The term anesthesia itself reveals the loss of sensation. The medicines that are the reason for anesthesia are called anesthetics.
The types of sedation given to patients during a medical procedure or surgery are of great significance. It is a matter of life or death.
Doctors should be extremely considerate about how much sedation they give patients.
Key Takeaways
- Anesthesia is a medical process that causes the patient to lose sensation, while an Anesthetic is a drug or substance used to induce anesthesia.
- Anesthesia is used to carry out medical procedures, while an Anesthetic is used to numb a specific body area for minor procedures.
- Anesthesia involves careful monitoring of the patient’s vital signs, while an Anesthetic requires less monitoring.
Anesthesia vs Anesthetic
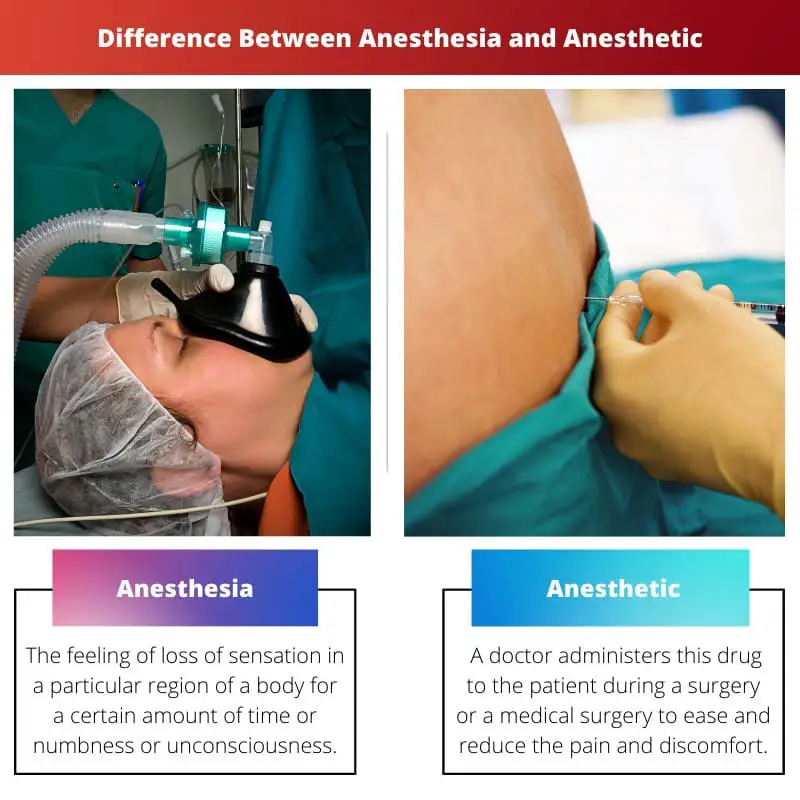
Anesthesia refers to a state of temporary loss of sensation and/or consciousness induced by administering drugs or other means to a patient undergoing a medical procedure. Anesthetic refers to the drug or agent used to induce anesthesia, including local, regional, and general anesthetics.

Anesthesia is when the patient loses the sensation at a particular part, becomes numb, or the patient’s entire body may be subjected to anesthesia.
This is an advanced yet, at times, risky medical advancement that helps and might as well affect the patient if he or she is not administered the right dosage of sedation.
Anesthetics function by stopping the communication and flow of nerve signals that help you to be in sense and consciousness by helping you stay awake and aware.
There are two types of anesthetics, local anesthetics, in which the particular part of your body becomes numb, and other is general anesthesia, where the entire body is unconscious and unaware.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of comparison | Anesthesia | Anesthetic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The feeling of loss of sensation in a particular region of a body for a certain amount of time or numbness or unconsciousness. | A doctor administers this drug to the patient during a surgery or a medical surgery to ease and reduce the pain and discomfort. |
| Types | Anesthesia is of two basic types, local anesthesia, which causes the effect in a specific region, and general anesthesia, which causes its effect t the entire body. | Anesthetics are available in different forms like sprays, ointments, injections, and also gases. |
| Meaning | Anesthesia is the state of the body physically and mentally. | Anesthetics are the name of the drug. |
| Effect | It produces an effect in the patient’s body that eases them to get out of the surgery or procedure with minimum pain. | Anesthetics are administered by the doctors called anesthetics on the patient’s body. |
| Precedency | Anesthesia happens only after the patient is administered anesthesia. | Anesthetics are administered to the patient’s body that causes anesthesia. |
What is Anesthesia?
Though local and general are the basic and commonly known types of anesthesia, there are several other types that are administered based on the type of operation, level of risk involved, pain that the patient has to endure, and also based on the medical history and condition f the patient.
Some of the different types of anesthesia are regional, which numbs only a particular region of your body where the surgery or the procedure is supposed to take place.
Epidural anesthesia is also another type of regional anesthesia that numbs the part o your body below the torso. This is especially used for childbirth as it will ease and relieve pain and stress.
As the name suggests, spinal anesthesia is used to perform surgeries that are better if the whole body loses consciousness and sensation. It retains the effect for three hours by numbing the lower parts of your lower back and lower spinal areas.
Sedation is a special type of anesthesia that makes you sleep, and it is great for crucial surgeries that require you to relax physically and mentally.
