In our daily lives, several scientific technologies are utilized to quantify the density of components around us. Hydrometers and hygrometers are two examples of such instruments.
A hydrometer measures the density of a liquid using Archimedes’ principle of flotation, whereas a hygrometer detects the degree of humidity and moisture in the atmosphere.
Key Takeaways
- Hydrometers measure the specific gravity of liquids, while hygrometers measure humidity levels in the air.
- Hydrometers are frequently used in the brewing and wine-making industries, whereas hygrometers find applications in meteorology and climate control systems.
- Hydrometers operate by displacement of liquid, whereas hygrometers rely on changes in materials that respond to humidity.
Hydrometer vs Hygrometer
A hydrometer and a hygrometer differ in their measuring principles and working principles. A hydrometer’s measuring principle measures a liquid’s density and works on the principle of flotation. A hygrometer measures humidity and moisture in the atmosphere and works on several different principles.

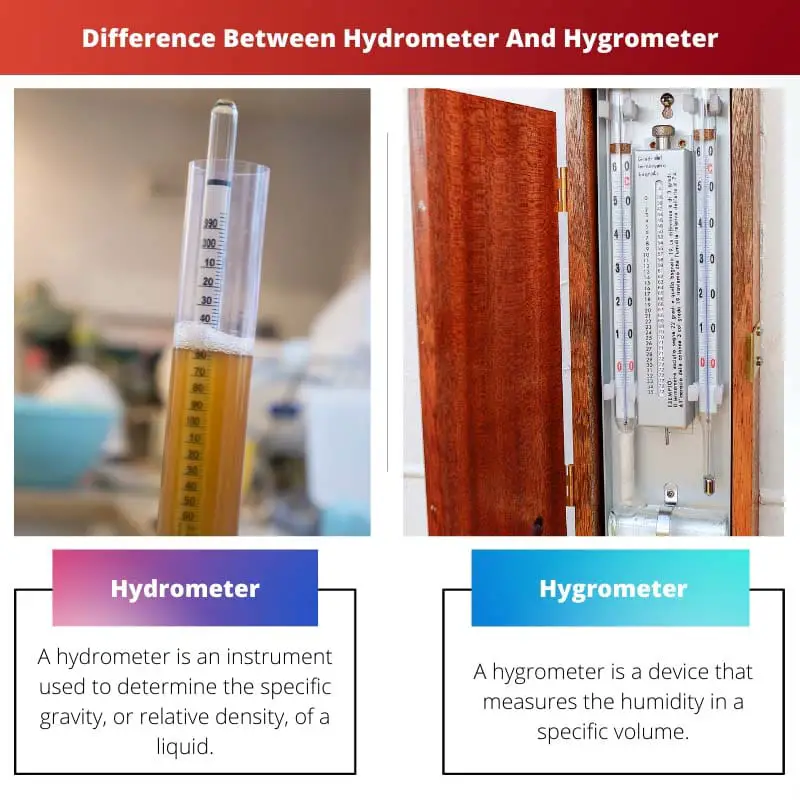
A hydrometer is an instrument used to determine a liquid’s density of gravity. A hydrometer’s measuring principle is measuring the depth of water using the Archimedes principle of flotation.
The word origin of hydrometer lies in the Greek word hydro, which means water. The hydrometer was invented by a Greek scholar named Hypatia.
A hygrometer is used to measure humidity or moisture content in the surrounding atmosphere. The word origin of hydrometer lies in Greek.
The hygrometer is derived from the Greek word Hygros meaning wet or moist. All hygrometers work on different principles. Leonardo Da Vinci invented the hygrometer.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Hydrometer | Hygrometer |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A hydrometer is an instrument used to determine the specific gravity, or relative density, of a liquid | A hygrometer is a device that measures the humidity in a specific volume |
| Inaccuracy/Accuracy | Simpler to manage the accuracy | Difficult to maintain accuracy and can provide inaccurate measurements |
| Factors influencing accuracy | To ensure accuracy, certain criteria like temperature, cleanliness, and correct immersion must be considered. | To assure precision, several parameters such as pressure, temperature, mass, and electrical charge must be standardized. |
| Thermometer built-in | Features built-in thermometers | A built-in thermometer is not always employed |
| Inventor | Invented by Hypatia | Invented by Leonardo Da Vinci |
What is Hydrometer?
A hydrometer is an instrument that utilizes buoyancy to assess the relative liquid limit. They are frequently validated and graded with the use of one or more indicators, such as specific gravity.
A hydrometer is normally constructed from a walled hollow glass tube with a wider lower quarter for buoyancy, a counterbalance such as lead or mercury for stabilization, and a slender stem with graded graduations for measurements.
The sample liquid is placed in a tall vessel, a weighing cylinder, and the hydrometer is progressively plunged into the liquid until it reaches the surface.
The relative density is determined by the height at which the liquid’s surface reaches the stem of the hydrometer. Any combination of scales anywhere along the stem of a hydrometer can correspond to density-related factors.
A hydrometer is used to calculate milk’s density (fluffy texture), a saccharometer to assess the thickness of glucose in a fluid, and an alcoholometer to measure higher concentrations of alcohol in drinks.
The hydrometer works on Archimedes’ principle, which says that a solid submerged in a fluid is buoyed by a pressure that is directly proportionate to the weight of the fluid displaced by the drowned section of the suspended material.
The deeper a hydrometer of a particular weight dips, the lesser the density of the fluid; the stem is regulated to provide a numerical measurement.

