A gland called the thyroid is present in the anterior of the neck. It controls the production of hormones in the human body. The hormones produced by this gland help synthesise fats, carbohydrates, et cetera and help control the heart rate, blood pressure, and body temperature.
Hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism are the results of the increase or decrease in hormone secretion. They’re fairly common diseases and can run in families.
Key Takeaways
- Hyperthyroidism results from an overactive thyroid gland producing excess hormones, while hypothyroidism is due to an underactive thyroid gland producing insufficient hormones.
- Hyperthyroidism can cause weight loss, irritability, and rapid heartbeat; hypothyroidism can lead to weight gain, fatigue, and slow heart rate.
- Treatments for hyperthyroidism aim to reduce hormone production, whereas hypothyroidism treatments involve hormone replacement.
Hyperthyroidism vs Hypothyroidism
Hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone causing symptoms such as weight loss, rapid heartbeat, sweating, anxiety, and tremors. Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormone causing weight gain, fatigue, and dry skin.

Hyperthyroidism is caused when the thyroid gland grows larger in size and is overactive. The immune system starts to see the thyroid as an invader and attacks it in this autoimmune disease.
In hypothyroidism, the thyroid gland either stops working or produces hormones in deficit. It is more common in women, and the reason for that is not known. It very commonly occurs in people over 60 years of age but can begin at any age.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Hyperthyroidism | Hypothyroidism |
|---|---|---|
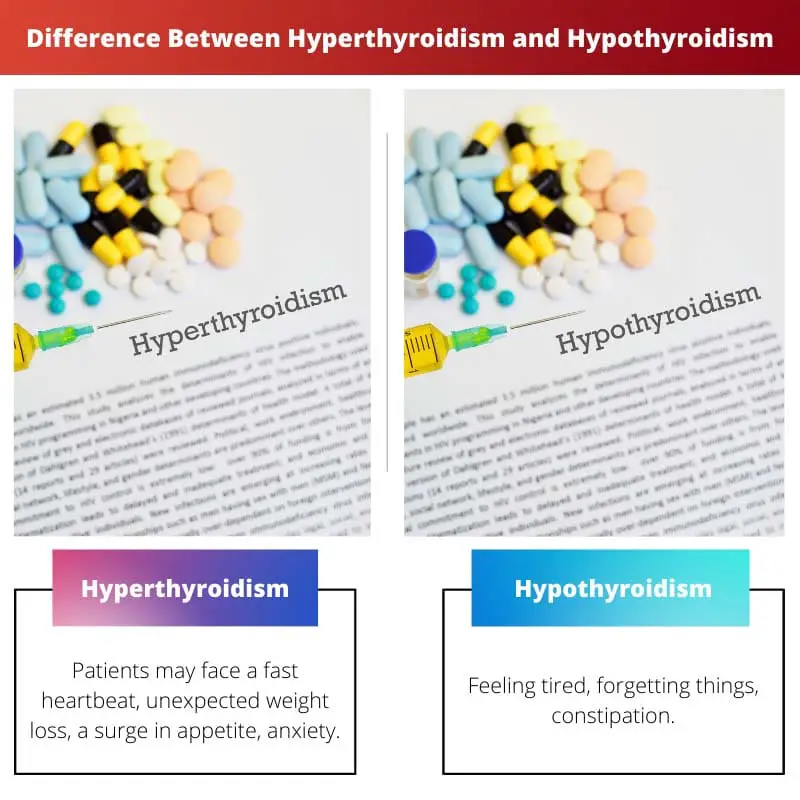
| Symptoms | Patients may face a fast heartbeat, unexpected weight loss, a surge in appetite, anxiety. | feeling tired, forgetting things, constipation |
| Causes | Graves’ disease is a common cause | Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is the most common cause |
| Treatment | Radioactive iodine and surgery among others. Beta-blockers are prescribed. | Most commonly treated with supplemental thyroid hormone |
| Diet | Focus on the intake of calcium and sodium | Eat a diet rich in zinc and iodine |
| Tests | Can be detected through a blood test for the thyroid-stimulating hormone. If it is low it means that you have hyperthyroidism. | Can be detected through a blood test for the thyroid-stimulating hormone.If it is high it means that you have hypothyroidism. |
What is Hyperthyroidism?
In hyperthyroidism, the body manufactures excess thyroid hormones(thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3)). The thyroid gland regulates the hormones and the metabolism through them.
People with a history of Graves’ disease can easily get hyperthyroidism. In Graves’ disease, the thyroid produces too much hormone due to stimulation by antibodies.