These are such a boon to the field of medicine as they help overcome unpleasant and excruciating procedures with much comfort, relaxation, and ease.
What is Anaesthetic?
Anesthetics are some of the most commonly and frequently used types of medication that help you t overcome the procedure with less or almost no pain.
Once these anesthetics lose their nature, the body will regain its original form, and your body will not become less numb, and you will gain consciousness.
Not all types of anesthesia lead to unconsciousness. Only general anesthesia does that, and mainly, they are given to specific parts of the body, and comparatively, this is a safer option.
Anesthetics are given in several forms. Some are given in the form of ointments, sprays, and drops. These ate used for minor applications to relieve pain in dental surgeries and procedures.
For major surgeries, anesthetics are used in the form of injections. The anesthetic is injected into the vein of the patient. In certain cases, you inhale the anesthetic in the form of a gas.
An anesthetic is a doctor who has a specialized degree in the study of this field, and before every surgery, he or she will prescribe you the right amount based on the type and severity of the procedure and also based on the nature of your body.
Main Differences Between Anesthesia and Anesthetic
- Anesthesia is the cause of sensation or numbness, whereas Anesthetics is the drug.
- Anesthesia is of several types, including local and general anesthesias, whereas anesthetics are available in the form of ointments, injections, sprays, and so on.
- Anesthesia is the state of the body, whereas Anesthetics is the type of drug that induces anesthesia.
- Anesthesia is the effect, whereas anesthetics is the cause.
- Anesthetics are administered, which succeeding leads to anesthesia.
- https://pubs.asahq.org/anesthesiology/article-abstract/106/1/33/8860
- https://pubs.asahq.org/anesthesiology/article-abstract/91/5/1509/39623

The intricate nuances of anesthesia and anesthetics demand a high level of expertise and vigilance in their deployment to ensure favorable patient outcomes and experiences. It’s a testament to the depth of medical science and practice.
Absolutely, the comprehensive understanding of anesthetic agents and their pharmacological effects is vital for delivering personalized and effective anesthesia care to patients undergoing diverse medical procedures.
The unique role of anesthetics in minimizing or eliminating pain during medical procedures and surgeries is pivotal in improving patient experiences and outcomes. It’s a testament to the advancements in modern medicine.
Absolutely, the development of anesthetics has revolutionized surgical practices and has significantly enhanced patient care and recovery processes.
The use of anesthesia involves many risks, including potential complications during and after the procedure. Doctors must exercise extreme caution to avoid any harmful effects.
The monitoring of vital signs and precise dosing of anesthetics are crucial for the safety and well-being of patients undergoing medical procedures.
The distinct characteristics and mechanisms of anesthetics underscore their tailored applications in addressing patients’ unique medical needs, thereby enhancing their overall experience and recovery. It’s a fascinating aspect of perioperative medicine.
The impact of precise, individualized anesthetic management in surgical and procedural settings highlights the critical role of anesthesiologists and medical teams in optimizing patient-centered care and clinical outcomes.
An understanding of the distinctions between anesthesia and anesthetic is critical for grasping their importance in the medical field. It is key to have the right balance to ensure safety for the patient throughout the entire procedure.
I agree, the careful administration of anesthesia plays an important role in ensuring the safety and health of patients before, during, and after surgery.
Anesthetics function by disrupting the flow of nerve signals, creating a state of awareness or insensitivity to pain. Proper management of anesthetics is essential to ensure a successful surgical outcome.
An in-depth understanding of the effects and mechanisms of anesthetics is fundamental in the field of medicine to provide optimal care for patients undergoing various surgical procedures.
The diverse types of anesthesia, such as regional, spinal, and sedation, cater to specific medical needs and contribute to elevating patient care standards. A thorough understanding of these anesthetic modalities is essential for medical professionals.
Precise and informed decisions on the selection and administration of anesthetics are indispensable in the provision of high-quality patient care across various medical specialties.
The nuanced analysis of patient conditions and procedural requirements guides the strategic use of anesthetics, highlighting the interdisciplinary nature of perioperative healthcare.
It’s fascinating to learn about different types of anesthesia, such as regional, epidural, spinal, and sedation, and their specific applications in various medical scenarios. Each type serves a distinct purpose based on the patient’s needs and requirements.
Indeed, the diverse forms of anesthesia offer tailored solutions to address different surgical, obstetric, and diagnostic procedures, enhancing patient comfort and care.
Anesthesia and anesthetics play pivotal roles in minimizing patient distress and discomfort during medical interventions, underscoring the significance of the anesthesiologist’s expertise and the interdisciplinary collaboration within perioperative care.
The multifaceted nature of anesthesia and the precise dosing of anesthetics are vital aspects that significantly influence patient safety and the overall quality of clinical outcomes.
The careful application and vigilant monitoring of anesthetics reflect the complex interplay of medical expertise, pharmacology, and patient-centered care in modern healthcare practices.
The careful selection and administration of anesthetics contribute significantly to patients’ comfort and recovery, as well as the success of medical interventions. It’s an intricate yet vital aspect of healthcare.
The precision and expertise required in the use of anesthetics underscore the critical role of anesthesiologists and healthcare teams in ensuring patient safety and well-being throughout the perioperative period.