Mental illness or disorders affect the thinking, mood, and behaviour of an individual. The day-to-day activities are also affected, and several changes in emotions, personality and feelings can be observed.
Key Takeaways
- Dementia is a progressive decline in cognitive function, while amnesia refers to memory loss that may be temporary or permanent.
- Alzheimer’s disease is the most common cause of dementia, whereas amnesia can result from various factors, such as brain injury or psychological trauma.
- Treatment for dementia is primarily focused on managing symptoms, while amnesia treatment addresses the underlying cause when possible.
Dementia vs Amnesia
Dementia is a medical condition that occurs when the awareness and intelligence of a patient are affected and is caused by Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease. Amnesia is a medical illness that causes the patient to lose their memory due to traumatic stress or injury to the brain cells.

Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease are considered the main causes of dementia. The intelligence and awareness of the patient are affected.
On the other hand, amnesia can be forced or induced due to past events, traumatic stress, or injury to the brain cells.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Dementia | Amnesia |
|---|---|---|
| Cause | From neurological disorders like Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s Disease or from vascular disorders like infarct dementia, strokes or through other infections that can affect the CNS (Central Nervous System) | Due to brain damage of injury like stroke, encephalitis, respiratory distress, subarachnoid hemorrhage, tumor, or other seizure disorders |
| Type | Two types – Alzheimer’s type and non-Alzheimer’s type | Two types – anterograde amnesia and retrograde amnesia |
| Symptoms | Memory loss, forgetting usual details or recent events, mood change and feeling emotionally low | Loss of recent memories, disorientation, confabulation, confusion, and remote memories are spared |
| Diagnosis | After reviewing symptoms, imaging tests like PET, MRI, and CT scans are done and several mental functioning tests are done to identify the issue | Symptoms and previous medical history is monitored and assessments are done to determine the extent of loss in memory and imaging scans like MRI, CT or EEG are also done |
| Treatment | Can be treated but not reversed or completely cured. Medications and drugs like cholinesterase inhibitors and NMDA receptors are prescribed | Some symptoms resolve by psychotherapy, hypnosis, digital aids, medications, and a balanced diet can help |
What is Dementia?
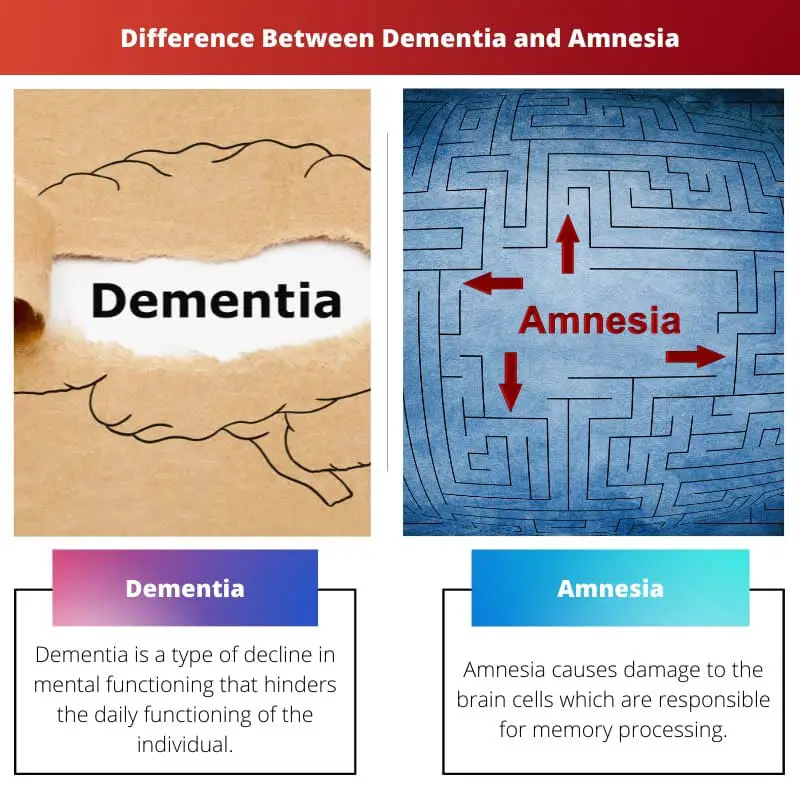
Dementia is a type of decline in mental functioning that hinders the daily functioning of the individual. Dementia affects the parts of the brain that are involved in decision-making, learning, and memory.
There are two main types of dementia – Alzheimer’s Dementia, which includes memory loss as well as other impairments in the functioning of the brain
Non-Alzheimer’s Dementia can degenerate the frontotemporal lobe and can affect speech and behaviour.
Most of the cases of dementia are from the older age groups, but even young people can develop dementia if they have a history of neurological disorders like Alzheimer’s disease,
Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s Disease, or vascular disorders like infarct dementia, strokes, and other infections.
Dementia can affect distinct regions of the brain that are responsible for a particular function. Dementia can rapidly worsen and cause other complications.

What is Amnesia?
Amnesia causes damage to the brain cells, which are responsible for memory processing. The memory loss in amnesia is permanent.
The common symptoms of amnesia include loss of recent memories, confabulation (occurrence of false memories), confusion, and remote memories being spared.
The most common reasons are due to brain damage or injury like stroke, encephalitis, respiratory distress, oxygen deprivation, subarachnoid haemorrhage, tumour, other seizure disorders,
or by treatment of other psychiatric diseases, which can include Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT).
Though there are two main types of amnesia, there are some other types, too, like transient global amnesia, traumatic amnesia, Wernicke-Korsakoff’s psychosis, hysterical amnesia, infantile amnesia,
posthypnotic amnesia, prosopamnesia, and many other types. Some cases of amnesia resolve by themselves.
Main Differences Between Dementia and Amnesia
- Dementia occurs in old age, but amnesia can occur in people of any age group.
- Dementia affects cognitive power and decision-making ability, while amnesia does not affect the cognitive power and decision-making power of the individual.
- https://psycnet.apa.org/doiLanding?doi=10.1037/0735-7044.101.3.347
- https://psycnet.apa.org/doiLanding?doi=10.1037/0096-3445.117.1.34

Amnesia and dementia are complex conditions. The article explains the differences clearly.
The reference links are useful for further study on this topic.
The article serves as a great resource for those looking to understand the differences between dementia and amnesia.
It’s interesting to see the distinct differences between the two conditions.
The article provides valuable insights into these mental health issues.
The article covers significant aspects of both dementia and amnesia in an easily understandable manner.
I find the comprehensive comparison quite enlightening.
This article is well-researched and the comparison table is very informative.
I agree, it’s a very useful read.
Great information. It’s helpful to know the differences.
Well-presented details about dementia and amnesia. The informative content helps in clarifying the distinctions.
A useful resource to learn about dementia and amnesia.
The article contributes valuable insights into these mental health conditions.
Good comparison between dementia and amnesia. The examples provided help in understanding the conditions better.
I appreciate the detailed comparison and explanations.
The article delivers clear and concise information on the topic.