Enzymes formed in the body have a similar working as a catalyst.
If such complex proteins combine with coenzyme (non-protein compound), entire chemical reactions such as digestion, respiration, endothermic reactions, exothermic reactions, and so on are accelerated.
If such complex proteins and coenzymes stop combining inside humans, the rate of all chemical reactions will slow down.
Both ubiquinol and ubiquinone are non-protein coenzymes produced naturally inside the body. These both are related to Co Q10, which acts as an antioxidant inside the mitochondria of the human body.
The body requires these coenzymes to perform physical tasks and to have a fit and healthy physique.
Key Takeaways
- Ubiquinol, the reduced form of CoQ10, has higher bioavailability and antioxidant properties than ubiquinone.
- Ubiquinone, the oxidized form of CoQ10, must be converted into ubiquinol in the body to be utilized effectively.
- Both ubiquinol and ubiquinone play essential roles in cellular energy production and maintaining overall health.
Ubiquinol vs Ubiquinone
The difference between ubiquinol and ubiquinone is that ubiquinol is a less complex form of the Q10 antioxidant. Q10, on the other hand, forms ubiquinone when it combines with oxygen. It means that coenzyme Q10 sometimes becomes ubiquinol, and sometimes it becomes ubiquinone, based on the requirements of the body.
Ubiquinol is a yellow-coloured coenzyme that is one type of Q10 coenzyme (discovered in 2006). It aids in the transfer of electrons for producing energy within the human body and can be dissolved easily.
Because naturally generated Ubiquinol coenzyme begins to diminish inside the body after age thirty, people must take artificial ubiquinol to stay fit.
When Q10 is oxidized, it produces ubiquinone, a white coenzyme. This coenzyme is more abundant in mitochondria than ubiquinol and is beneficial to the heart and liver.
Furthermore, it is less expensive than ubiquinol, and many research studies have been conducted on it. Patients with high blood pressure also consume it to normalize BP.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Ubiquinol | Ubiquinone |
|---|---|---|
| Function | It being antioxidant protects the cell membrane. | It protects the heart. |
| Discovered in | It was discovered in 2006. | It first appeared in 1957. |
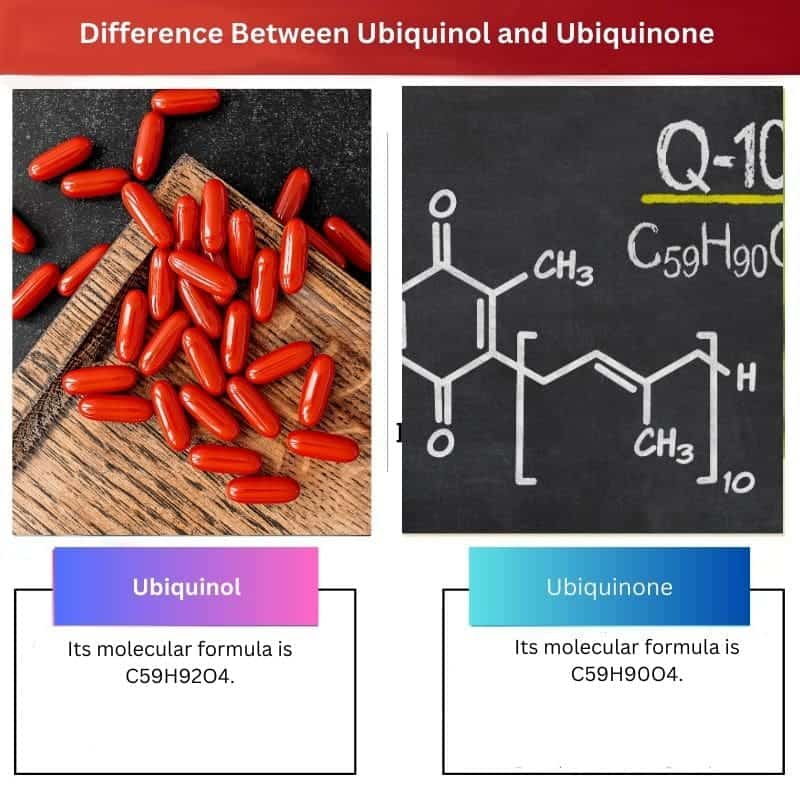
| Molecular Formula | Its molecular formula is C59H92O4. | Its molecular formula is C59H90O4. |
| Denoted by | It is also known as QH. | It is also known as CoQ10. |
| Recommended | It is less recommended because it changes its form twice inside the body and is costly. | It is highly recommended because it is inexpensive and stable inside the body. |
What is Ubiquinol?
