Whenever reading a piece of writing, especially of literature, a reader encounters numerous literary devices such as the figure of speech, consonance, paradox, etc.
A literary tool is used to elucidate ideas, thoughts, themes, etc., in a work. Each tool has a uniqueness of its own and is utilized at different levels while writing.
Key Takeaways
- Motifs are recurring elements in a work that contributes to its theme, while symbols represent abstract ideas or concepts.
- Motifs can be visual, auditory, or thematic, while symbols are primarily visual or textual.
- A motif helps to develop and support a work’s theme, whereas a symbol’s meaning can change depending on the context.
Motifs vs Symbols
A motif is a recurring idea, theme, or image that appears throughout a work of art or literature. Motifs can be used to create a sense of unity or to reinforce certain ideas or themes. A symbol is a concrete object or image that represents an abstract idea or concept. Symbols are used to convey a deeper meaning or to represent complex ideas or emotions.
A motif is a salient element, such as a tool or reference, which is repetitive in terms of its usage in works of literature. It can be used in several forms like images, music, phrases etc.
It is used by writers frequently to indicate the development of the theme along with the plotline.
The symbol, also termed ‘sign proper’, falls under the three classifications of signs. In symbols, the relation between the signifying thing and its representation is completely a matter of social agreement, not a natural one.
For example – Shaking a hand with someone is a conventional mark of greeting or leaving.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Motifs | Symbols |
|---|---|---|
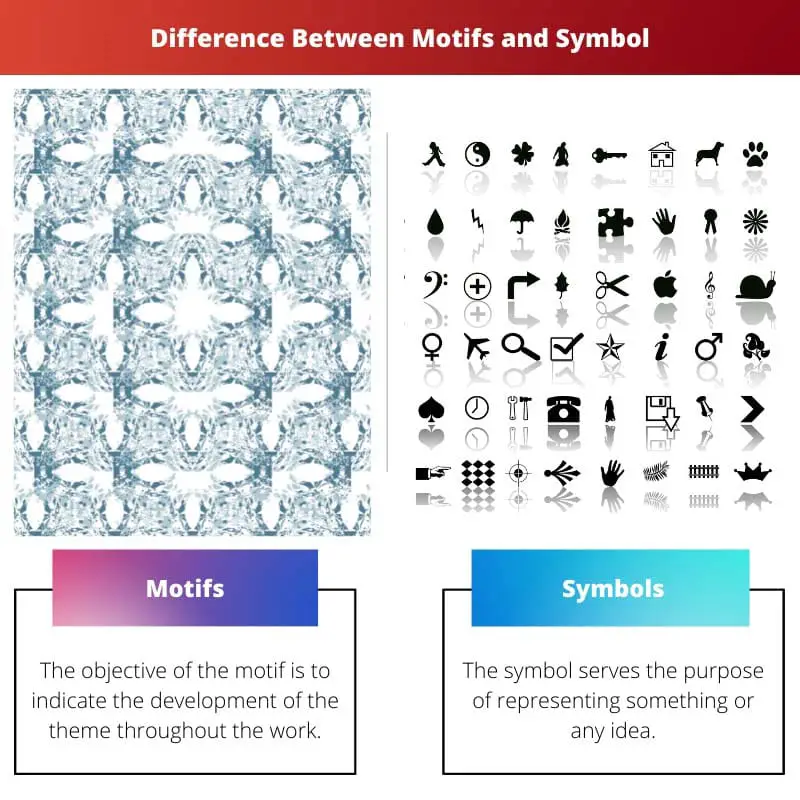
| Objective | The objective of the motif is to indicate the development of the theme throughout the work. | The symbol serves the purpose of representing something or any idea. |
| Usage | Motifs are frequently used in literary pieces of work. It is used in a repetitive pattern. | Symbols are used only once or twice in work altogether. It is not repetitive in terms of usage. |
| Context Dependency | Motifs are used according to the context of the piece of writing. | Symbols represent something that is socially agreed upon. It doesn’t change its core significance for context. |
| Representation | It is represented through a medium like an image, music, phrase, act, etc. | It is represented through object, word, sign, sound, etc. |
| Relation with theme | Motifs are confused with the theme as they represent the central theme of any writing. | Symbols are not directly related to the theme. It only represent an idea or something. |
What are Motifs?
Any sound, act, picture, or any other form of representation that is used to indicate the theme, is known as Motif. It is widely used to represent a central idea or the main topic about which the work of art is about.
Though it represents the theme, it is sometimes used interchangeably with it. However, the word theme is more inclined to a general doctrine while the motif is merely used to depict that concept through the work.
Its usage is repetitive, and the reader keeps noticing the motif in the work. It pinpoints the notions and happenings which portray the central theme of the work.
Motifs are implanted by the writer meticulously so that reader can trace the development of the theme. It always fortifies the author’s lead message, which he wants to convey through the writing.
For example – In the novel Jane Eyre by Charlotte Bronte, the motifs used were fire and ice, where the former shows her spirit and fierceness, and the latter depicts the forces which tried to extinguish her fire nature.
Letters and journeys acted as a motif in the infamous novel Pride and Prejudice.

