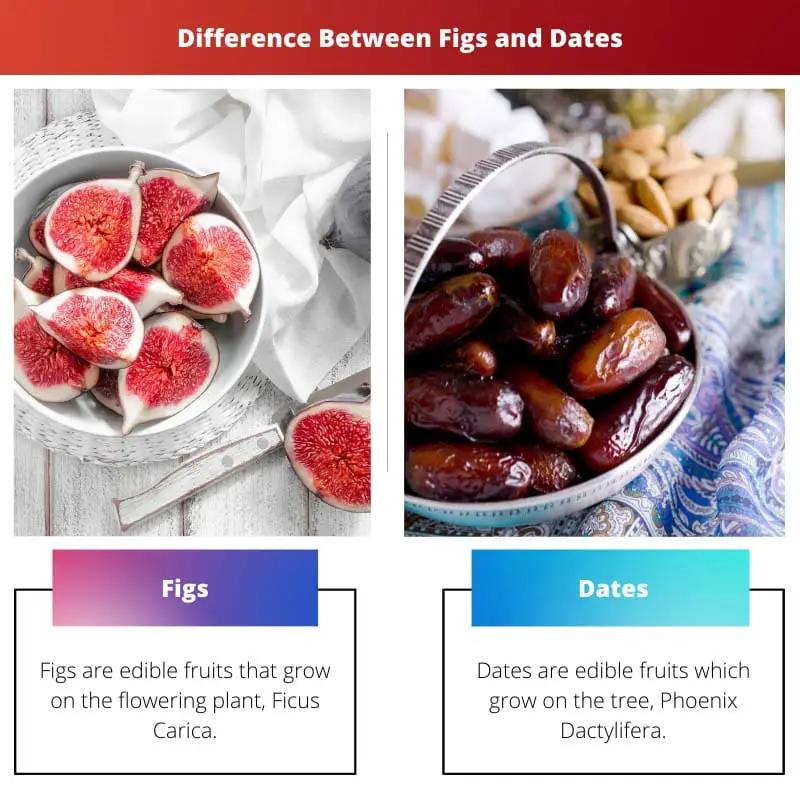
| Plant | Figs are edible fruits that grow on the flowering plant Ficus Carica. | Dates are edible fruits that grow on the tree Phoenix Dactylifera, commonly known as the date palm tree. |
| Origin | Figs originated in Western Asia and the Mediterranean. | The origin of the dates is unknown. However, they are believed to have come from the Fertile Crescent region between Mesopotamia and Egypt. |
| Color | The color of figs depends on how mature the fruit is; the skin color ranges from green to purple, while the fruit’s flesh is either red or white. | Fresh, ripe dates tend to be bright red or yellow; when dried, the color ranges from golden brown to black. |
| Shape | Figs commonly have a pear-like bulbous shape. | Dates are commonly oval-cylindrical in shape. |
| Texture | The pulp of a ripened fruit is soft and jelly-like, while the tiny seeds inside are crunchy; dried figs tend to be leathery yet moist. | The texture of fresh dates is like that of an apple; when dried, the fruit becomes soft and sticky. |
| Taste | Figs have a sweetness similar to honey and a subtle berry-like flavor. | Dates have a sweet caramel-like taste due to their high sugar content. |
| Suitable climate for production | Figs need a subtropical climate to grow but can survive in mild winters. | Dates are grown in semi-arid and arid regions with long and hot summers. |
| Producers | Turkey is the leading producer of figs, followed by Egypt, Algeria, and Iran. | Egypt produces 17% of the total global production of dates, making it the largest producer. |
What are Figs?
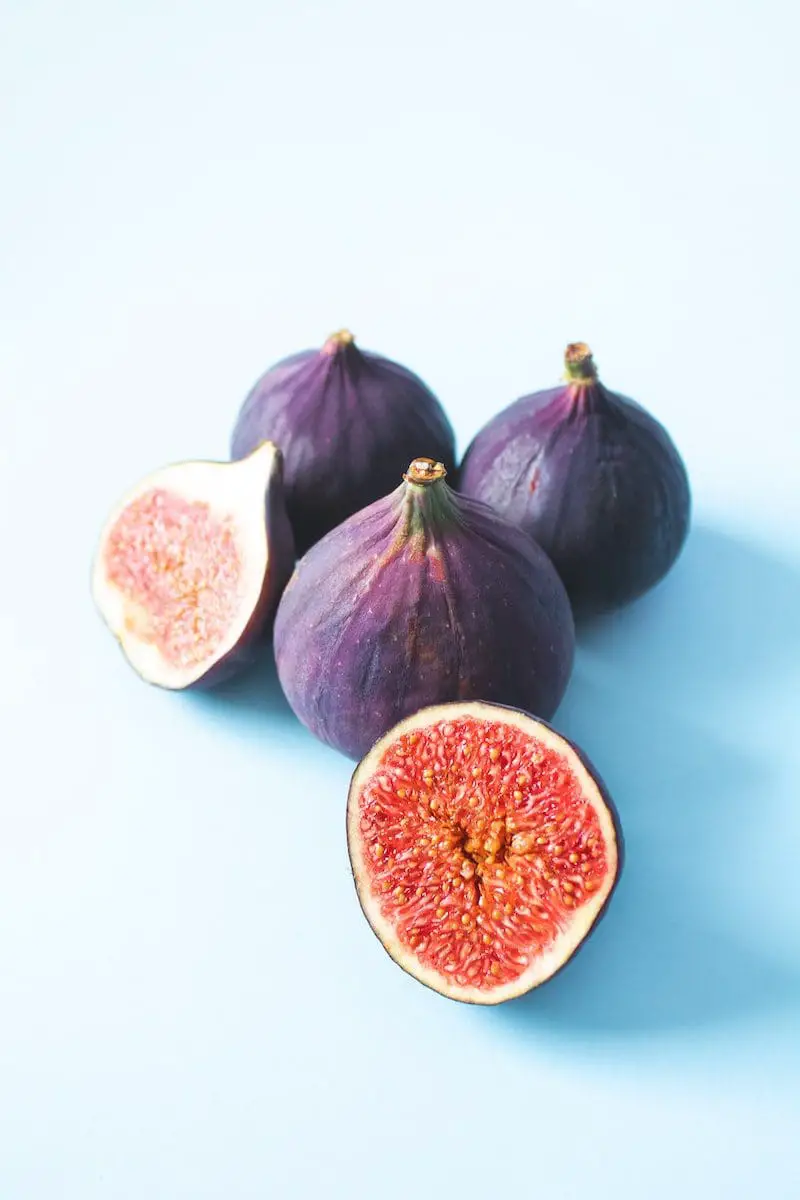
Figs are highly nutritious fruits eaten fresh, cooked, or dried. They grow on Ficus Carica trees, which belong to the same family as mulberry trees.
Figs have a thin outer layer which may be green, yellow, red, or purple, depending on how mature the fruit is. On the inside, the fruit has many tiny seeds and pulp that are either red or white.
The seeds are crunchy to eat, while the flesh and skin of figs have a soft texture. The flesh can also be described as a sweet jelly-like pulp with a honey and berries flavor.
The process in which figs pollinate is an excellent example of co-evolution. When female fig flowers are ready for pollination, they radiate an aroma that attracts a specific kind of wasp to lay her eggs inside the fruit.
The wasp also carries pollen from the previous tree where she gave birth. The pollen which falls into the female flower is used by it to reproduce.
Interestingly, there are more than 750 species of figs, each having their wasp. Some common species of figs include Brown Turkey, Brunswick, and White Marseilles.

