When it comes to problems in clinical practice, bacteremia and sepsis are two of the common clinical condition. Most people erroneously used both these terms synonymously. They can be associated with one another but not used as synonyms.
Bacteremia is caused when bacteria are present in small numbers and removed rapidly from the bloodstream with the help of the immune system. If bacteria are present in large numbers in a person with a weakened immune system can lead to sepsis.
But the difference does not end here. This article focuses on covering the differences between bacteremia and sepsis.
Key Takeaways
- Bacteremia occurs when bacteria enter the bloodstream, while sepsis is a life-threatening response to an infection.
- Sepsis can develop from bacteremia and involves organ dysfunction or failure.
- Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent sepsis from becoming severe or leading to septic shock.
Bacteremia vs Sepsis
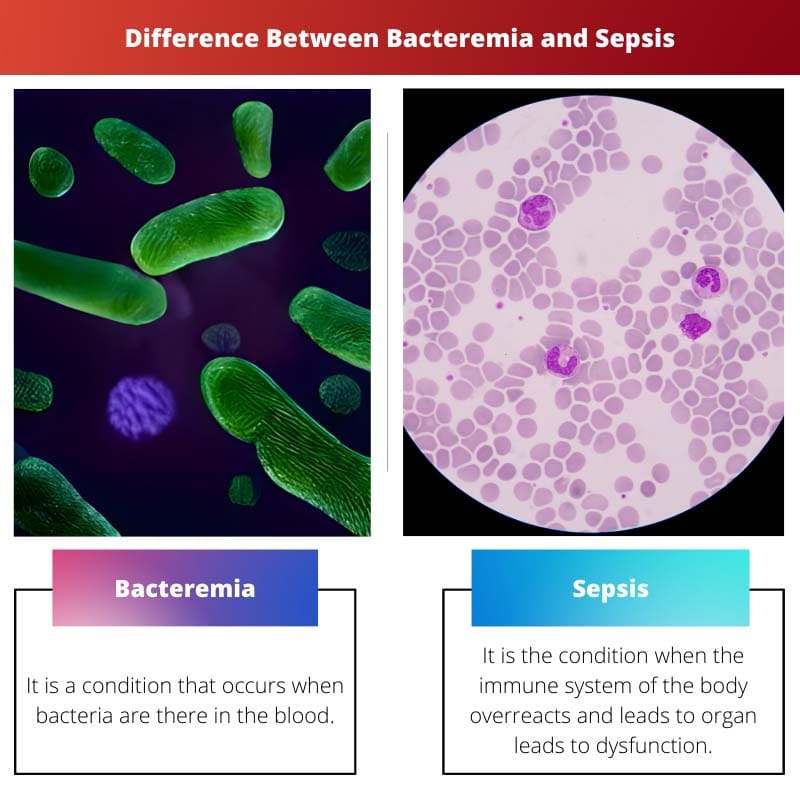
The difference between bacteremia and sepsis is that bacteremia is the condition that occurs when bacteria are there in the blood. On the other hand, sepsis is the condition when the immune system of the body overreacts and leads to organ leads to dysfunction.
From ordinary activities, medical or dental procedures, or infections, bacteremia can be caused. Antibiotics are given before dental or medical procedures if a person has a high risk of complications.
If the immune system fails to remove bacteria, then they can accumulate in several places throughout the body.
Sepsis is a term that is a bit more complex. This word comes from the Greek word ‘sepein’ or simply ‘sepsis’, which means putrefaction or the decomposition, breakdown, or due to bacterial action leading to the rotting of an organic substance.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Bacteremia | Sepsis |
|---|---|---|
| Interpretation | It is a condition that occurs when bacteria are there in the blood. | It is the condition when the immune system of the body overreacts and leads to organ leads to dysfunction. |
| Complications | Septic shock, SIRS, and sepsis | Septic shock and death |
| Morality rate | After 30 days of illness, it can be 22% | After 28 days of illness, it can be 33.2% |
| Causes | Bacteria | Viral infection or bacterial infection |
| Contiguous | Yes | No |
What is Bacteremia?
