Physics is the foundation for all other technical principles that are currently in use. The sounds we hear and the light we see and interact with are significant because they are associated with a variety of things.
Sound waves are a sort of mechanical wave that transmits information from one medium to another by exerting pressure and vibration.
They differ in terms of their traits and characteristics. This idea is made possible through the use of concepts such as intensity, speed, and velocity, as well as wave number, wavelength, and frequency. Although wavelength and frequency are connected, they are inversely proportionate.
Key Takeaways
- Wavelength refers to the distance between two successive crests or troughs of a wave.
- Frequency is the number of waves that pass a point in a given amount of time.
- The shorter the wavelength, the higher the frequency, and vice versa.
Wavelength vs Frequency
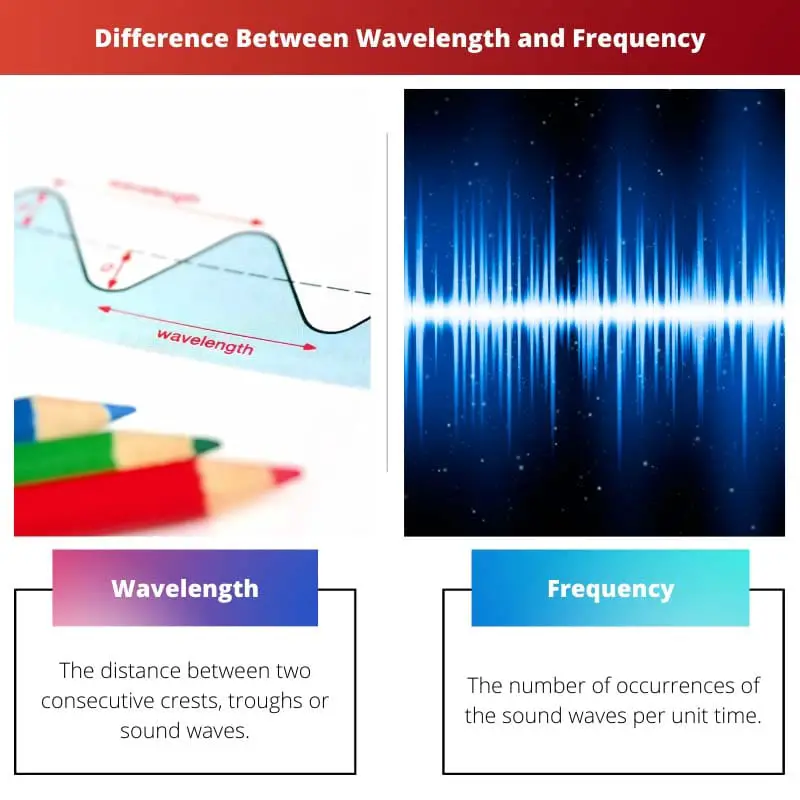
The difference between wavelength and frequency is that the distance between two consecutive crests or troughs, or sound waves, is measured in wavelength. However, on the contrary, The number of times sound waves recur per unit of time is referred to as frequency. Moreover, wavelength and frequency are inversely proportional to each other. This means the higher the value of wavelength, the lesser the frequency and vice versa.
The term “wavelength” refers to the spacing between sound waves. The term “Lamba” is used to describe and denote the length of a wave. When dealing with Wavelength, the unit of measurement utilised is the metre, which is also the international standard unit of measurement.
The wavelength, or lambda, is calculated as the velocity or speed of light divided by the frequency. The wavelength of visible light is constant from 400 nm to 700 nm. The most significant quantity is distance, which is computed using wavelength.
The recurrence of waves is referred to as frequency. The letter “f” stands for frequency. Hertz, which is also the SI unit of frequency, is the unit of measurement used when dealing with frequency.
When calculating frequency, divide the velocity of light travelled by the wavelength value of that particular sound wave to get the result in Hz. The audible sound waves have a frequency ranging from 20 Hz to 20 kHz. The measurement of time is dealt with by frequency.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Wavelength | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The distance between two consecutive crests, troughs or sound waves. | The number of occurrences of the sound waves per unit time. |
| Concept Concerned with | Distance between the sound waves. | Recurrence of the waves. |
| Denoted as | Lambda/ λ | f |
| SI Unit | Meter | Hertz |
| Range | 400nm – 700nm | 20Hz – 20 KHz |
| Calculated as | Wavelength= Speed of light/Frequency | Frequency= Speed of light/Wavelength |
| What is obtained? | Distance | Time |
What is Wavelength?
The distance between two consecutive crests or troughs, or sound waves, is referred to as the wavelength. The term “wavelength” refers to the measurement of the separation between sound waves.
“Lamba” describes and denotes the length of a wave. When dealing with Wavelength, the unit of measurement employed is the Meter, which is also the international standard unit of measurement.
The wavelength, also known as lambda, is calculated by dividing the velocity or speed of light by frequency. The visible light wavelength is constant between 400 and 700 nanometers. The most significant measurement is distance, which is determined by wavelength.
When someone hears various pitches, tones and intonations of sounds, which can be either high or low, however, it is because of the difference or spacing between the waves of sound.
When the waves are closer, the wavelength is shorter, and then they produce a sound that is high in tone. However, in the reverse scenario, when the waves are farther from each other, they make lower-pitch sounds.

