HTTP and HTTPS are the two data transfer protocols that are differentiated with a thick line of data integrity and security.
HTTP is very popular among blogging beginners as no data privacy is required in the early stage of blogging. How both transfer protocols are used at different platforms is elaborated below:
Key Takeaways
- HTTP is a protocol for transmitting data over the internet without encryption.
- HTTPS is a secure version of HTTP that encrypts data using SSL or TLS.
- Using HTTPS is critical for securing sensitive data and improving user trust.
HTTP vs HTTPS
HTTP is an unencrypted protocol that transfers data between a web server and a web browser, making it vulnerable to interception and reading by third parties. HTTPS is a secure version of HTTP that uses encryption to protect data transmitted between a web server and a web browser. It is commonly used for online transactions.

HTTP is a web-based transfer protocol and can be implemented with another protocol over the internet. It does not demand any runtime support.
The pages of HTTP are stored on desktop and internet caches, making it speedy, and data over the internet is quickly accessible through it.
HTTPS is the highly advanced version of HTTP, which creates a secure connection between the server and the browser.
It is secured with the key-based encryption algorithm, which is 40 or 128 in bits in terms of strength. SSL certificate in HTTPS contains unique authentication information and data of the licensee.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | HTTP | HTTPS |
|---|---|---|
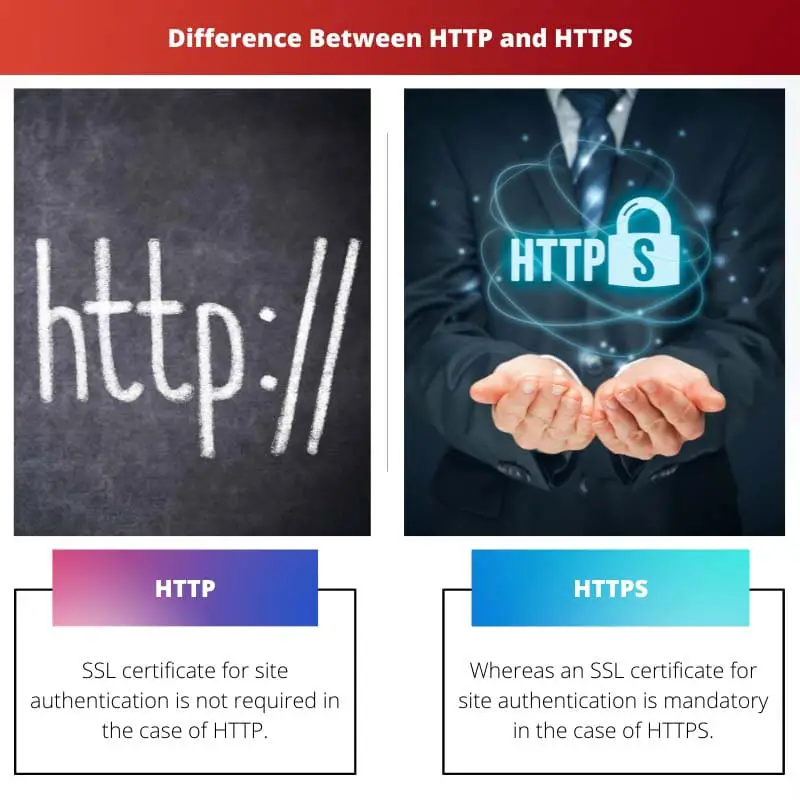
| Domain Validation | SSL certificate for site authentication is not required in the case of HTTP. | Whereas an SSL certificate for site authentication is mandatory in the case of HTTPS. |
| Data Encryption | Data Encryption facility is not available in the case of HTTP. | HTTPS, on the other side is completely secure. |
| Security | HTTP is not much secure as data is vulnerable to unethical hackers. | There is no separate protocol in the case of HTTPS; it uses TSL/SSL certificate. |
| Protocol | Operation Protocol in HTTP is TCP/IP level. | There is no separate protocol in the case of HTTPS, it uses TSL/SSL certificate. |
| Purpose | HTTP is a prominent option for Websites designed for blogging purposes. | HTTPS is designed for websites that deal with private data consumption. |
What is HTTP?
HTTP is not able to regulate the data transfer over it. It helps web users for a fast web browsing experience.
The standard protocol used for data transmission over the internet is Transmission Control Protocol or Internet Protocol, and protocols other than TCP/IP is HyperText Transfer Protocol.
It is much demand in the case of websites used for information consumption.
It performs the over-command and response cycle of the user requesting the web page.
While browsing over G,Google, when a user requests a web page,, transfer protocols help them arrive at the page. It is a stateless protocol that makes it free for every transaction over HTTP.
Universal applications can run over HTTP. Being an independent platform on the browser, it allows cross-platform services.
It is unsafe to use when a user shares sensitive information over HTTP; which can be credit card details, passwords, or any typed data over the internet.
This application layer protocol is built over the top of the TCP/IP level. It uses a structured, hypertext structured text, that enables a logical link between nodes, including the text data.
The fetching of resources like HTML documents is one of the essential tasks performed by this transfer protocol.
What is HTTPS?
HTTPS is the more secure version of HTTP instead of being converse of HTTP. All the problems and hurdles of HTTP can be resolved by switching from HTTP to HTTPS protocol.
It cannot prevent data stealing from the pages cached over the browser. Using it can cause overhead expenses at the organizational level.
Data is encrypted during the transmission phase only in the case of HTTPS protocol.
Online banking is safe over HTTPS websites, and most commercial transactions are secured via 2-way authentication. HTTPS transfer the data in ciphertext instead of plain text.
HTTPS is not as speedy as HTTP as it consumes computational energy.
Operations of HTTPS are performed over the transport layers, unlike HTTP, which operates over application layers. High security makes it suitable in search ranking over google chrome.
The data communication is performed at the 443 port through auto-configuration.
HTTPS websites are equipped with both encryption and data decryption in exchange activity. The secure bridge is created using Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure between host and browser.
The browsing speed is slow due to data verification and redirects over secure transfer protocol. It is an SEO-friendly protocol. The secured feature of HTTPS protects website data from hackers.

Main Differences Between HTTP and HTTPS
- Port: The Port used by HTTP is 80 by default on the other hand Port used by HTTPS is 443 by default.
- Search Ranking: Search ranking is not improved by HTTP whereas Search ranking is improved with the help of HTTPS since it’s a secure protocol.
- Speed and Accessibility: The runtime speed and accessibility are fast in the case of HTTP, whereas it is slow in the case of HTTPS.
- Vulnerability: Data is more vulnerable to illegal hackers in the case of HTTP and Data is less vulnerable to hackers in the case of HTTPS since it contains an SSL certificate.
- Scrambling: Data is not scrambled in HTTP before transmission or in HTTPS before any transmission.

Very informative content! This article greatly explains the differences and importance between HTTP and HTTPS protocols.
These protocols are often misunderstood. It’s refreshing to read a comprehensive breakdown of their characteristics and functionality.
I concur with Oliver Clarke. The article effectively debunks misconceptions about HTTP and HTTPS.
I disagree. There’s a lack of emphasis on the security concerns associated with data transmission over HTTP.
I don’t agree. The article fails to highlight the technical aspects of data encryption in HTTPS and its implications on data privacy.
The post is quite comprehensive, but it overlooks the historical evolution of HTTP and the context behind its implementation in the early days of the web.
I appreciate the detailed comparison. It is crucial for website owners to understand the significance of migrating from HTTP to HTTPS.
This article is biased towards HTTPS. The advantages of HTTP and its practical use cases have not been adequately addressed.