Aquaculture and fisheries are inextricably linked, and there is little distinction between these two. Aquaculture and fisheries primarily deal well with producing and trading fish and marine items.
Though aquaculture and fisheries share many parallels, they also have some distinctions.
Key Takeaways
- Aquaculture involves cultivating aquatic organisms in controlled environments, while fisheries capture wild fish and other aquatic species.
- Aquaculture can produce a consistent seafood supply, while fisheries depend on the availability of wild stocks.
- Aquaculture significantly impacts the environment due to its concentrated nature, while fisheries face challenges like overfishing and bycatch.
Aquaculture vs Fisheries
The difference between Aquaculture and Fisheries is that Fisheries are involved with the capture of fish or shellfish. They are primarily concerned with capturing, preparing, and selling fish. Aquaculture whereas is concerned with the production of both aquatic animals as well as aquatic vegetation.
Aquaculture (also called aquaculture) is the regulated growth (“breeding”) of aquatic animals such as fish, shrimp, mollusks, plankton, and other valuable organisms such as aquatic species (e.g., lotus). Aquaculture is the cultivation of marine and freshwater animals in under-regulated or semi-controlled conditions, as opposed to fishing activities, which would be the capture of wild fish.
The fishery can refer to either the business of producing or collecting fish and other aquatic animals or, more typically, the location where such business is conducted (a.k.a. fishing ground). Commercial fisheries comprise wild fishing and fish farms, operating in freshwater ecosystems (approximately 10% of total capture) and oceanic ecosystems (about 90 percent ).
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Aquaculture | Fisheries |
|---|---|---|
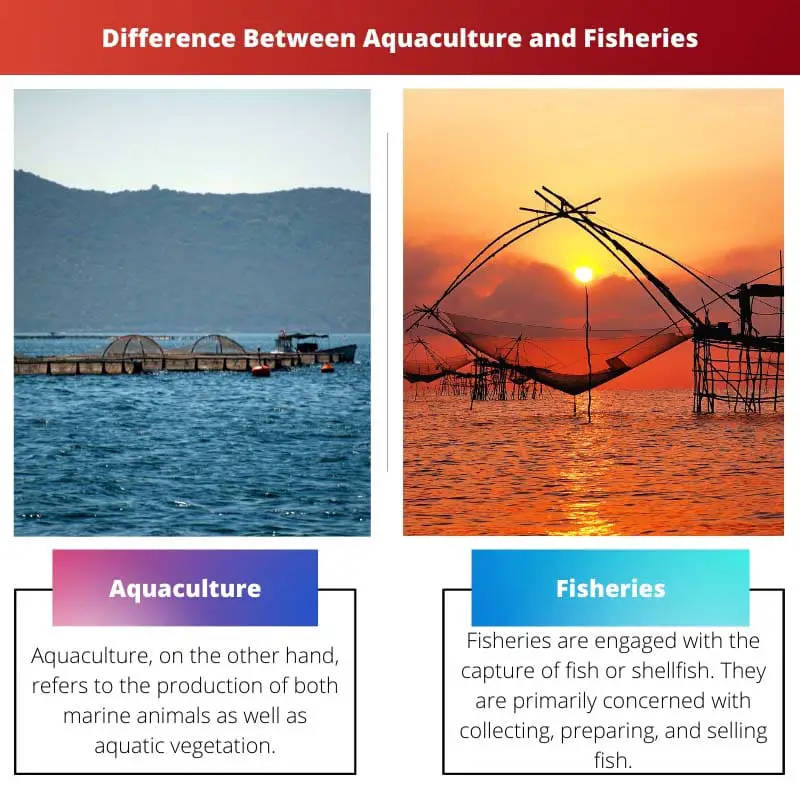
| Connotation | Aquaculture, on the other hand, refers to the production of both marine animals as well as aquatic vegetation. | Fisheries are engaged with the capture of fish or shellfish. They are primarily concerned with collecting, preparing, and selling fish. |
