Every living being’s body consists of several organs, systems, senses, skills etc. In order to carry out all the processes in the body harmoniously, it is important for all the processes to work out smoothly and efficiently.
Every process plays an important role in keeping the living being healthy and fit.
There are various processes that take place in a living being’s body that, include respiration, digestion, circulation, excretion, movement, nutrition, growth, reproduction, sensitivity etc.
There are subtypes of these processes that are also carried out. For instance, the subtypes of respiration include aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration.
Subtypes of reproduction include sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction, and so on. However, two types of circulation include 1. Pulmonary circulation, and 2. Systemic circulation.
Key Takeaways
- Pulmonary circulation is the circulation of blood between the heart and lungs.
- Systemic circulation is blood circulation between the heart and the rest of the body.
- The main difference is the purpose of circulation, with pulmonary circulation providing oxygenation and systemic circulation delivering oxygenated blood to the body.
Pulmonary vs Systemic Circulation
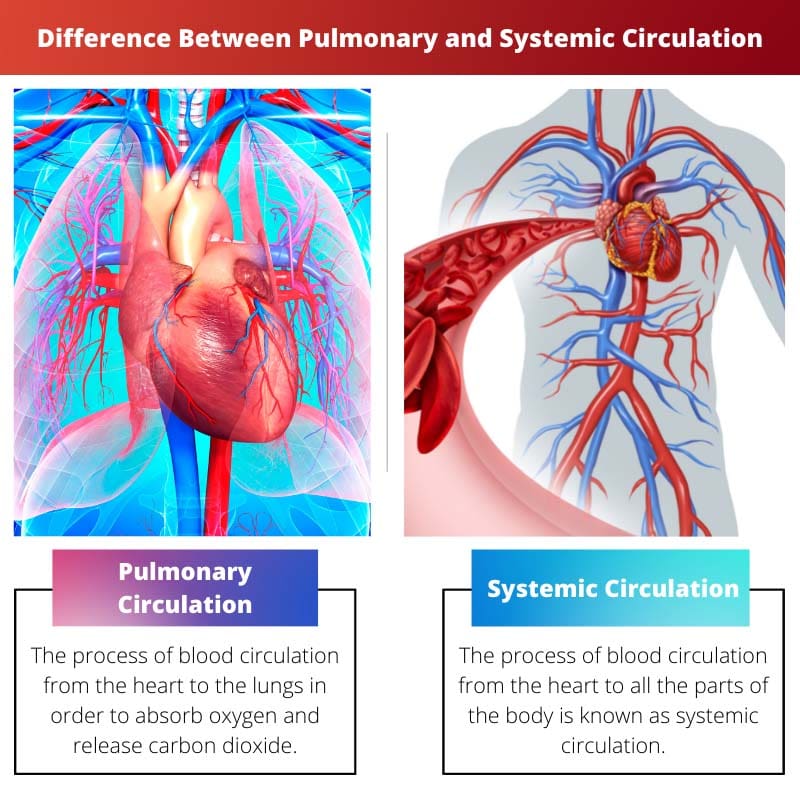
The difference between pulmonary circulation and systemic circulation is the place to which the blood is circulated in these respective circulations. In pulmonary circulation, the blood is circulated between the heart and the lungs, and further, transportation of deoxygenated blood to the lungs for absorption of oxygen and release of carbon dioxide is also done. On the other hand, in systemic circulation, the blood is circulated between the heart and the rest of the body.
The process of blood circulation from the heart to the lungs in order to absorb oxygen and release carbon dioxide by transporting deoxygenated blood to the lungs is known as pulmonary circulation.
In this process of blood circulation, a closed circuit is formed between the heart and the lungs because of the formation of the system of blood vessels.
The process of blood circulation from the heart to all the parts of the body is known as systemic circulation. Blood is supplied to all the tissues of the body during this circulation.
It also supplies oxygen and other necessary nutrients to the body cells and drains out carbon dioxide along with other waste products.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Pulmonary Circulation | Systemic Circulation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition/ Meaning | The process of blood circulation from the heart to the lungs in order to absorb oxygen and release carbon dioxide by transporting deoxygenated blood to the lungs is known as pulmonary circulation. | The process of blood circulation from the heart to all the parts of the body is known as systemic circulation. |
| During hypoxia | Blood vessels are narrowed because of the muscles that are present in the walls. | Blood vessels are dilated, and thus blood pressure is decreased. |
| During hypercapnia | Blood vessels are narrowed because of the muscles that are present in the walls. | Blood vessels are dilated, and thus blood pressure is decreased. |
| Blood flow | The occurrence of active regulation and blood flow is affected by gravity and alveolar recruitment. | Less effect of gravity on blood flow is seen |
| Blood flow between | Heart to lungs | Heart to all the parts of the body |
What is Pulmonary Circulation?