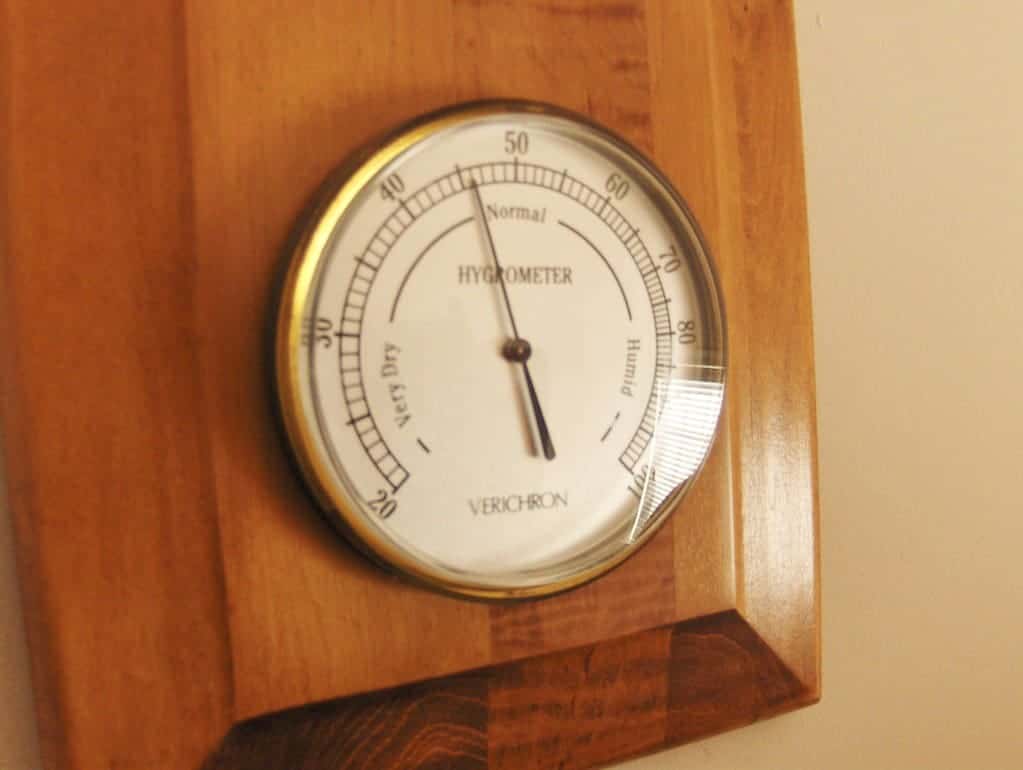
What is Hygrometer?
A hygrometer is a device that monitors the amount of water vapour in the air, soil, or other confined areas.
Humidity meters frequently rely on other measures, such as heat, tension, quantity, or an electromechanical alteration in a component when moisture is consumed.
These measured values can be used to calculate humidity using calibration and computation. Modern electronic gadgets use the temperatures of precipitation (called the dew point) or fluctuations in electronic capacitance or susceptibility to detect humidity swings.
Around 1480, Leonardo da Vinci built a crude hygrometer. The optimum quantity of water vapour that can be maintained in each amount of air (saturation) changes significantly with temperature; cold air can contain less water per unit volume than hot air.
The temperature may influence humidity levels.
Hygrometers are used in labs, salons, humidors, galleries, conservatories, and businesses. They are also used to care for wooden stringed instruments like pianos, guitars, and violins, which excessive humidity levels can damage.
In wildfires, hygrometers are useful because the lower the percentage of humidity, the quicker the fuels burn. Hygrometers are used in residential settings to help with humidity control.
Hygrometers are frequently employed in the painting business since the application of paint can be particularly sensitive to humidity and dew point.

Main Differences Between Hydrometer And Hygrometer
- A hydrometer is an instrument used to determine a liquid’s density of gravity, whereas a hydrometer is used to measure humidity in a specific volume.
- A hydrometer is simpler to manage accuracy, whereas a hygrometer is more difficult to maintain accuracy and provides erroneous measurements below the freezing point.
- To ensure accuracy in hydrometer, certain criteria like as temperature, cleanliness, and correct immersion must be considered. Whereas to assure precision in the hygrometer, several parameters such as pressure, temperature, mass, and electrical charge must be standardized.
- Advanced hydrometers feature built-in thermometers that allow them to readily measure the temperature of the liquid, whereas a built-in thermometer is not always utilized in hygrometers but is required for relative humidity calculations.
- The hydrometer was invented by a Greek scholar named Hypatia, and Leonardo Da Vinci invented the hygrometer.

This article does a commendable job of explaining complex scientific instruments in a clear and engaging manner. The content is rigorous and enlightening.
Very well explained. Not only did I learn about the differences between hydrometer and hygrometer, but I also learned who invented them. This is an extremely well-written article!
I found the comparison table very useful. It’s impressive to see how details about the accuracy and inventor of each instrument are included.
This information about the hydrometer and hygrometer is precise and well-presented. It’s an enriching read that provides insight into the functioning of these scientific instruments.
Definitely, the detailed descriptions of how a hydrometer measures density and the principles governing hygrometers offer a clear picture of their applications.
This article is quite educational. It provided an in-depth understanding of the operational principles of hydrometers and hygrometers. The historical background is a compelling addition.
Absolutely, the historical background adds value. Leonardo Da Vinci’s invention of the hygrometer and the use of Archimedes’ principle for the hydrometer are fascinating.
The post provides a wealth of knowledge about hydrometers and hygrometers. The clear explanations make the differences between these instruments easy to understand.
Indeed, this article is an outstanding source of information about these scientific instruments. I appreciate how it covers both historical and operational aspects.
Agreed, and the usage of specific examples to illustrate their applications is beneficial.
This post offers a comprehensive explanation of the difference between a hydrometer and a hygrometer. It provides a useful comparison of their defining features and uses.
Agreed. It’s very informative. I didn’t know the word ‘hydrometer’ comes from the Greek word hydro. It’s interesting to learn about the fascinating history of these tools.