Heat exchange is an essential part of the cooling or heating system. Heat exchange is done with the help of a system named a heat exchanger.
The system “heat exchanger” works by transferring heat from one medium to another, especially fluid and gas, or it can be a mixture of both.
Key Takeaways
- Condensers are heat exchangers that cool and condense refrigerant vapor into a liquid, releasing heat to the surroundings.
- Evaporators absorb heat from their surroundings and use it to evaporate the refrigerant, turning it from a liquid into a vapor.
- Both components are essential for the refrigeration cycle, with condensers releasing heat and evaporators absorbing heat.
Condenser vs Evaporator
A condenser releases heat absorbed from the system, converting refrigerant vapor into liquid by transferring heat to the surrounding environment. An evaporator absorbs heat from the environment, turning liquid refrigerant into vapor, which cools the space or substance being refrigerated.

Condensers are the ones that condense a gaseous substance into a liquid state using cooling techniques. In simple terms, condensers are those devices that help in exchanging heat.
The condenser works to condense the substances that cause heat loss and eventually result in a change of state.
Evaporators are the ones who convert a liquid into its gaseous form. With the help of evaporators, the liquid is converted into its gaseous form or vaporized.
Evaporators are used to absorb the environmental heat for the exchange of liquid into a gaseous state.
Comparison Table
| Parameters Of Comparison | Condenser | Evaporators |
|---|---|---|
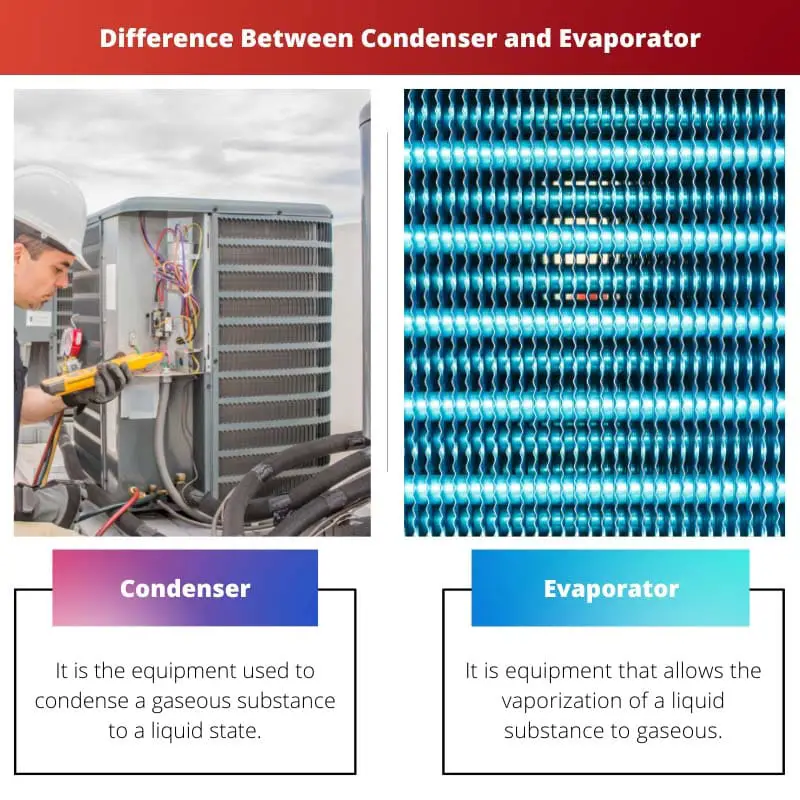
| Definition. | It is the equipment used to condense a gaseous substance to a liquid state. | It is equipment that allows the vaporization of a liquid substance to gaseous. |
| Method of Heat exchange. | Condensers release the heat to their circling environment. | Evaporators absorb the heat from their circling environment. |
| Mechanism. | Condenser works by changing high-temperature gaseous substances into liquid states. | Evaporators work by increasing the temperature and pressure of liquid substances to change them into gaseous forms. |
| Surface Area. | The condenser is known to have a large area for better cooling of gas for the conversion. | Evaporators have less surface area than condensers. |
| Uses. | A condenser is a part of the AC or refrigerator in their cooling system to cool their compressed refrigerant gas. | Evaporators are also a part of the same system where extracting heat from one substance and transferring it to another for maintaining its cooling condition. |
What is Condenser?
A condenser is a device that works on the principle of condensation. Condensation is the transfer of a gaseous state particle to a liquid state.
A condenser is a device that works to transfer gaseous substances into a liquid form.
This happens when a high-temperature gaseous substance is cooled down with enough heat exchange. Then the gaseous substance gets changed into a liquid form.
Condensers are known to have a larger surface area. A large surface area helps with better cooling of vapors and easily transformation of heat.
They work on the exothermic process. The exothermic process stands for the thermodynamic process, in which the energy is released to its surroundings in the form of heat, light, or sound.
When we talk about condensers, the energy is released in the form of heat.
When the temperature of a substance inside is higher than the surrounding temperature. In such cases, the working substance or the inner substance loses its heat to the surroundings.
Hence causing the drop in its temperature and condensing the liquid.
The condensers are used at many places such as in refrigerators, air cooling systems, power plants, etc.

What is an Evaporator?
Evaporation is a simple device working somewhat inverse to the work of a condenser. Evaporators work on the principle of evaporation.
Evaporation is the process in which liquid substances get converted into their gaseous form.
Evaporators are a type of endothermic process. The endothermic process is a process in which the substance absorbs the heat from its surroundings to increase the temperature.
Evaporators work to transfer the liquid substances into their gaseous form by vaporizing them or in simple words, they absorb the heat which eventually increases their temperature casuing vaporization of substance.
Evaporators are a part of the heat exchangers. When the working substance or the inner substance has a low temperature as compared to the surrounding substance.
Then the working substance is prone to accept heat from its surroundings. Due to the acceptance of heat, there is a gradual increase in its temperature.
This increased temperature causes the vapors to form. If the heat exchange has taken place in this method, then it is done by evaporators.
Evaporators are found in refrigerators, air cooling systems, outdoor plants, etc.

Main Differences Between Condenser and Evaporator
Both Condenser and Evaporator are a part of the same system. Their work is the same, however, the pattern they follow is different. Some of the relevant differences are:
- They both work for heat exchange, however, the condenser is known to release heat and the evaporator is known to absorb the heat.
- The surface area of the condenser is kept larger for easy condensation. However, the surface area has no meaning for evaporators.
- If the heat exchange takes place by transferring surrounding heat into the main substance, then it is a type of evaporator and if the process is an absolute invert of this, then it can be a condenser.
- Evaporators work on the basis of endothermic process whereas condenser follows the exothermic process.
- The condenser changes gas into a liquid and the evaporator changes liquid into its gaseous form to follow the same thing called heat exchange.
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0378778814006288
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1876610215010310
