Everything is being digitalized as we move towards the generation. Innovation is at its highest peak, specifically in technology. Technology is everything in today’s world.
For example, where the early generation was satisfied with the computer nowadays, even a laptop sometimes does not satisfy the individual. Along with this, privacy and security have become an issue, such as the security of data (information).
Today we are going to discuss the types of data, i.e., encrypted and unencrypted. It is not only important to understand this but to know its importance and consequences as well.
Key Takeaways
- Encrypted data is secure and protected by a password or key, making it unreadable without authorization.
- Unencrypted data is not protected and can be easily accessed by anyone with physical or remote access to the device or network.
- Encryption adds a layer of security to sensitive data, such as personal information, financial records, and confidential business data.
Encrypted vs Unencrypted
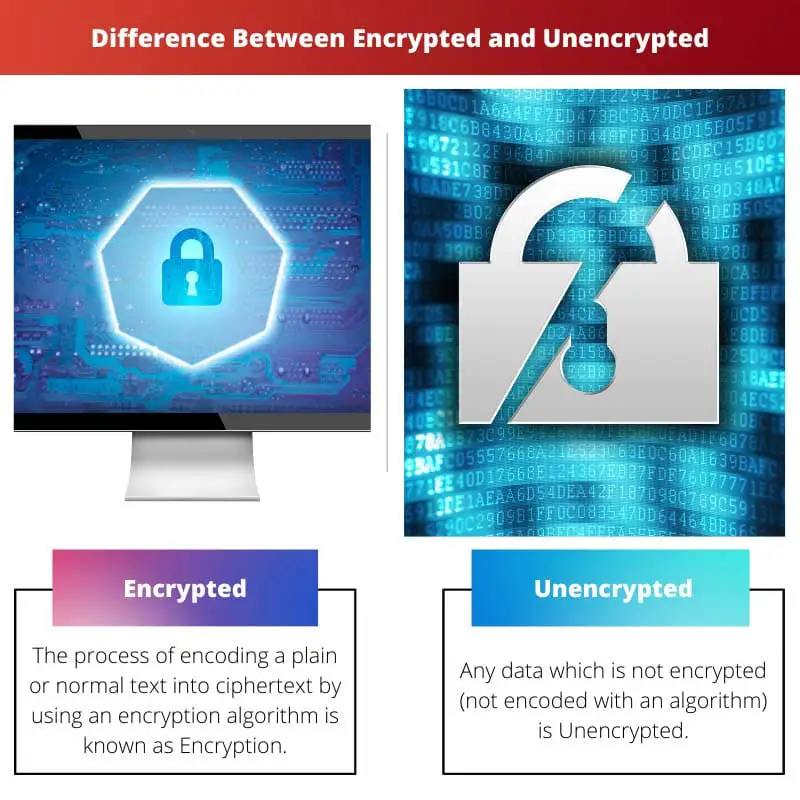
Encrypted is the data that is turned into ciphertext using an encryption algorithm and has access to the only authorized party. By doing this, the data is made more secure, whereas unencrypted is nothing but plain and normal text which is not secure or encoded by any algorithm.
Encrypted is the type of secure data which is encoded. Only a key provided to an authorized party can help decode it. Otherwise, no one can understand what information that data has.
It is a way of protecting crucial information/data from any frauds or mishappenings. This process is done by using various encryption tools.
Unencrypted is the opposite of encrypted, i.e., any data that is not secure and is available t be understood without decoding. This could be a document or e-mail. Most data that is not very crucial and can cause nor harm is left unencrypted or as plain.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Encrypted | Unencrypted |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Encoded data | Normal data |
| Referred as | Cipher Text | Plain text |
| Security | It is more secure. | It is not secured at all. |
| Access to data | Only the authorized party can have access. | Anyone can have access. |
| Tools | There are several tools. | No tools are used as such. |
What is Encrypted?
Encoding a plain or normal text into ciphertext using an encryption algorithm is known as Encryption.
The reason for encrypting the data can be:
- Privacy: being more digitalized does not imply a breach of privacy and ensures this Encryption is done. Sometimes people want privacy in data that only chosen people can have access to it. Therefore data is encrypted.
- Security: it is important to make sure data is secured from falling into the wrong hands. Cybercrime and fraud are prevented by doing so.
- Authentications: a key is provided to the owner and everyone who can have access to the data. Except for them, no one can understand the data.
- Regulations: many organizations have few rules to encrypt the data.
Types of techniques of Encryption are:
- Symmetric Encryption Method: it is also known as private-key cryptography or a secret key algorithm. Under this method, the sender and receiver must share the same key for access. This is considered best as no access to a third party is provided.
- Asymmetric Encryption Method: it is also known as public-key cryptography. This technique has two mathematically connected keys: private and public keys.
- Hashing: Under this technique, once data is encoded, it cannot be decoded. It creates a unique signature.