What are Symbols?
In a wider sense, a symbol can be anything that manifests something. In this way, every word is a symbol of something.
In literature also, Symbol signifies an object or happening which itself manifests something else depending upon the context.
The symbol is made by social conventions, where a huge number of people agree on a symbol and what it would depict.
Though, in the world of literature, writers do make their symbols and use them in their works, which in turn makes the interpretation difficult for the readers.
Symbols are used only a time or two to increase the understanding of a particular thing. It could be anything like an image, object, music or act, setting, characters, etc. It adds more meaning and structure to the piece of writing.
It is something of a concrete object to illustrate an idea. Conventional symbols are widely accepted, and thus they get popularized for their manifestation rather than their structure.
Not only in literature but Symbols are also used in other subjects such as science, mathematics, music, etc.
For example – Black signifies death, white depicts peace, Red is for blood, anger, passion and danger, and the rainbow shows hope and promises, etc.

Main Differences Between Motifs and Symbols
- Motifs, the literary elements, are used to indicate the central theme of the piece of work, whereas symbols are used to depict any idea or something prevailing in the plot.
- Motifs are recurring in nature and are used in literary pieces of writing. In contrast, symbols are engaged in the work only once or twice throughout the work.
- Motifs are cautiously implanted in the work so that a reader can easily trace the development of the theme. In contrast, symbols are used to portray an idea or thought of the writer concerning the context.
- The utilization of motifs differs from writer to writer. Each writer creates unique motifs according to the plot. While symbols are made by social conventions and become universal for their significance.
- The presence of motifs in the work fortifies the lead message of the writer, which he wants to display through writing. In contrast, symbols are used to add more meaning and structure to the work.

The examples of motifs and symbols in classic novels are an insightful way to demonstrate their usage and impact on the interpretation of literary works.
The comparison table clearly outlines the distinctions between motifs and symbols, shedding light on their different objectives and usage in literary works.
The clear definition and explanation of motifs and symbols in literature and their role in conveying themes and ideas is an enlightening read for anyone interested in literary analysis and interpretation.
The distinction between motifs and symbols, particularly in the context of literary works, is elucidated clearly in this article. Understanding these literary tools enhances the reader’s interpretation of themes and ideas in literature.
The notion that symbols are used once or twice to enhance the understanding of a concept in literature is an important distinction from motifs, which are repetitive and contribute to the development of themes.
Understanding the significance of motifs as salient elements and symbols as a matter of social agreement is crucial in discerning their different roles in literature. This article provides a clear delineation of their characteristics.
The examples provided, such as the motifs of fire and ice in ‘Jane Eyre’ and the use of letters and journeys in ‘Pride and Prejudice’, effectively illustrate how motifs are utilized in literature to highlight underlying themes.
The detailed explanations of motifs and symbols are essential for comprehending their roles in literary analysis. The examples provided are invaluable in understanding their practical application.
The explanation of symbols as objects or happenings that manifest something else, based on social conventions, is thought-provoking. Understanding symbols adds a layer of complexity to literary analysis.
This article provides a comprehensive explanation of the differences between motifs and symbols in literature. It is crucial for readers to understand how they are used to convey deeper meanings and themes in writing.