There are a lot of coloring agents available in the market that are used for coloring objects, clothes, paper, etc. Dyes and Stains are two such coloring agents.
Although not many people are aware of this that they differ from each other in several ways.
Key Takeaways
- Dye penetrates the material and changes its color, while stain sits on top of it and adds colour.
- Dye is used for fabrics and hair, while stain is used for wood and other porous materials.
- Dye produces more vibrant and uniform colors than stain.
Dye vs Stain
A dye is a substance that is soluble in a particular solvent like water and is used to color textiles, paper, leather, and other materials. A stain is a colorant that penetrates into a material and changes its color by reacting with its components and is commonly used to color wood.

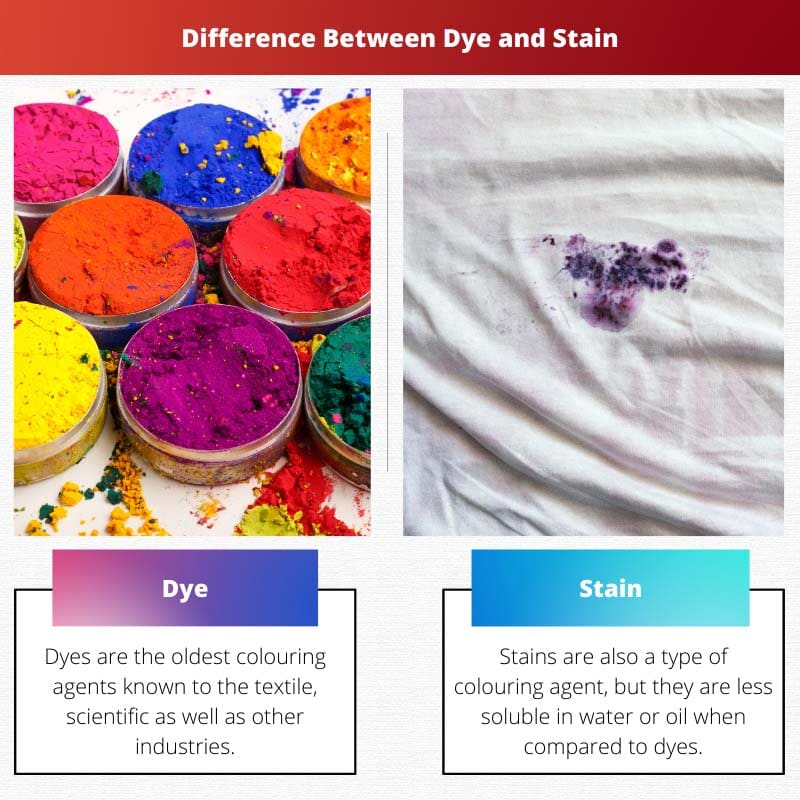
Dyes are the oldest colouring agents known to the textile, scientific, and other industries. They require water, alcohol, oils or mineral spirits as carriers.
Dyes are composed of small molecules and are best for woodwork and textile since they are capable of colouring them without necessarily altering the features.
Stains are also a type of colouring agent, but they are less soluble in water or oil when compared to dyes. Therefore they require constant stirring of the solution; otherwise, the stain components will settle at the bottom.
They are made up of larger molecules, too, in comparison to Dyes.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Dye | Stain |
|---|---|---|
| Solubility | Dyes are more soluble in water, oil, alcohol, etc. | Stains are less soluble in water, oil, alcohol, etc. |
| Composition | The composition of Dye includes a carrier and dye pigment. | The composition of Stain includes a carrier, a binder, and colour pigment. |
| Light-fast | Dye is more lightfast in nature. | Stains are less lightfast in nature. |
| Preparation | They are made with fewer specifications and have impurities. | They are made with many specifications and have very little to no impurities. |
| Price | These are cheaper. | These are expensive. |
What is Dye?
Dyes are excellent colouring agents used by many industries, from textiles, toys, and colouring objects to even scientific use.
Dyes are transparent and change beautiful colours when used with wood and clothes. They are considered very versatile since they do not alter the features of the object to which they are being applied.
The composition of dyes includes carrier and dye pigment.
Dyes are composed of small molecules that are so porous that they allow light to pass through them. Also, they are very easily soluble in carriers such as water, alcohol, alcohol-based liquids, mineral spirit, oils and many more solvents.
The best type of dice that can be used to make shaders are the dyes that are mixed with alcohol.
The separation of dyes is not very specific, and therefore this results in many impurities. Due to this reason, they are considered crude in nature.
When compared under the same brand, it is observed that dies are a lot cheaper than stains.
When talking about lightfast, which means the property of a component to retain its colour under sunlight or exposure, dyes are less lightfast in nature.

What is Stain?
Stains are colouring agents that are primarily oil- or water-based paints. The composition of stains includes a binder, a carrier and colour pigment.
This Institute of large molecules ultimately makes them less soluble. Stains are more lightfast as compared to dice dyes.
Also, the preparation of the stage requires a lot of specifications, making them very natural and not containing any impurities.
They are categorised into three categories that are film-forming, penetrating, and acid. Film-forming is the oldest type of stain and is the most popular too.
But the drawback to film-forming stains is that they are not very durable, and due to weather conditions, atmosphere, and other reasons, the layer of the stains may peel off or flake.
If we want a permanent or long-lasting stain, the penetrating still will be the best option. The polymer bonding water-based technology used in penetrating stains drastically minimises the flaking and peeling properties.
They are not very good at hiding defects, flaws or surface defects. The acid stain is an entirely different kind of stain.
It reacts with the surface chemically and creates a finished look that appears almost natural. They are the most durable but also a much more expensive type of stain.

Main Differences Between Dye and Stain
- Dyes are more soluble in solvents like water, oil, alcohol, mineral spirits, and etch, while Stains are comparatively less soluble in them.
- While looking under the same brand, Dyes are supposed to be much cheaper than Stains.
- The preparation of Dyes does not involve many specifications, and as a result, they contain impurities giving them the title of crude. On the other hand, the preparation of stains consists of a lot of specifications, making them impurity free.
- The composition of Dyes includes a carrier and pigment, whereas that of Stains has a carrier, binder and pigment.
- Dyes are composed of smaller molecules, while Stains are made up of larger molecules.
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/bjd.12130
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/lsm.1102

I am thoroughly impressed by the comprehensive analysis presented in this article. Each aspect, from solubility to composition and preparation methods, has been clarified concisely, making it an enlightening read.
I found it fascinating to learn about the characteristics, properties, and applications of dyes and stains. I am impressed with the detailed explanations provided.
This detailed comparison has broadened my understanding of dyes and stains, emphasizing their distinct properties and uses. It certainly enhances my appreciation for the science behind coloring processes.
An excellent and very informative comparison of dyes and stains. It makes clear several differences between the two.
The informative content, along with its intellectual depth, provides an engaging and educational perspective on the key differences between dyes and stains. A commendable piece of writing indeed.
This article is a clear and comprehensive summary of the contrasting features of dyes and stains. The information is well-organized and has greatly expanded my knowledge of coloring agents.