| Encompasses | Aquaculture is a study that encompasses all elements of marine life. | Whereas fisheries are only concerned with capturing wild fish or producing and collecting fish. |
| Seawater of Freshwater | Aquaculture could be fisheries management or coordinated multi-trophic aquaculture. | Fisheries can be seawater or freshwater, untamed as well as farmed. The distinction between fisheries as well as fishery as words is that fisheries are fishing: the catching, preparing, and commercialization of fish or other seafood. |
| In the case of Pearls | Pearls are a commodity that can only be obtained through aquaculture rather than fishing. | Therefore, Pearls can’t be obtained from Fisheries. |
| Fishery Stocks | Because wild fishery stocks have been declining in recent years, aquaculture is thought to be a viable option for maintaining these stocks. | Approximately 90% of all fish and shellfish are caught in wild fisheries. |
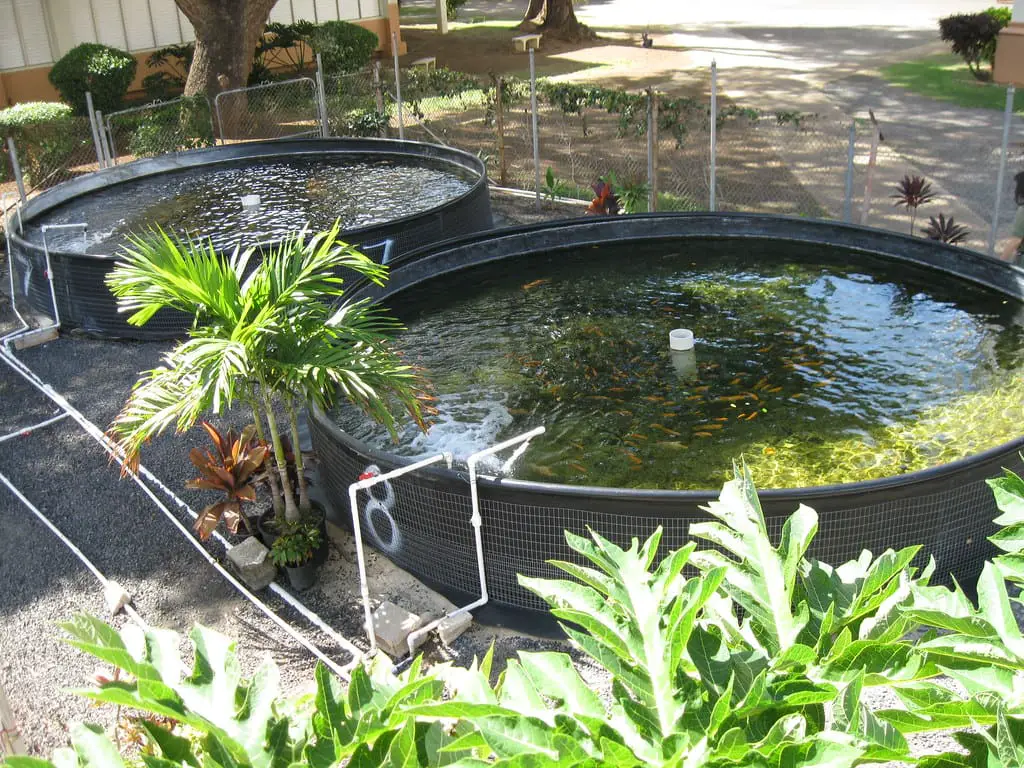
What is Aquaculture?
Aquaculture (also called aquaculture) is the regulated growth (“breeding”) of aquatic animals such as fish, shrimp, mollusks, plankton, and other valuable organisms such as aquatic species (e.g., lotus). Aquaculture is the cultivation of marine and freshwater animals in under-regulated or semi-controlled conditions, as opposed to fishing activities, which would be the capture of wild fish.
Mariculture, referred to as maritime farming, is the technique of aquaculture in marine water settings as contrasted to freshwater aquaculture. Aquaculture can also be carried out in totally artificial infrastructure built on land (onsite aquaculture), like fish tanks, ponds, or conduits.
This can be carried out where humans control the living standards; in very well-deep waters near the coast of a waterbody (inshore aquaculture), in which the cultivated organisms are confined to comparatively more realistic environments; or in fenced/enclosed segments of waterways away from the coast (offshore aquaculture), in which the cultured species are confined to comparatively more natural cycles.