Ubiquinol is a coenzyme with the abbreviated form QH that creates energy in every living organism’s cell’s powerhouse (mitochondria). In the case of low energy, it is taken as a pill. It is suggested for people who are in their 30s and 40s.
This type of coenzyme was identified in 2006 and is beneficial for decreasing blood pressure and anxiety and strengthening the immune system.
Protecting cell membranes also reduces the likelihood of disorders, such as the formation of damaged cells inside the body.
Ubiquinol is an excellent supplement for athletes to stay energetic while playing. Moreover, as per discovery, over 90% of athletes benefitted from this coenzyme in providing better field performances.
To reap the benefits of ubiquinol, take 100-150 mg each day.
The color of this coenzyme is yellow. Since when it goes inside the body, it changes its form two times.
When it enters the intestine for the first time, it transforms into ubiquinone, and when it passes through the lymph ducts, it transforms into ubiquinol.
As a result, it is less stable. Furthermore, it is rather costly to purchase and is only studied in a laboratory for a shorter period. It has the chemical formula C59H92O4, indicating it is a reduced version of Q10.
What is Ubiquinone?
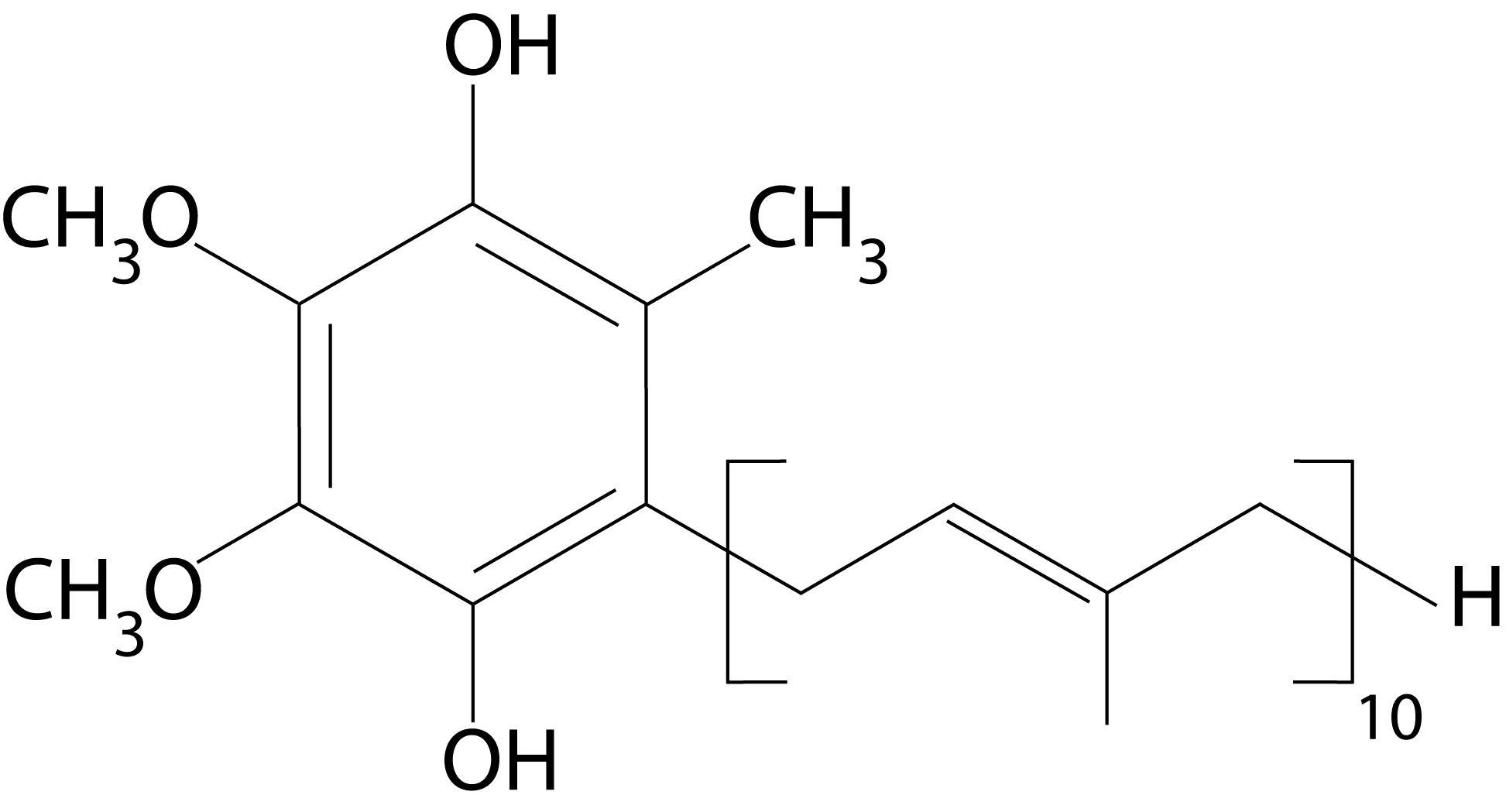
Ubiquinone is a typical coenzyme that was discovered in 1957 by scientists. CoQ10 is its molecular symbol, and its chemical formula is C59H90O4. It is known as a fat-soluble nutrient (absorbed in lymph).
These are scavenging free radicals since it protects the body cells from the damaged ones). It makes ATP in the mitochondria, which means it creates energy for the body to function.
So, if something is a cleansing agent as well as a source of energy, it must have anti-ageing properties.
Because of its anti-ageing properties, it is strongly suggested to individuals who want to seem younger. Another reason to take its pills is that the conversion of ubiquinone to ubiquinol slows with age.
It is a coenzyme that has been oxidized (reacted with oxygen).
People who experience muscle soreness or are taking medicine to reduce their cholesterol level must ingest ubiquinone in the form of meals (animal protein, meat, legumes, and nuts) or tablets (100-300 mg).