When bacteria are present in the bloodstream, then it causes bacteremia. In some cases, it can be asymptomatic, which means there are no symptoms present in a person.
In other cases, bacteremia symptoms may be present and cause a potential risk for intense complications.
Sepsis and septic shock can be developed if the bloodstream infection is untreated for a long time. When septic shock occurs there is a drop in blood pressure dramatically occurs. It can also lead to organ failure.
Additional complications include pneumonia, osteomyelitis, meningitis, cellulitis, endocarditis, infectious arthritis, and peritonitis.
It is necessary to turn to a doctor if the patient experiences chill, shaking, or fever that comes on suddenly.
There is a risk for infection in the bloodstream of a person who has recently been hospitalized, undergone surgery, medical procedure, or tooth extraction, and currently fighting an infection in the body.
Prompt use of antibiotics is required to treat bloodstream infections. It can prevent complications from occurring in a person who can be hospitalized during treatment.
According to severity and cause, the length of treatment is dependent. Antibiotics maybe need to be on for 1 to 2 weeks.
What is Sepsis?
Sepsis is a life-threatening illness caused by a body’s response to an infection. The immune system aims to protect from several infections and illnesses, but an immune system overdrive in response to an infection can also be possible.
According to CDC, there are 1.5 million cases each year.
Sepsis develops due to the release of immune system chemicals into the bloodstream to fight infection. But the inflammation causes it throughout the body instead.
In case of severe sepsis can cause septic shock and is a medical emergency.
There are mainly three stages of sepsis: septic shock, sepsis, and severe sepsis. Sepsis can happen if the patient is still in the hospital and recovering from a procedure, but always this is not the case.
Medical attention is important to seek if the patient is showing symptoms like temperature below 96.8°F or a fever above 101°F.
The doctor order tests to make a diagnosis to determine the severity of infection if symptoms of sepsis are shown in a patient.
The first test is a blood test to check complications like clotting problems, abnormal kidney or liver function, infection, and decreased infection.
Main Differences Between Bacteremia and Sepsis
- Bacteremia can be prevented by practising good hygiene and good control of diabetes. On the flip side, sepsis can be prevented by staying up to date on vaccinations and immediate care if infection signs develop.
- In compromised individuals, bacteremia can occur in patients as a secondary infection, while sepsis can occur in patients due to the cytokines and inflammatory response released by the body in reaction to the coronavirus.
- When it comes to symptoms, mild symptoms to acute fever and chills are symptoms of bacteremia. But rapid breathing and low blood pressure are symptoms of sepsis.
- The help of antibiotics through IV given in the hospital treats bacteremia. On the other hand, increased blood pressure medicine, extra oxygen, and IV antibiotics given in the hospital can treat sepsis.
- Individuals with a debilitated immune system, already hospitalized or very sick, and with an underlying disease like cancer are at higher risk of getting bacteremia. But people being treated in ICU, seniors, and young children are at higher risk of developing sepsis.
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2599470/
- https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMra043632

The impact of early diagnosis and treatment cannot be overstated, especially when dealing with life-threatening conditions like sepsis.
The preventive measures for bacteremia and sepsis are important to highlight, as they empower individuals to take proactive steps to protect their health.
The comparison table provides a clear and concise overview of the key differences between bacteremia and sepsis.
It’s important to understand the differences in clinical conditions like bacteremia and sepsis, as the consequences of misdiagnosis can be severe.
You’re absolutely right. This article provides useful information that can save lives when applied correctly.
Understanding the causes and risk factors for bacteremia and sepsis is crucial for improving patient outcomes.
The detailed explanation of symptoms and treatments for both conditions provides valuable insights for healthcare professionals and patients alike.
The article effectively emphasizes the need for prompt medical attention when symptoms of bacteremia and sepsis are observed, which can make a significant difference in patient outcomes.
The references provided in the article offer credibility and further resources for those seeking in-depth knowledge about bacteremia and sepsis.