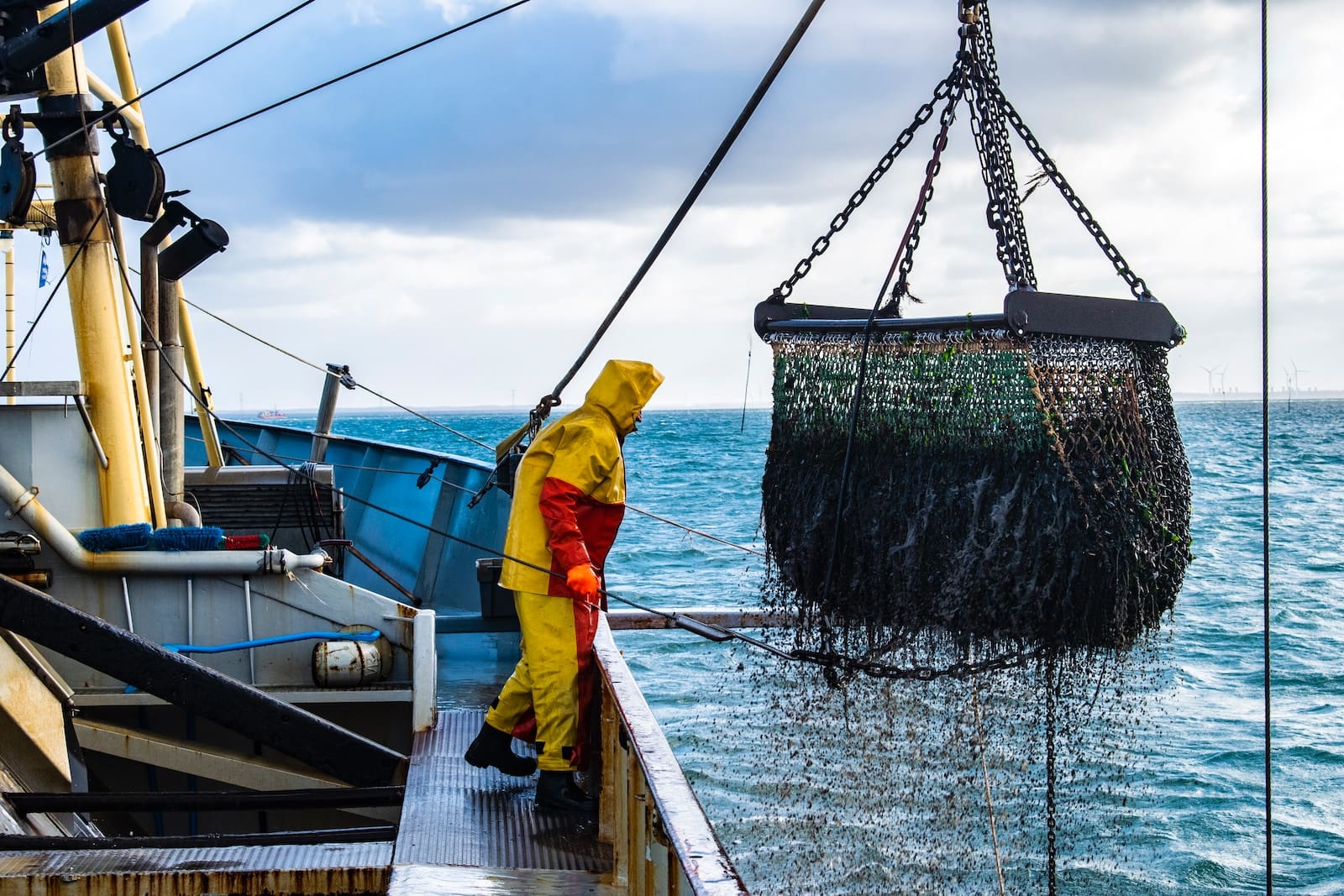
What are Fisheries?
The fishery can refer to either the business of producing or collecting fish and other aquatic animals or, more typically, the location where such business is conducted (a.k.a. fishing ground). Commercial fisheries comprise wild fishing and fish farms, operating in freshwater ecosystems (approximately 10% of total capture) and oceanic ecosystems(about 90 percent ).
Fisheries provide a living for around 500 million individuals worldwide. In 2016, 171 million tonnes of fish were harvested.
However, overfishing is becoming more of an issue, causing population decreases in some species.
Declining fish stocks, water contamination, and the degradation of crucial coastal habitats have increased uncertainties in key fisheries around the world, jeopardizing socioeconomic and nutritional products in many regions of the world. These difficulties are exacerbated by alterations in the ocean caused by extreme weather events, which may extend the range of certain fisheries while drastically diminishing the viability of others.

Main Differences Between Aquaculture and Fisheries
- Aquaculture, on the other hand, refers to the production of both marine animals as well as aquatic vegetation. Whereas fisheries are engaged with the capture of fish or shellfish. They are primarily concerned with collecting, preparing, and selling fish.
- Aquaculture is a study that encompasses all elements of marine life. Whereas fisheries are only concerned with capturing wild fish or producing and collecting fish.
- Aquaculture could be fisheries management or coordinated multi-trophic aquaculture. On the other hand, Fisheries can be seawater or freshwater, untamed as well as farmed. The distinction between fisheries as well as fishery as words is that fisheries are fishing: the catching, preparing, and commercialization of fish or other seafood.
- Pearls are a commodity that can only be obtained through aquaculture rather than fishing. Therefore, Pearls can’t be obtained from Fisheries.
- Because wild fishery stocks have been declining in recent years, aquaculture is thought to be a viable option for maintaining these stocks, whereas approximately 90% of all fish and shellfish are caught in wild fisheries.
- https://books.google.co.in/books?hl=en&lr=&id=NkkOyiBC_UAC&oi=fnd&pg=PR3&dq=Difference+Between+Aquaculture+and+Fisheries+(With+Table)&ots=4U7w9Rg59G&sig=FoDwkyxgUxxgx1-CePYlEp9xuEs&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q=Difference%20Between%20Aquaculture%20and%20Fisheries%20(With%20Table)&f=false
- https://www.proquest.com/openview/2fef338b4dfd7621db0bc9f37bb2bf82/1?pq-origsite=gscholar&cbl=237320



