If an institute or organisation needs to spend money to buy a thing or invest it in a certain concept, they need to keep track of their funds.
However, the expenses that they have to face also turn out to be profitable, or they suffer losses sometimes.
There are several concepts that encompass the entire idea of the expenses that are managed and completed by a certain organization or institution of any type. Two of these concepts are 1. Capital expenditure, and 2. Revenue expenditure.
Key Takeaways
- Capital expenditure involves the purchase of long-term assets or improvements to existing assets, which provide benefits for more than one financial year. In contrast, revenue expenditure pertains to expenses incurred in the normal course of business operations.
- Capital expenditure increases the earning capacity of a business and is recorded on the balance sheet, whereas revenue expenditure maintains the earning capacity and is recorded on the income statement.
- Capital expenditure is non-recurring and results in the acquisition of fixed assets, while revenue expenditure is recurrent and associated with the day-to-day functioning of a business.
Capital Expenditure vs Revenue Expenditure
Capital expenditure refers to funds used by a company to acquire or upgrade physical assets such as property, industrial buildings, or equipment, with a long-term view. Revenue expenditure is short-term spending used for the day-to-day running of a business, such as repair and maintenance, salaries, and office supplies.
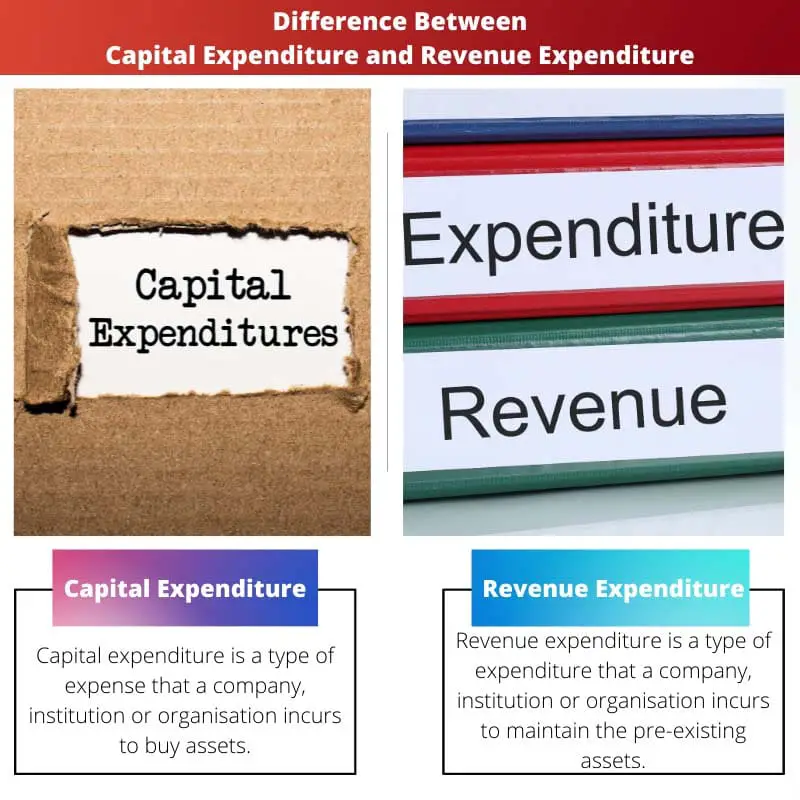
Capital expenditure is a type of expense that a company, institution or organisation incurs to buy assets and thereby increase the lifespan of the pre-existing asset.
The assets can be anything depending on the type of company and what business the company is into.
Revenue expenditure is a type of expenditure that a company, institution or organisation incurs to maintain pre-existing assets. It is also known as operational expenditure or OPEX.
The maintenance of a certain pre-existing asset is considered an expense under the revenue expenditure.
Comparison Table
| Parameters Of Comparison | Capital Expenditure | Revenue Expenditure |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning/ Definition | The expenditure that is accepted by an organization or an institution to buy an asset and increase the lifespan of the present asset is known as capital expenditure. | The expenses that arise for the maintenance of the present assets are known as revenue expenditure. |
| Duration | Long | Short |
| Asset value | The value of an asset is increased. | The value of an asset is not increased. |
| Capitalization | Available | Unavailable |
| Business revenue | The business revenue stays unaffected. | The business revenue is reduced. |
What is Capital Expenditure?
