Our body is a complex mechanism that involves the right functioning of numerous parts. It comprises a variety of muscles, bones, organs, and cells.
The smooth and skeletal muscles are essential muscles of the human body that have different compositions, functions, and locations.
Key Takeaways
- Smooth muscles involuntarily control internal organs and blood vessels; skeletal muscles voluntarily control body movements and posture.
- Smooth muscles appear non-striated and spindle-shaped; skeletal muscles are striated with a cylindrical shape.
- Smooth muscles contract slowly and tire less easily; skeletal muscles contract rapidly but fatigue more quickly.
Smooth Muscle vs Skeletal Muscle
Smooth muscle is a type of muscle tissue found in the walls of internal organs such as the stomach and intestines. Skeletal muscle is a type of muscle tissue attached to bones, is under voluntary control, responsible for the body’s movement and allows us to perform activities.
Smooth muscles are an essential type of muscle in our body. They are located in the inner walls of our internal organs. These are essential to transport fluids and food to our internal organs, which are very important for our body.
They are self-stimulated, meaning they do not require any stimulation from the nervous system.
The skeletal muscle is yet another essential type of muscle present in our body. These are located under the skin and the bones. The skeletal muscles are fast and non-synchronised.
These help in our body’s movement and also require motor neuron stimulation from our nervous system.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Smooth Muscle | Skeletal Muscle |
|---|---|---|
| Muscle type | Different lengths of myofibrils from an unstriated muscle | An ordered arrangement of myofibrils forms striated muscle. |
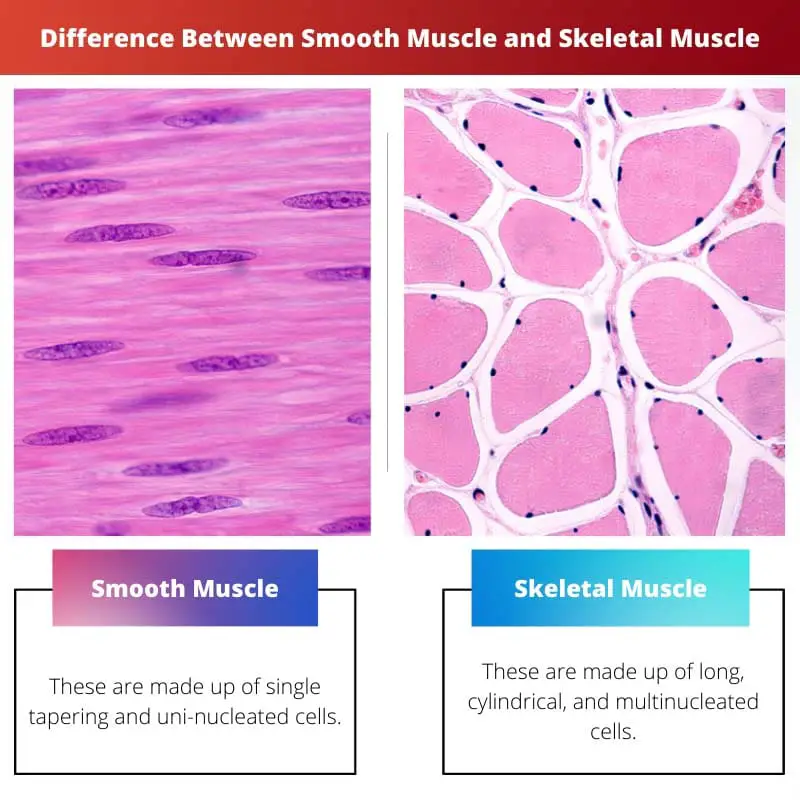
| Cells | They help maintain the flow of fluids and foods in the internal organs. | These are made up of long, cylindrical, and multinucleated cells. |
| Location | The inner linings or walls of the internal organs. | The skeletal muscles are attached to the bones or the skin. |
| Contraction Speed | In some organs, the contraction speed is slow and rhythmic. | The contraction speed in skeletal muscles is non-rhythmic and fast. |
| Function | They help in maintaining the flow of fluids and foods in the internal organs. | They are responsible for locomotion and movement. |
What is Smooth Muscle?
Smooth muscles are essential for the proper functioning of a body. The muscle type of smooth muscle is different lengths of myofibrils that ultimately form unstriated muscles.
Their movement is involuntary, so their functioning does not require a command from the brain. Also, theyy are self-stimulating,sos there is no need for the nervous system to stimulate their functioning.
The endocrine and nervous systems control them with the help of chemicals and stretching.
The function of the smooth muscles is to circulate food and fluids through the internal organs from time to time. These internal organs can be the intestine, stomach, bladder, uterus, urethra, bronchi, blood vessels, oesophagus, etc.
They do not experience fatigue and have a stress-relaxation response. The energy requirement for their functioning is shallow. Since they need to maintain fluid flow inside the internal organs, their location is also in their inner walls or linings.
The cells of smooth muscles are single tapering and uninucleated. Their contraction speed is rhythmic and relatively slow in some of the organs.

