Spasticity is related to damage to pyramidal tracts, and Rigidity causes damage to extrapyramidal lots. Muscle pain is caused by rigidity. Rigidity arises when muscles are unable to relax usually.
The brain and spinal cord, which control muscles and stretch, get damaged spasticity arises. Spasticity also causes acquired brain trauma and stroke.
Key Takeaways
- Spasticity is a type of muscle stiffness that results in involuntary muscle contractions, while rigidity is a sustained resistance to passive movement.
- Spasticity is caused by damage to the central nervous system, while rigidity is primarily associated with Parkinson’s disease and other neurological conditions.
- Spasticity is characterized by increased muscle tone, while rigidity is characterized by constant resistance to movement, making it difficult to initiate and control movements.
Spasticity vs Rigidity
Spasticity is a persistent rise in tension when a muscle is passively stretched or extended. It depends on velocity and gets worse at high speeds. While rigidity is increased muscle tone that is constant throughout the range of action, independent of speed. It may be a sign of basal ganglia disease.

Spasticity occurs when continuous tightness occurs in the number of muscles. The upper Motor lesion in the pyramidal tract causes spasticity.
The stiffness affects normal movement. It is uni-directional. In this brain and spinal cord get damaged.
Rigidity refers to the state in which a person cannot bend, twist or stretch. It is bi-directional. It is seen in extrapyramidal tracts.
It refers to a state of deformity under pressure. There is a disease called Parkinson’s disease, which is a particular type of neurological disease.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Spasticity | Rigidity |
|---|---|---|
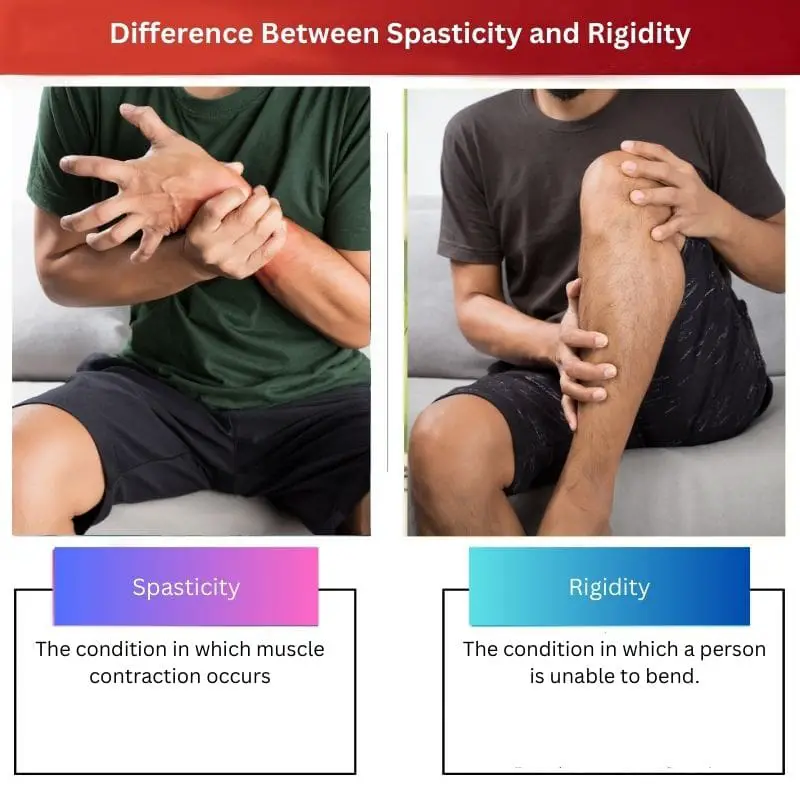
| Definition | The condition in which muscle contraction occurs | The condition in which a person is unable to bend. |
| Lesion | Pyramidal tract | Extrapyramidal rigidity |
| Muscles | Either Antagonist or agonist | Both the Antagonist and agonist |
| Rigidity | Sensitive on stretch | Not sensitive on stretch |
| Hypertonia | Clasp knife | Lead pipe |
What is Spasticity?