What is Unencrypted?
Any data which is not encrypted (not encoded with an algorithm) is Unencrypted. It can be easily read and understood without and password or knowledge of Encryption.
An unencrypted that has the following limitations:
- Lack of Security: Well, obviously, if the data is not encoded and is plain text, there is no security to it. It can be understood even by the person who will misuse it for his benefit. Therefore, unencrypted data’s main and biggest disadvantage is that it is not secured. This has led to an increase in cybercrime and fraud all over the world.
- Vulnerable: it is vulnerable to crimes and misuse by any person. Data is being held in the wrong hands, and a price always has to be paid for this circumstance.
- Lack of privacy: there is no privacy with unencrypted data, as everything is public. Therefore any private detail needs to be encrypted.
Advantages:
The only advantage it has is that no extra effort has to be made to read or understand the data. It is written in the raw form; therefore, no time has to be wasted to get access or some key.
It is a decision that must be made whether data has crucial information that should be secured. Otherwise, data should remain unencrypted.

Main Differences Between Encrypted and Unencrypted
- Encrypted means any data which is protected by an encryption algorithm. In contrast, unencrypted is the opposite of encrypted, which means anything which is not encrypted or protected.
- Encrypted is also known as the ciphertext, which cannot be understood easily, whereas unencrypted is also known as plain or normal text.
- Only the authorized party has access to the encrypted information; therefore, no other person can have access to it, whereas unencrypted being insecure, can be accessed by anyone.
- A decryption key is required to decode the encoded encrypt, but no such key is required in case of unencrypted.
- Encrypted is far more secure than unencrypted, which is not secure at all.
- There are various tools used for encryption methods, but no such tools are used for unencrypted.
- Encryption data cannot be understood until decoded, while there is no difficulty arises while understanding the unencrypted data.
- https://dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.1145/30401.30404
- https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/1337277/
- https://dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.1145/1666420.1666444

The comparison table detailing the differences between encrypted and unencrypted data is particularly informative. Understanding how encryption works is essential in today’s digital world.
Technology has truly evolved and now encryption is crucial for protecting sensitive data. This is a very informative article, thanks for sharing.
The comparison between encrypted and unencrypted data provided in this article is valuable. It’s clear that unencrypted data lacks the security and privacy that encrypted data provides.
The difference between encrypted and unencrypted data is crucial to understand, especially in today’s digital age. I appreciate the breakdown of the advantages of encryption and the types of encryption techniques used.
Understanding the importance of data security and encryption is essential, especially for individuals and businesses. I found the detailed explanations of the types of encryption techniques and algorithms very informative.
The importance of encryption in maintaining data privacy and security cannot be overstated. This article provides valuable insights into the various encryption techniques and their significance.
This article effectively highlights the importance of encryption for protecting sensitive information. The breakdown of different encryption techniques and algorithms is insightful.
It’s evident that encryption plays a critical role in safeguarding sensitive data from cyber threats and unauthorized access. The article provides a comprehensive understanding of encrypted and unencrypted data.
Encryption is a key component of data security, and this article provides a comprehensive overview of the differences between encrypted and unencrypted data. The advantages and disadvantages of both are well-explained.
The comparison between encrypted and unencrypted data is well-explained, and the article effectively emphasizes the importance of encryption for privacy, security, and authentication.
The article provides a clear understanding of the purpose of encryption and its role in data security. The advantages and disadvantages of encrypted and unencrypted data are well-presented.
The article effectively explains the significance of encryption and its role in enhancing data security and privacy. The different encryption techniques and algorithms are well-detailed.