Profit is the goal of any business. It is achieved when the total revenue generated exceeds the total costs.
Sales and marketing are the primary tools for generating revenue. To set the price of a product, a company looks into the cost accounting function.
The break-even point and margin of safety are cost accounting functions used to calculate the sales analysis. These revolve around the concepts of costs, sales, volumes, price, and production.
They have a futuristic approach.
Key Takeaways
- The break-even point is the level of sales at which total costs equal total revenue, while the margin of safety is the difference between actual sales and the break-even point.
- The break-even point is a measure of profitability, while the margin of safety is a measure of risk.
- A higher break-even point means more sales are needed to reach profitability, while a higher margin of safety means a company is less vulnerable to losses.
Break-Even Point vs Margin of Safety
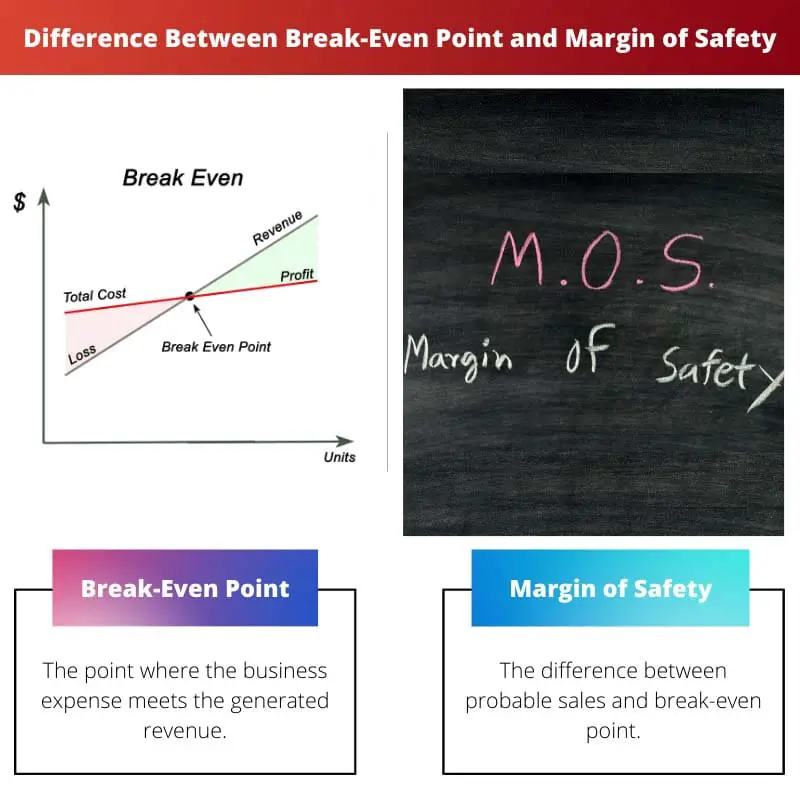
The difference between the break-even point and the margin of safety is that the break-even point is a level where there is no loss or gain, while the margin of safety is the difference between actual sales and the break-even point. Both these concepts come under cost-profit analysis. The characteristics and functions are different for each. The Break-even point suggests the survival of a company. But the margin of safety is an indicator of risk.

The Break-even point is the level where the total expenditure equals the total revenue. The price of the product can be determined by analyzing the break-even point.
According to the pricing, break-even points can differ. Although determining the BEP is helpful in terms of attaining optimum results, it has a set of limitations.
It is based on cost analysis and doesn’t explain the sales in different price ranges. The margin of safety is the probable decline in sales before a goes into loss.
It shows the safety level of the company according to its sales. Every company tends to keep a higher range of the margin of safety to strengthen their business.
It is a kind of buffer. The business is free from high risks as long as there is a buffer.
When the margin of safety reaches negative, the company is likely to lose money.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Break-Even Point | Margin of Safety |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The point where the business expense meets the generated revenue | The difference between probable sales and break-even point |
| Hierarchy | Determined first | Determined only after BEP is calculated |
| Risk | No risk at the break-even point | When it is low, the risk is higher and vice versa |
| Analysis | Lower is better | Higher is advantageous |
| Relevance | Sales decisions | Cost decisions |
What is Break-Even Point?