What is Skeletal Muscle?
The other type of muscle is skeletal muscle. These are attached to the bones and skin of the body. The movement of skeletal muscles is entirely voluntary. We can control them; they will move and stop on our command.
Skeletal muscles are made up of cylindrical, long, and multinucleated cells. These skeletal muscles are attached to the skin and bones with the help of tendons.
The function of skeletal muscles is quite helpful and necessary for the body. They help in locomotion and movement as well as in maintaining our posture.
The muscle fibres of skeletal muscles are low and have high levels of myoglobin and mitochondria. They carry high levels of Oxygen and appear red.
The nervous system controls the skeletal muscles. This is why they are also called non-self from stimulating muscles, which means they require stimulation from the nervous system with the help of motor neurons.
Since their function is responsible for the movement of our body and keeping posture correct, they also require high amounts of energy to withstand our weight. The strength of skeletal muscles can be easily increased with the help of stretching.
Also, many foods and exercises can help improve the performance of these muscles. The contraction speed of skeletal muscles is non-rhythmic and fast, unlike that of smooth muscles, which are rhythmic and slow.

Main Differences Between Smooth Muscle and Skeletal Muscle
- Smooth muscles are formed with the help of different lengths of myofibrils, whereas skeletal muscles are an ordered arrangement of myofibrils.
- Smooth muscles are made up of single tapering and uninucleated cells, while Skeletal muscles are made up of long, cylindrical, and multinucleated cells.
- The location of smooth muscles is in the inner walls of internal organs. On the other hand, the skeletal muscle area is attached to the bones and the skin.
- In some organs, the contraction speed of smooth muscles is slow and rhythmic, whereas the contraction speed of skeletal muscles is fast and non-rhythmic.
- The smooth muscle functions to circulate food and fluid in the internal organs. The function of the skeletal muscles is to assist in movement and locomotion.
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/mus.880180612
- https://journals.physiology.org/doi/abs/10.1152/ajpheart.00227.2014

Such an elaborative piece. The information presented is undoubtedly a great addition to the existing knowledge.
The article is well-thought and provides an excellent breakdown of smooth and skeletal muscles. It greatly improves the reader’s understanding.
This article is misleading, the author is attempting to oversimplify complex processes. This undermines the intellect of the reader.
The article is not misleading; it is an educational and valuable source of information.
You are entitled to your opinion, but I found the article enriching and informative.
This is fascinating. To understand the concept of muscles with such depth is a treat for the intellect.
Thank you for enlightening us with this incredibly enlightening information. I will share this with my peers.
Absolutely outstanding work. The clear comparison is genuinely beneficial to understand the differences between the two muscles.
Yes, indeed. This is a truly valuable piece of information. Scientific knowledge is always impressive.
This is highly informative and intriguing. I never took the time to understand the complexity of the human body. Thank you for providing such a valuable article.