What is Frequency?
The number of occurrences of sound waves per unit of time is referred to as frequency. The concept of frequency is concerned with the recurrence of waves.
The letter “f” is commonly used to represent frequency. When dealing with frequency, the unit of measurement is Hertz, which is also the SI unit of frequency.
When determining the frequency, divide the velocity of light travelled by the wavelength value of that particular sound wave to get the result in Hz. The audible sound waves have a frequency between 20 Hz and 20 kHz. The measurement of time is what frequency is all about.
In some cases, the frequency can be heard. However, in other cases, the frequency can not be heard. In the case of ultrasonic sound waves, where the frequency is considerably high, the sound of the frequency can not be heard.
However, it can be heard in audio frequencies. The frequency of the trembling of the earth or the natural disaster earthquake is very low. On the other hand, ultrasound waves possess considerably high frequencies.

Main Differences Between Wavelength and Frequency
- Wavelength is measured as the distance between two consecutive crests or two consecutive troughs or sound waves. On the other hand, Frequency is referred to as the number of occurrences of sound waves per unit of time.
- Wavelength is a concept to measure the distance between sound waves. On the other hand, Frequency is a concept concerned with the recurrence of the waves.
- Wavelength is characterized and denoted as “Lamba”. On the other hand, Frequency is denoted as “f”.
- The unit of measurement used while dealing with Wavelength is the Meter. However, it is the international standard unit of measurement as well. On the other hand, the unit of measurement used while dealing with frequency is Hertz, which is the SI unit of frequency as well.
- While calculating wavelength or lambda, it is given as velocity or speed of light divided by frequency. On the other hand, while calculating the frequency, the answer in terms of Hz is given as the velocity of light travelled divided by the value of the wavelength of that particular sound wave.
- 400 nm to 700 nm is the fixed value of the wavelength of visible light. On the other hand, the frequency of the audible sound waves ranges between 20 Hz and 20 kHz.
- Distance is the most important measure, which is calculated by wavelength. On the other hand, frequency is concerned with the measurement of time.
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/lpor.201500226
- https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/1130391/

The comprehensive explanations of wavelength and frequency, along with the inclusion of practical examples, make the physics of sound waves accessible and engaging for readers.
The practical examples and comparative analysis of wavelength and frequency enrich the article, making it an informative and intellectually stimulating read.
The article adeptly communicates the complexities of wavelength and frequency, providing a valuable resource for those seeking an in-depth understanding of sound wave physics.
The article provides a detailed understanding of wavelength and frequency in sound waves, coupled with real-world examples that illustrate their impact on sound tones. The comprehensive comparison table adds further clarity to the content.
The detailed explanation and comparison table make the concepts of wavelength and frequency easy to comprehend, catering to readers with varying levels of prior knowledge.
The inclusion of practical applications and examples solidifies the understanding of wavelength and frequency, making the article informative and engaging.
The article effectively captures the complexities of wavelength and frequency in sound waves, making them accessible to readers through clear and precise explanations.
The detailed coverage of wavelength and frequency provides comprehensive insights into the physics of sound waves, catering to readers with a keen interest in the subject.
The detailed explanations of wavelength and frequency are well-presented, providing a comprehensive understanding of these concepts. The practical examples of how wavelength and frequency affect the tones of sound waves are insightful and enhance the learning experience.
The practical examples effectively illustrate the relationship between wavelength, frequency, and the pitch of sound. It makes the content more relatable and engaging.
The coverage of wavelength and frequency in this article is thorough and offers valuable insights for readers interested in the physics of sound waves.
The article explains in detail the concepts of wavelength and frequency in sound waves, making it easier to understand the physics behind these principles. The comparison table provided is very helpful in differentiating between the two parameters.
I agree. The detailed explanation of wavelength and frequency in sound waves is very informative and well-researched.
The article meticulously outlines the concepts of wavelength and frequency, offering readers a thorough understanding of sound wave physics. The comparison table serves as a valuable reference point for differentiating between the two parameters.
The comprehensive explanation of wavelength and frequency, supported by the visually appealing comparison table, enriches the learning experience for readers.
The article provides a clear distinction between wavelength and frequency, highlighting their significance in understanding sound waves and their characteristics. The calculation methods and units of measurement for both wavelength and frequency are also explained effectively.
The comparison table is a great visual aid in understanding the differences between wavelength and frequency. It adds value to the overall clarity of the article.
The article offers an in-depth analysis of wavelength and frequency in sound waves, enhancing the reader’s knowledge of these fundamental principles.
The article presents a comprehensive overview of wavelength and frequency in sound waves, enhancing the reader’s knowledge of the underlying physics. The practical implications of wavelength and frequency on sound tones are well-articulated.
The article delves deep into the concepts of wavelength and frequency, providing a comprehensive understanding of sound wave physics. The explanations are clear and well-supported with relevant information.
I appreciate the clarity of the explanations regarding wavelength and frequency, as well as the practical applications in understanding sound wave characteristics.