The process of blood circulation from the heart to the lungs in order to absorb oxygen and release carbon dioxide by transporting deoxygenated blood to the lungs is known as pulmonary circulation.
It is found in the evolutionary cycle that pulmonary circulation first occurred in lungfishes. The lungfishes were also the first animals to acquire a heart that had three chambers.
In this process of blood circulation, a closed circuit is formed between the heart and the lungs because of the formation of the system of blood vessels.
However, pulmonary circulation is different in mammals, crocodiles, and birds. The process takes place in a different manner in these living beings.
Whenever the division of the ventricle takes place into two parts, a four-chambered heart is formed, and it results in the initiation of the pulmonary circuit from the right ventricle.
The right ventricle plays the role of pumping the deoxygenated blood from the pulmonary artery, which is further divided into two branches. These two branches divide to the left and right lungs and get divided into even smaller arteries further.
The small branches of arteries are subdivided until the capillaries are reached in the pulmonary air sacs. The oxygen present in the air that is breathed into the air sacs is absorbed by the capillaries that are present in the blood.
The blood flow continues to the larger vessels until it reaches the pulmonary veins that open into the left atrium of the heart.
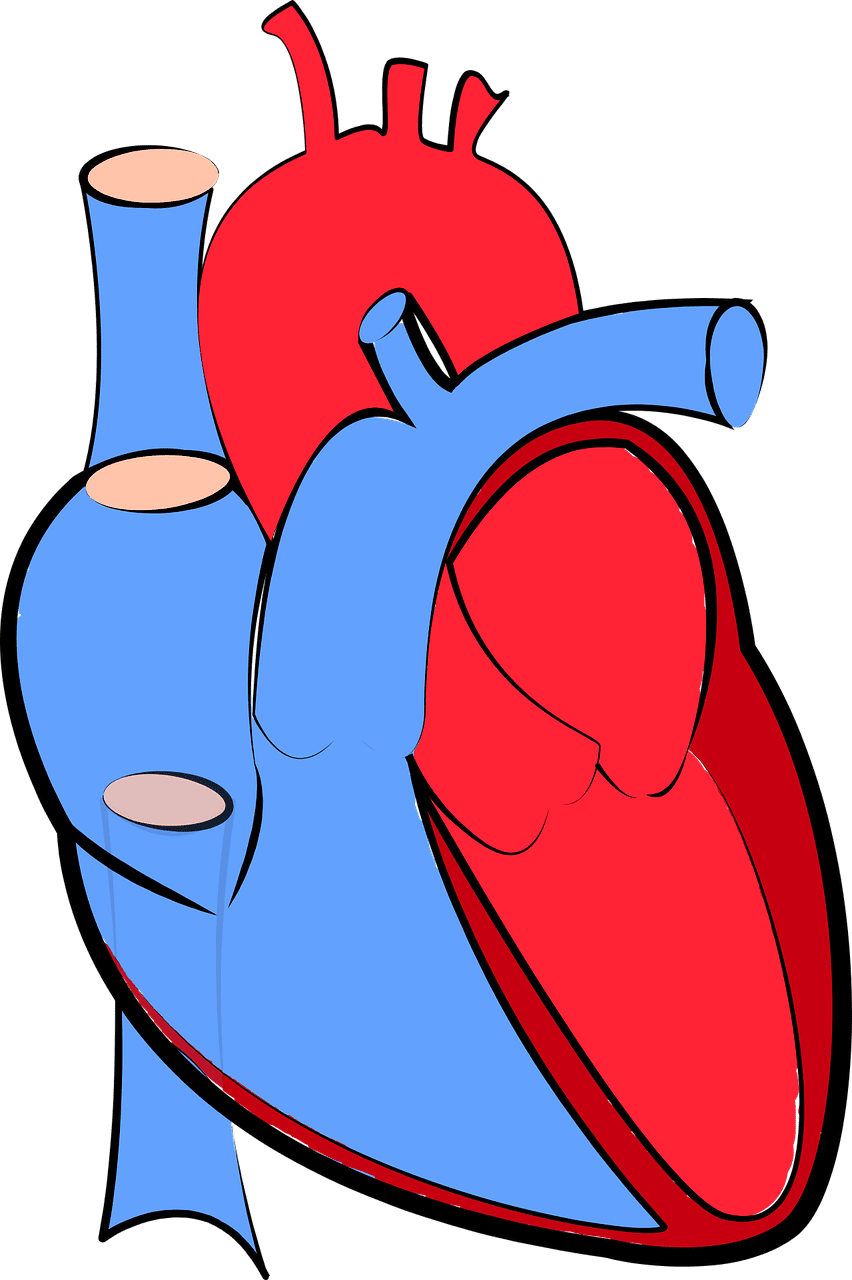
What is Systemic Circulation?
The process of blood circulation from the heart to all the parts of the body is known as systemic circulation. Blood is supplied to all the tissues of the body during this circulation.