The break-even point or BEP for a business is when the cost of setting up the business and the revenue generated are equal. There is no loss or gain.
In sales terms, the break-even point or level denotes the sales amount needed to even the total costs. To achieve the criteria, a company must sell the product at a higher price.
Then they have paid for producing it. Only after reaching the break-even point can a company gain profits.
BEP is not only used in financial analysis but also in marketing, entrepreneurship, accounting, management, and so on. This is helpful in improving performance.
And give the necessary boost for the employees to pave the way for profits. When a sales team identifies the BEP, it is easier to calculate the needed sales.
Every employee can contribute to reaching the target by selling the required number of products. If a business cannot meet the break-even point, it can reduce the cost of production.
The function of BEP is to know what minimum effort is required to get a profit. Business owners can calculate the impact of the marketing team.
Low sales are mostly due to the inefficiency in outputs like sales and marketing. Not reaching the break-even point can collapse the business and makes its future troublesome.
What is the Margin of Safety?
The difference between the current sales level and the break-even point is referred to as the margin of safety. A high margin of safety suggests that the business is less vulnerable to loss.
This concept is used in budgeting and investing. The margin of safety in budgeting is the gap between the probable sales output and the sales decrease that can wreck the company.
Management can identify the expected risk of loss due to fluctuations in sales. In investing, the margin of safety suggests the relation between the real worth of a stock and its current market price.
If an investor buys a stock when the intrinsic value is less than the market price, the difference between them is the margin of safety. A clear understanding of the market price is needed to do this.
Benjamin Graham coined the concept of margin of safety. It was then popularized by Warren Buffet.
When investing, determining the margin of safety protects the investor. From errors in judgment as it is a subjective idea to know the true worth of any company.
The margin of safety is presented as a ratio in accounting. It is used to encourage sales to reach the break-even point. This forecasting helps the company to protect itself from loss.
Main Differences Between Break-Even Point and Margin of Safety
- The Break-even point is attained when a business retains all the money invested through the generation of equal revenue. But the margin of safety is the measure of the difference between actual or probable sales and the break-even point.
- At the break-even point, there is no risk. But the margin of safety denotes either high risk or low risk.
- The break-even point shows the minimum amount of sales needed to achieve the production cost. While the margin of safety is just an indicator of risk at each sales level.
- Absolute terms are used to determine the break-even point. But percentage or ratio is adopted to express the margin of safety.
- Only after calculating the break-even point a margin of safety can be determined. So BEP comes first, and a margin of safety is found afterwards.

This article presents a detailed comparison of the break-even point and margin of safety, providing valuable insights for businesses to make informed decisions.
The in-depth analysis of the break-even point and margin of safety helps readers understand their significance for business profitability.
The article effectively addresses the concepts of the break-even point and margin of safety in a clear and concise manner, making it a valuable resource for business professionals.
The comparison table and detailed descriptions of the break-even point and margin of safety enhance the understanding of these concepts and their implications for businesses.
The article’s examination of the relationship between the break-even point and margin of safety provides a comprehensive understanding of their roles in business operations.
The practical application of the concepts discussed in the article is valuable for businesses seeking to improve their financial performance.
The article provides a comprehensive explanation of the concepts of the break-even point and margin of safety in business accounting.
The article’s emphasis on the futuristic approach of the break-even point and margin of safety offers a forward-looking perspective for businesses to manage risk and optimize sales.
The break-even point and margin of safety play a crucial role in a company’s cost accounting and sales analysis. These concepts are essential for businesses to understand in order to optimize their profitability.
The break-even point and margin of safety are key metrics for businesses, and this article provides a clear comparison between the two.
The article effectively outlines the differences between the break-even point and margin of safety, as well as their relevance in sales and cost decisions.