Capital expenditure is a form of expenditure accepted by several companies, businesses, institutions, and organisations for buying a new asset altogether, thereby increasing the lifespan of the pre-existing asset.
It is also addressed as a capital expense or CAPEX. Many fixed assets are bought for a company’s necessity which is all a part of capital expenditure.
If a company is any plant, it would require many more fixed assets. Other than that, the property’s building expenses are also considered capital expenses.
Several companies also require equipment and raw materials for their further production, which is also calculated in the capital expenditure, which is further decided if it is a major or minor financial decision.
Once the decision is made, the expense is completed, and if the expense is considered a major financial decision, then many key people working for the respective company come together and take further action. Keeping track of the capital expense also helps in taxation.
For various taxation procedures, the expenses under the category of capital expenditures are compulsorily capitalized.
Other than that, a company also takes into consideration the use of the asset and how it would increase the lifespan of a pre-existing asset.
If a company buys an asset, it is also bought for various reasons like fixing an asset, replacing a pre-existing asset, preparing an asset for business purposes etc.

What is Revenue Expenditure?
Revenue expenditure is a type of expenditure that is accepted by a company for the maintenance of various other existing assets.
It fixes the pre-existing assets from a certain company as the funds are used to maintain the condition of the asset and bring it back to a better condition.
Revenue expenditure is also known as revenue expenses or simply as an operational expense or OPEX. There are two main types of revenue expenses, indirect revenue expenditure and direct revenue expenditure.
The process of the various goods and services that are engaged in a company’s entire manufacturing and the costs and expenses that are incurred during that time falls under the category of direct expenditure.
The various costs and expenses that are incurred during the distribution of various goods and services fall under the category of indirect expenditure.
The direct expense is the expense that occurs when the process is ongoing, while the indirect expense is an expense that occurs when the process is finished.
There are various examples of revenue expenditure. If a company buys equipment for carrying out various tasks and the monthly maintenance cost of that equipment is supposed to be paid, then that cost comes under the revenue expenditure section.
All the monthly entries and transactions that are made for that particular equipment are a part of revenue expenditure.
Main Differences Between Capital Expenditure and Revenue Expenditure
- Capital expenditure includes the expenses that are occurred for buying new assets. On the other hand, revenue expenditure includes the expenses that are occurred for maintaining the pre-existing assets.
- The business revenue stays unaffected by capital expenditure. On the other hand, the business revenue is curtailed because of revenue expenditure.
- Capital expenditure is also known as CAPEX. On the other hand, revenue expenditure is also known as OPEX.
- A business can gain long-term profits because of capital expenditure. On the other hand, a business can gain short-term profits because of revenue expenditure.
- Capital expenditure is non-recurring. On the other hand, revenue expenses are recurring.
- Capitalization is available in capital expenditure. On the other hand, capitalisation is not available in revenue expenditure.
- Some of the capital expense appears either in the income statement or the balance sheet. On the other hand, the entire revenue expense all ears in the income statement.
- https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/00137917508965140
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0161893810000475

This analysis sheds light on the differences between capital and revenue expenditure. It’s interesting to see how the profits from these expenditures differ and how they affect a company’s financial health.
The examples in this article clearly show how capital and revenue expenditures play a crucial role in the financial decisions of a business.
This is just a simple overview of the concepts, there are much deeper financial discussions that should be addressed.
The article fails to address the complexities of real-life examples of capital expenditure and revenue expenditure, making it somewhat superficial and not fully informative
The article provides a very detailed explanation of the difference between capital expenditure and revenue expenditure, making it easier for readers to understand these complex financial concepts.
The proper classification of capital expenditure and revenue expenditure is crucial for tax purposes, this separation can greatly affect the business’s financial health.
It is interesting to note how revenue expenditure ultimately affects the overall business income, showing the importance of effective management of these expenses.
It is important for a company to have a clear understanding of how the expenses are managed, and it is vital to add these expenses to the balance sheet to have a clear understanding of the organization’s financial status.