Memories are created and saved to be cherished over a long period and relived through images, movies, and moments.
And all of these priceless memories are preserved in one’s phone, laptop, or system, and a number of software, such as clouds, are available to prevent them from being erased or lost.
Key Takeaways
- The “distributed cloud” spreads data and applications across multiple cloud servers while “edge computing” processes data near its source on devices or local servers.
- Distributed cloud improves latency, reliability, and security by distributing resources across various locations, while edge computing reduces latency by bringing computation closer to the data source.
- Edge computing is better suited for IoT devices and real-time applications, while distributed cloud works well for applications requiring global reach and improved redundancy.
Distributed Cloud vs Edge Computing
Distributed cloud refers to the distribution of cloud computing resources across multiple geographic locations. Edge computing is the practice of processing and analyzing data as close to the source as possible, rather than sending all data to a centralized cloud computing resource.

Creating a distributed cloud brings computation near to the actual customer, resulting in lower latencies and greater security. A blockchain-based safety design or periodic information audit to verify authenticity are two potential safety options.
Information too is processed in live time via a distributed cloud. Cloud computing and edge computing both are types of distributed clouds.
Transmission lines, modems, Internet, or regional server farms are instances of edge connection nodes. Encrypt, network transparency, surveillance, intrusion detection systems, and security systems are all components of a protected edge.
Edge computing seems to have become an actuality. Large growth in linked equipment is expected to raise the need for edge computation to reduce network congestion. The Internet of Things is a large determinant of its expansion.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Distributed Cloud | Edge Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | A distributed cloud includes computation, processing, and transmission in a micro-cloud located beyond the centralized information cloud. | Edge computing refers to processing that happens only at the system’s edge. |
| Model | Distributed computing model of distributed systems, that are comprised of multiple processing devices communicating with others. | Edge computing is a modern version of cloud computing that’s also focused on a distributed computing paradigm that offers data storage. |
| Security | The system is safe since its elements are dispersed among numerous computers. | It incorporates specialized edge server farms to give extra security measures. |
| Cost | When contrast to standard cloud computing infrastructure, operating and maintenance costs are marginally greater but still relatively affordable. | Reduced operating and maintenance expenses because the instruments and computing are handled nearby. |
| Scalability | A distributed computing infrastructure is laterally scalable, which means that the performance of the units could be enhanced. | Towards greater scalability, edge technologies employ the concept of dispersed information collection and analysis. |
What Is Distributed Cloud?
The phrase “distributed cloud computing,” which has been around for generations, refers to processing, memory, and communication pooled by several machines and operated as one unit but to achieve a set objective.
Machines, processors, and terminals may be housed in the very same server farm or facility and linked via a local area network. They could be in many regions, in some very varied geographic regions, or linked via a broad range of systems or the cloud.
The term “distributed cloud” refers to using a cloud platform that connects shared resources instead of local or wide area networks. As a result, edge computing is now a component of a distributed cloud service.
A distributed cloud is a new cloud architecture whereby a group’s cloud planning and implementation takes into account the actual location of supporting infrastructure components.
Distributed clouds, on the other hand, arose first from the initial cloud notion, which separated the concept of infrastructure placement from the brains of cloud consumers.
In practice, the dispersed cloud has nevertheless isolated the cloud concept from the placement of the supporting infrastructure.
However, cloud developers can now explore additional flexibility in utilizing infrastructure components nearer to where they are truly required, i.e., by moving those assets out towards the edge wherever computation and storage are consumed, and delay can be considerably reduced.
What Is Edge Computing?
Edge computing innovation is utilized to manage the tremendous flow of data produced every instant. However, what exactly is edge computing?
This is a component of a distributed cloud network that promotes decentralization over centralized control, which means it moves storage of data and operations as near to the edge as feasible towards where information is produced and activities are conducted.
Because loT equipment possesses restricted computation and storage abilities, significant processing must take place on-premises, with its edge establishing an environment that manages its computing and administers a vast number of loT systems and networks.
Edge systems are remote computer devices that function in favour of the cloud, including such things as cell phones, access points, or smart appliances.
This allows data to be exchanged swiftly, safely, and without delay. Furthermore, it enhances data processing capability due to less reliance on the cloud.
The edge structure distributes data analysis and delivery of services across numerous devices to process data and provide services closer to the source of data or computing unit.
This relative proximity to an end customer, whether a worker or client using a mobile phone or a store utilizing a store, ensures quick and correct operations.
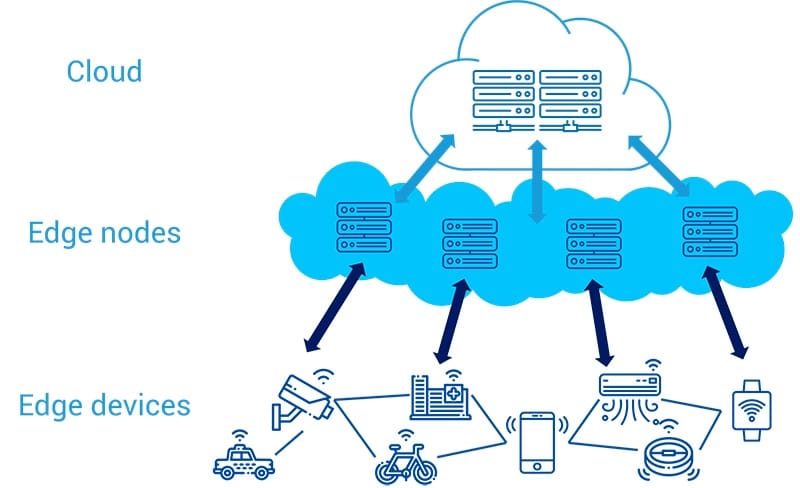
Main Differences Between Distributed Cloud and Edge Computing
- A distributed cloud involves computing, operations, and transmitting in a micro-cloud beyond the centralized data cloud. In contrast, edge computing relates to processing that occurs solely at the system’s edge.
- Distributed computing is a distributed system paradigm comprising several processing devices talking with one another. In contrast, edge computing is a contemporary form of cloud computing centred on a distributed computing framework that enables data storage.
- Distributed clouds are secure because their pieces are spread over multiple machines, whereas edge computing includes technical edge data centres to provide additional safety measures.
- Operating and maintenance expenses are slightly higher but cheap compared to traditional cloud computing technology. Still, edge computing has lower operating and maintenance costs since the equipment and processing are handled locally.
- The performance of the units can be improved with a distributed cloud system because it is horizontally expandable. Edge computing, on the other hand, utilizes the notion of scattered data collection and processing to achieve better scalability.
- https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9140317/
- https://researchberg.com/index.php/rrst/article/view/18

This entire piece was enlightening. I appreciate the detailed comparison between distributed cloud and edge computing.
The topic was elaborated quite clearly and efficiently. If you have any further sources supporting your insights, I would love to read them.
I second that. I’d be keen on reading more from verified resources about this subject.
I completely agree, I’m also interested in any additional sources to delve deeper into the subject.
This article sheds light on the key differences between distributed cloud and edge computing. I believe both these concepts have the potential to revolutionize the way data is stored and processed.
The explanations in this article are informative and articulate. They helped clarify the distinction between distributed cloud and edge computing for me.
The extensive comparison provided comprehensive insights into the distributed cloud and edge computing. A truly enlightening read.
I find the concept of distributed cloud and edge computing quite fascinating. However, I’d like to see more evidence in support of the detailed comparison presented in this article.
Fully agree with your comment. More concrete evidence from reputable sources would enhance the credibility of the article.