It also supplies oxygen and other necessary nutrients to the body cells and drains out carbon dioxide along with other waste products.
In systemic circulation, the oxygenated blood is carried from the left ventricle, and the arteries act as a medium. After that, it is carried to the capillaries in the tissues that are present in the body.
Before returning to the right atrium of the heart, the deoxygenated blood from the tissue capillaries flows through a system of veins.
Several major systemic arteries and major systemic veins participate in the systemic circulation.
These systemic veins help the blood to return to the heart after it supplies oxygen and other nutrients to the tissues and clears out the carbon dioxide. The gaseous exchange occurs in the capillaries.
Several nutrients and oxygen that are extremely important for the body are supplied to the body during circulation. One must understand the importance of this process as it helps a living being in staying healthy and fit throughout.
In order to understand the importance of fitness and a healthy lifestyle, one must be careful about the diet and other factors that help in boosting this process.

Main Differences Between Pulmonary and Systemic Circulation
- The process of blood circulation from the heart to the lungs in order to absorb oxygen and release carbon dioxide by transporting deoxygenated blood to the lungs is known as pulmonary circulation, on the other hand, the process of blood circulation from the heart to all the parts of the body is known as the systemic circulation.
- The blood is circulated between the heart and the lungs during pulmonary circulation. On the other hand, the blood is circulated from the heart to the rest of the body during systemic circulation.
- Pulmonary circulation consists of the pulmonary artery and the pulmonary vein. On the other hand, systemic circulation consists of the inferior vena cava, superior vena cava, blood vessels etc.
- In pulmonary circulation, oxygenated blood is carried by pulmonary veins to the left atrium of the heart from the lungs. On the other hand, in systemic circulation, deoxygenated blood is carried out by the superior vena cava and the inferior vena cava to the right atrium of the heart from the body.
- In pulmonary circulation, carbon dioxide is released, and oxygen is absorbed in the blood. On the other hand, in systemic circulation, the metabolizing cells that are present in the body are provided with the necessary nutrients and oxygen.
- https://physoc.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1113/jphysiol.1894.sp00049
- https://www.annualreviews.org/doi/pdf/10.1146/annurev.ph.32.030170.001525

The initiation and continuation of pulmonary circulation from the right ventricle illustrate the coordinated functioning of the heart and circulatory system.
Absolutely, the synchronized actions of the heart and blood vessels in pulmonary circulation are essential for efficient oxygenation of blood.
The evolutionary perspective of pulmonary circulation in lungfishes adds an interesting dimension to the discussion.
Agreed, it’s fascinating to learn about the origins of these physiological mechanisms.
The explanation of pulmonary circulation provides a comprehensive understanding of how blood moves from the heart to the lungs and back.
Yes, understanding the physiological processes of the body can help us appreciate its complexity.
The absorption of oxygen by capillaries in the pulmonary air sacs and subsequent blood flow through larger vessels provides a detailed account of oxygen transport in pulmonary circulation.
Indeed, the intricate processes of gas exchange and nutrient supply in pulmonary circulation highlight the vital role of the respiratory system in maintaining homeostasis.
The discussion on the active regulation and gravitational effects on blood flow in pulmonary and systemic circulation emphasizes their distinct characteristics.
Absolutely, these factors play significant roles in the dynamics of blood circulation in the body.
It’s intriguing to see the different physiological responses of blood vessels in hypoxia and hypercapnia conditions.
The distinction between mammals, crocodiles, and birds in pulmonary circulation demonstrates the variations in this process across different species.
Indeed, the adaptation of pulmonary circulation in diverse organisms reflects evolutionary changes and functional adaptations.
The evolutionary and anatomical aspects of pulmonary circulation provide valuable insights into the diversity of biological mechanisms.
The detailed breakdown of the blood flow from the right ventricle to the pulmonary air sacs is enlightening.
The multi-step journey of blood flow in pulmonary circulation highlights the complex nature of this vital process.
Indeed, the intricate process of oxygen absorption in the capillaries provides a deeper insight into pulmonary circulation.
The comparison table effectively summarizes the key differences between pulmonary and systemic circulation, allowing for a clear understanding of their distinct functions.
Absolutely, the tabulated comparison enhances the clarity of information and facilitates a comprehensive grasp of these essential circulatory processes.
The comparison between pulmonary and systemic circulation clearly outlines the differences in function and purpose.
Absolutely, the detailed parameters of comparison offer a thorough analysis of these circulatory processes.
The formation of a closed circuit in pulmonary circulation and the functional role of the right ventricle provide a clear picture of this process.
The detailed explanation of how blood is divided into smaller arteries and capillaries in the lungs sheds light on the intricacies of pulmonary circulation.
Absolutely, understanding the structural and functional aspects of pulmonary circulation contributes to a holistic view of the circulatory system.