Botany is the most enthralling part of biology. It is primarily the study of plants and their life cycle. Botany is sub-classified into many sub-categories, an anthology being one of them.
The anthology is the study of the life and reproductive cycle of flowers, as flowers are the essential reproductive part of the plant.
From an amateur’s perspective, many scientific terms can confuse, for instance, carpel and pistil. Both are related to the female reproductive part of a flower but differ from each other.
Key Takeaways
- A carpel is the basic unit of a flower’s female reproductive system, consisting of an ovary, style, and stigma. At the same time, a pistil is a structure composed of one or more fused carpels within a flower.
- Carpel and pistils play essential roles in plant reproduction, with carpels serving as individual components and pistils functioning as the collective female reproductive organ.
- Both terms are used in the study of plant anatomy and botany to describe the various structures involved in the sexual reproduction of flowering plants.
Carpel vs Pistil
The carpel is the female reproductive organ of a flower, consisting of three parts: the stigma, style, and ovary. The pistil is the collective term for all of the female reproductive structures in the flower, including one or more carpels, as well as the stigma and style.

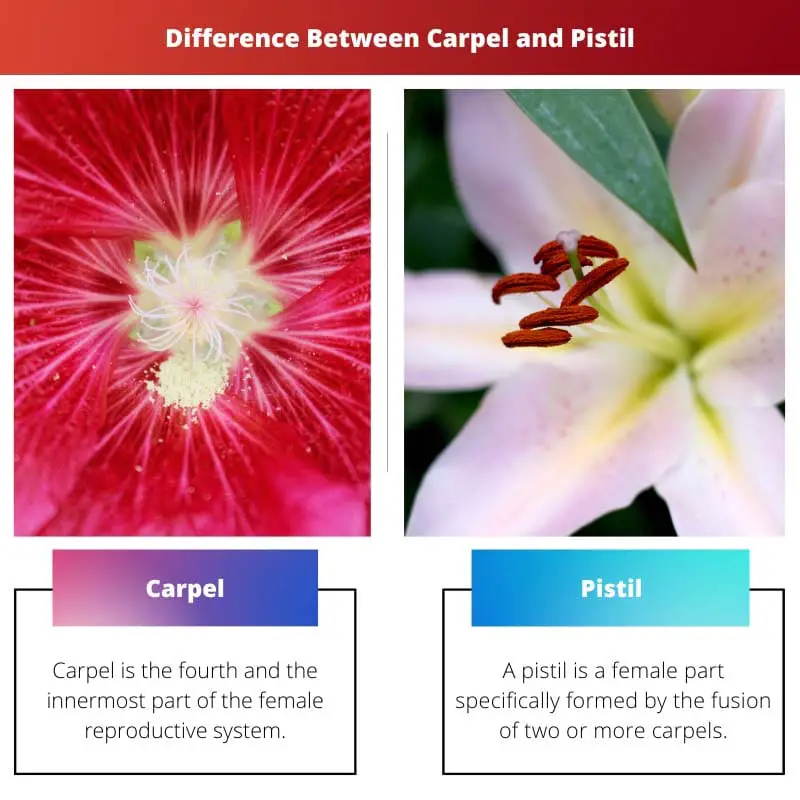
Carpel is the fourth and the innermost part (whorl) of the female reproductive system. It comprises a sticky base called- a stigma, where the pollen reaches to germinate and reproduce, a long stalk-style, and a swollen base- ovary.
A carpel undergoes fertilization and produces seeds. The carpel develops and disperses seeds.
A pistil is a female part specifically formed by the fusion of two or more carpels. It is at the centre of the flower and structurally has a swollen base that comprises ovules- these ovules later on form the seeds.
Pistils do not undergo the fertilization process but are still one of the female reproductive parts.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Carpel | Pistil |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Female reproductive structure | Seed-bearing part of the flower |
| Comprises | Stigma, Style, Ovary | Ovules |
| Fertilization | Yes | No |
| Identified by | Number of styles | Number of ovaries |
| Key Features | Dispersal and production of seeds | Does not disperse or produce seeds |
What is Carpel?
As aforementioned, the carpel is a part of the female reproductive part of a flower referred to as the essential whorl of the flower. It comprises stigma, style, and ovary.
It carries out all the reproductive functions of the flower, from fertilization to seed germination and dispersal.
The word carpel originated from the French word- Carpellum. It was initially considered a whorl full of leaves to cover and protect the ovary, which then developed to form a structure-bearing ovule.
The carpels of some flowers do not contain a style.
The pollen from a male flower enters the female reproductive system through the sticky part stigma. It germinates there, passes through the long stalk style, and then reaches the ovary, which contains ovules of egg cells.
The pollen grain fertilizes the eggs, which then form the seeds. The ovary forms the fruit, while the ovule forms the seed.
The seeds are dispersed through a carpel.
A flower can have one or more carpels, a monocarpous flower denotes a flower with a single carpel, while we term a flower with many but unfused carpels as apocarpous, and we term a flower with fused carpels as syncarpous.
Some flowers do not have carpels at all. It is not an issue, as the ovules develop on the shoot apex. We can identify the number of carpels by counting the number of styles.
What is Pistil?
As mentioned above, the pistil is a part of the female reproductive system, primarily made up of ovules (potential seeds). It does not undergo fertilization as it does not produce eggs/ egg cells. Carpels characterize it.
The pistil is known as the fusion of carpels. We identify the number of pistils by counting the number of ovaries.
We derived the word pistil from the Latin Pistillium, which denotes a device- mortar/ Pestle used in the past. It gained its name because of its structure. Some plants do not contain a pistil we term these types of plants pistillode.
A pistil is at the centre of the flower with a huge swollen base structure containing ovules, which are then fertilized to form ovules, although fertilization does not occur inside the pistil.
The ovules in a pistil can be of many types, with or without a septum. Placenta- which is found in mammals, is also present in some plant pistils as a source of nutrition for the developing seeds.
Modern-day studies show that the carpel is a leaf-like appendage protecting the essential whorl pistil.
The pistil comprises one-to-many carpels. For instance, we would term a pistil with a single carpel as a monocarpellary.
Two carpels would mean bi-carpellary, and so on. Identifying the number of pistils helps to classify taxonomically and decode the floral formula.

Main Differences Between Carpel and Pistil
- The carpel is the female reproductive part of the flower, whereas the pistil is the seed-bearing part of the female flower.
- Carpel comprises a stigma, style, and ovary, while the pistil comprises one or more carpels.
- Carpel aids in seed dispersal, whereas Pistils do not help in seed dispersal.
- Carpel produces egg cells. On the other hand, Pistils do not develop eggs.
- Carpel undergoes the process of fertilization. In contrast, Pistils do not undergo fertilization.
- We identify the number of carpels by counting the number of styles, whereas we can identify the number of pistils through the number of ovaries.
References
- https://www.journals.uchicago.edu/doi/abs/10.1086/321919
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmc160356/