What are Dates?
Dates are edible fruits that are eaten fresh or dried. They grow on trees called Phoenix Dactylifera, which are commonly known as date palm trees.
When raw, dates have a crisp flesh like that of an apple. On drying, the fruit becomes sticky and soft.
Dates require a semi-arid or arid climate to be cultivated. They are loaded with vitamins and fructose, which have various health benefits, making them an excellent food source for people living in deserts and drylands.
Unsurprisingly, they have been farmed and eaten for over 5000 years in Egypt and the Middle East. Date trees that grow in deserts and drylands use the wind to pollinate.
However, trees grown in commercial orchards and traditional Oasis horticulture are pollinated manually. They start bearing fruit 4-8 years after being planted.
In about 10 years, the trees produce enough fruit for commercial harvest. Historically, dates have been a popular fruit across the world.
Hebrews used the fruits to make wine, vinegar, bread, and cakes. In Ancient Rome, it was common for gardens to have date palms.
Pompeii and parts of Italy are known to use them as garden plants.

Main Differences Between Figs and Dates
- Figs are fruits of the Ficus Carica tree, while dates are fruits of the Phoenix Dactylifera tree, commonly called date palm.
- Fresh figs have a soft pulp and tiny crunchy seeds, while fresh dates have a crispy flesh like an apple.
- Fresh figs may be yellow, red, green, or purple, while fresh dates are yellow or red.
- Figs have a pear-like bulbous shape, while dates have an oval-cylindrical shape.
- Figs taste sweet like honey and have a subtle berry-like flavor, while dates taste sweet and caramel-like because of their high sugar content.
- Figs grow in a subtropical climate, while dates grow in a semi-arid or arid climate.
- Turkey is the leading producer of figs, while Egypt is the top producer of dates.
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169534703000624
- https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/10408390701724264





The detailed description of fig pollination and the history of date cultivation was particularly fascinating. Well done!
Yes, very informative and well-researched content.
I agree, the depth of information provided here is impressive.
This article is a valuable resource for anyone interested in learning more about figs and dates. The rich history and unique characteristics of these fruits are well-explained here.
I appreciate the in-depth exploration of the origin, taste, and texture of figs and dates. A very enlightening read.
Absolutely, I feel much more knowledgeable about the subject after reading this article.
A highly informative and engaging piece. The in-depth comparison allows for a thorough understanding of the unique qualities of figs and dates.
I found the insights about the fig pollination process to be particularly intriguing.
This article provides a wealth of knowledge about figs and dates. Well-researched and well-written.
The detailed comparison table really helps to highlight the distinctions between figs and dates. This article is a valuable resource for anyone interested in these fruits.
Yes, the table is very useful for understanding the key differences between figs and dates.
I completely agree. The comparison table is a fantastic addition to this informative piece.
Great detailed comparison between figs and dates. I learned so much about the differences in origin, taste, and texture. Very informative article!
I agree, this article definitely taught me a lot about figs and dates.
The description of the fig pollination process was fascinating!
I never knew there were so many varieties of figs. The insight into the unique characteristics of each species was truly enlightening.
I was also surprised by the diversity of fig species. This article is very educational.
A comprehensive breakdown of the features of both figs and dates. I’m impressed by the detailed information provided here.
Agreed, the comparison table is particularly helpful for understanding the differences between figs and dates.
Yes, this article is very thorough. I feel like I’ve gained a lot of knowledge about these fruits.
A well-articulated and thorough exploration of the differences between figs and dates. I appreciate the depth of information provided here.
The information about the pollination process and the unique characteristics of various fig species were particularly fascinating. A very well-researched article.
Yes, a truly enlightening piece on figs and dates.
I agree, I learned a lot from this article.