However, when humans take ubiquinone at a higher age, its absorption rate inside the body is lower than ubiquinol (easily digested). As a result, emulsify these coenzymes with specific oils for enhanced bioavailability.
Its advantage is that since it only changes its form once, it is more stable and even cheap.
Main Differences Between Ubiquinol and Ubiquinone
- The reduced form (simpler version) of coenzyme CoQ10 is ubiquinol. On the other hand, when coenzyme Q10 combines with oxygen, ubiquinone is formed.
- Ubiquinol is dissolved easily in the body without the assistance of emulsification. However, ubiquinone is dissolved into the body better with oils.
- The molecular formula of ubiquinol is C59H92O4, and it was invented in 2006. On the other hand, ubiquinone was formed in 1957 and had the chemical formula C59H90O4.
- Since ubiquinol changes its form twice inside the body, it is less stable than ubiquinone (only changes once).
- QH stands for ubiquinol, which is a costly substance. However, ubiquinone (CoQ10) is less expensive and protects against heart failure.
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0003269797921874
- https://accp1.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/cpdd.73

What a great article! Very informative and interesting, I particularly liked the whole discussion about the difference in molecular formulas between ubiquinol and ubiquinone. Great research!
I agree, what a beautifully written article. Great job!
There’s so much unnecessary information in this article. Could have been more concise and still conveyed the message effectively.
This article raises interesting points about the benefits of ubiquinol and ubiquinone. I believe the research is still ongoing and inconclusive. Very interesting read nevertheless!
Spot on! The research is intriguing but still needs more evidence for a concrete conclusion.
The discussion about the difference in stability and cost of ubiquinol and ubiquinone is compelling. It’s interesting that ubiquinol changes form twice inside the body, making it less stable than ubiquinone.
The research studies mentioned make a strong case for ubiquinone. It’s not too expensive and has many significant health benefits. I believe that makes it a better choice than ubiquinol.
The mention about taking artificial ubiquinol after the age of thirty is rather interesting. I learned a lot from that.