The thyroid gland may grow larger in size, the shape of which may be symmetrical or larger on one side only.
Some of the signs that you might face during hyperthyroidism include nervousness, increased heart rate due to a heightened metabolic state, brittle skin, irritability, anxiety, weaker periods, weight loss, and trouble sleeping.
It is essential to get immediate medical attention in case of excess dizziness, loss of consciousness, heightened heartbeat, and prolonged shortness of breath. When you go for a check-up, the doctor may ask for your medical history.
This will reveal some common symptoms to help better diagnose some of them, including unexpected weight loss, protruding eyes, and a large thyroid gland.
The cholesterol tests are conducted to check if the metabolic rate is elevated and the body is burning through cholesterol quickly. Other tests include the thyroid-stimulating hormone level test, the triglyceride test, an ultrasound, and CT or MRI scans.
If you are currently suffering from the disease, it becomes even more important to look after yourself as it can cause some complications like heart problems, brittle bones, eye problems, swollen skin, and red skin.
What is Hypothyroidism?
In hypothyroidism, the thyroid gland either stops working or produces hormones in deficit. It is more common in women, and the reason for that is not known.
It very commonly occurs in people over 60 years of age but can begin at any age. A mild form of hypothyroidism in the early stage is called subclinical hypothyroidism.
The thyroid gland helps regulate metabolism, and when the production of hormones slows down, so does the metabolism. This can lead to weight gain.
Some signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism are fatigue, dryness of skin, forgetting things, sensitivity to cold, depression, elevated blood cholesterol, dry skin, stiff or tender muscles, slowed heart rate, and constipation.
Some factors which may increase your risk of developing hypothyroidism are:
In hypothyroidism, the thyroid gland either stops working or produces hormones in deficit. It is more common in women, and the reason for that is not known. It very commonly occurs in people over 60 years of age but can begin at any age.
A mild form of hypothyroidism in the early stage is called subclinical hypothyroidism. The thyroid gland helps regulate metabolism, and when the production of hormones slows down, so does the metabolism. This can lead to weight gain.
According to the American Thyroid Association reports, there is no cure for hypothyroidism, and the patient will have to stay on medication for their entire lives.
It can be detected by conducting a blood test regularly or if the symptoms begin to appear regularly or if the symptoms begin to appear.
People with a history of Hashimoto’s thyroiditis or commonly known to get hypothyroidism. In this condition, the body starts attacking the immune system, and over time the thyroid stops producing hormones, which results in hypothyroidism.
Some signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism are fatigue, dryness of skin, forgetting things, sensitivity to cold, depression, elevated blood cholesterol, dry skin, stiff or tender muscles, slowed heart rate, and constipation.
Some factors which may increase your risk of developing hypothyroidism are:
- Being a female. It is more likely for women to develop hypothyroidism after menopause than earlier in their life.
- Elderly people who are over 60
- Family with a history of hypothyroidism
- Having other autoimmune conditions, for example, diabetes
The dosage of medication will have to be increased in case a woman is on birth control pills. The estrogen and progesterone present in the pills can have an effect on the thyroid-binding protein, which may lead to an increase in the levels.
It is very crucial to take care of yourself during pregnancy if you have hypothyroidism. Ask your doctor to adjust your medications accordingly. Proper thyroid hormones are essential for the growth of the baby.
Hypothyroidism can be diagnosed through a blood test for the thyroid-stimulating hormone. The doctor may also conduct other tests for others and diagnose conditions that may have led to the development of hypothyroidism.
Main Differences Between Hyperthyroidism and Hypothyroidism
- In hyperthyroidism, the body manufactures excess thyroid hormones(thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3)), while in hypothyroidism, the thyroid gland is underactive.
- A patient suffering from hypothyroidism has a slower metabolism, feels tired all the time, and may face unexpected weight gain. On the other hand, a patient suffering from hyperthyroidism experiences a surge in energy and may experience unexpected weight loss.
- There is a decrease in hormones in hypothyroidism and an increased production in hyperthyroidism.
- If the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone is low, then the patient has hyperthyroidism, while if the level of the hormone is high, the patient has hypothyroidism.
- Hypothyroidism is not permanent. In case it comes back after taking medication, the doctor may recommend removing the thyroid gland. Hypothyroidism does not go away, and the patient will have to take medication for the rest of their lives.
- In hyperthyroidism, beta-blockers are prescribed for treatment. Supplemental thyroid hormone is the most common treatment for hypothyroidism.
- https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00223-005-0068-x
- https://journals.physiology.org/doi/abs/10.1152/ajpendo.00043.2003