Spasticity happens when numerous muscles suffer stiffness. When a person tries to move a joint, then spasticity seizes the movement.
. The messages from the central nervous system do not reach the spinal cord in this condition. The degeneration of myelin causes spasticity.
Myelin is a fatty white substance that forms an insulating membrane. It also occurs due to the contraction of the extensor muscles.
Cerebral palsy causes spasticity. Spasticity also causes acquired brain trauma and stroke.
Muscle tone rises and causes rigidity which is called hypertonicity. Nocturnal awakening is one of the symptoms of spasticity.
Tense muscles, jerky movement, non-proper positioning of the arm, wrist, or any other body part-Clonus, which are uncontrollable muscle spasms, is one of the symptoms of spasticity. Velocity is a significant factor in spasticity due to faster movements.
The contraction of extensor muscles causes deep pain in joints and weak coordination. The upper Motor lesion in the pyramidal tract causes spasticity.
What is Rigidity?
Rigidity is muscle tension or rigour. The problem in the movement can be sensed despite the speed and direction.
Wilson’s disease is when copper metabolism occurs in the lungs, liver, brain, and other tissues. Catatonia, acute cerebral infarction, basal ganglia, and lupus are some rigidity causes.
Viral and bacterial infections are one of the causes of rigidity. Lupus is a chronic disease that causes stiffness in the joints.
Bradykinesia is slowness in movement, which is one of the causes of rigidity: high fever and decreased appetite cause rigidity in a person.
The velocity does not affect rigidity. Speed is not a factor in rigidity.
Rigidity leads to Parkinson’s disease. Muscle cramps, muscle weakness, pain, and stiffness lead to rigidity.
It refers to a state of deformity under pressure. Muscle pain is caused by rigidity.
Main Differences Between Spasticity and Rigidity
- The contraction of muscles is known as spasticity, whereas Rigidity is the state of being unable to bend.
- Spasticity most affects the arms, neck, and lungs, but Rigidity can disturb any body part.
- Unusual posture can lead to Spasticity, whereas cramps can lead to Rigidity.
- Velocity matters in Spasticity instead of Rigidity and has no relation with velocity.
- Spasticity occurs in pyramidal tract lesions, whereas Rigidity occurs in extrapyramidal tracts.
- Spasticity happens with hyperreflexia, whereas Rigidity happens with hyporeflexia.
- https://europepmc.org/article/med/3288246
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780444895967500122

The article is an essential read for those needing detailed insight into spasticity and rigidity.
Absolutely. The information will be of immense benefit to many.
Yes, the comparison table was instrumental in understanding the differences clearly.
This article’s tone is very professional and its content is very informative. The technical insights provide a deeper understanding of the topic.
Agreed, this article compiles and presents complex information in a simple, effective manner.
The level of detail and clarity in this article is impressive. It’s a great piece of work.
The detailed comparison and explanation of both conditions is remarkable. It really helps to understand the concepts better with the direct comparison.
The direct comparison and in-depth analysis are highly commendable.
The author’s approach in clarifying the differences is truly enlightening.
The article is intellectually stimulating and formally presented. It’s engaging and informative.
The formal documentation is quite impressive, making it an intriguing read.
This article provides an in-depth, comprehensive analysis of the differences between spasticity and rigidity. The level of detail presented helps improve understanding about the topic.
I agree, the article really delves into the subject in a way that is very informative.
The level of detail in this article is truly commendable.
The content is well-organized, providing a clear comparison between spasticity and rigidity. The use of different parameters for comparison adds clarity and depth to this article.
It makes the point of comparison quite easy to understand. Good job!
Agreed, the article lays the information out very well.
The intellectual depth and analyses in this article offer an excellent resource for understanding the complexities of spasticity and rigidity.
Indeed, the depth of the content makes it an informative read.
Absolutely, the thoroughness of the topic is truly commendable.
This article gives a comprehensive understanding of spasticity and rigidity. It’s a valuable resource for anyone interested in this topic.
This article helped me to recognize the major differences between the two. The information is accurate and thorough.
Yes, especially the data in the tables makes this distinction quite clear.