Gametophytes and Sporophytes are nothing but two generations of a plant. In all plants, an alternation of generation exists.
Although they are two generations of a plant and, hence will have some similarities, they differ from each other in a lot of aspects.
Key Takeaways
- Sporophyte is the diploid generation of plants that produce spores, while Gametophyte is the haploid generation that produces gametes.
- Sporophyte is larger and more complex than Gametophyte and is more visible to the naked eye.
- Sporophytes and Gametophytes alternate in the life cycle of plants and have distinct characteristics and functions.
Sporophyte vs Gametophyte
The difference between Sporophyte and Gametophyte is that of the phase they are a part of in the life cycle of a plant. The gametophyte is the haploid segment or stage in the life cycle of a plant, whereas the Sporophyte is the diploid segment or stage in the life cycle of a plant.

The generation of plants that produces ‘spores’ is known as Sporophyte. The Sporophyte is the segment or stage in the plant life cycle that owns Diploid cells.
The generation of plants that forms’ gametes’ is known as a Gametophyte. The gametophyte is the segment or stage in a plant’s life cycle that owns Haploid cells.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Sporophyte | Gametophyte |
|---|---|---|
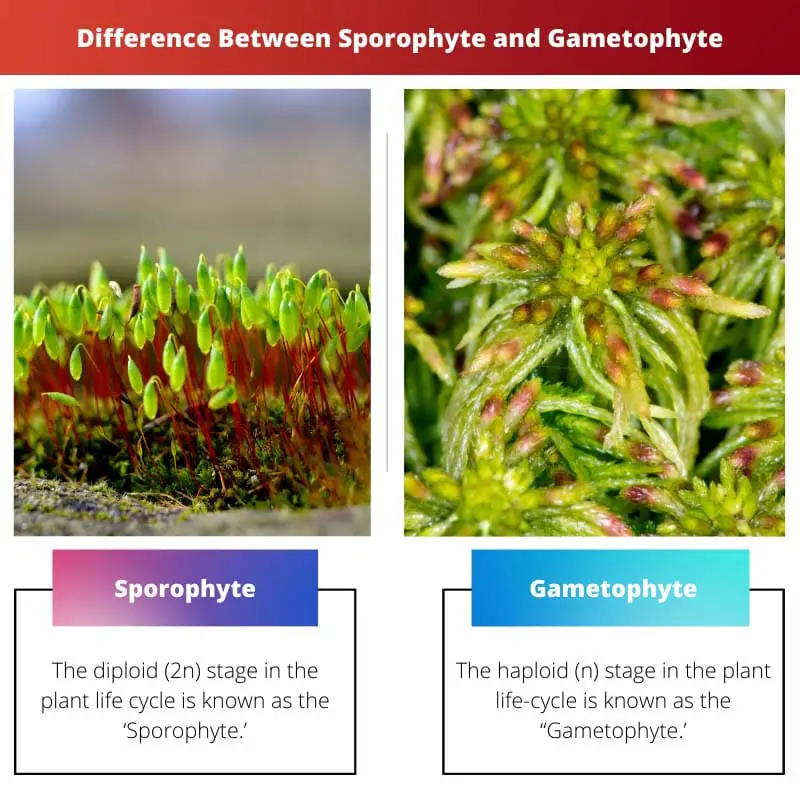
| Phase or Generation | The diploid (2n) stage in the plant life cycle is known as the ‘Sporophyte.’ | The haploid (n) stage in the plant life-cycle is known as the “Gametophyte.’ |
| Production | Sporophytes result in the formation of spores. | Gametophyte generation results in the production of gametes. |
| Chromosomes | Sporophytes own Diploid cells, which means they have two sets (2n) of chromosomes. | Gametophytes own Haploid cells, which means they have one set (n) of chromosomes. |
| Process | Sporophytes use the process of meiosis. | Gametophytes use the process of mitosis. |
| Reproduction | Sporophytes reproduce asexually. | Gametophytes undergo sexual reproduction. |
| End Product | During the process of meiosis, Sporophytes produce haploid spores (n) or meiospores in the diploid cells. | Gametes together take part in Fertilization or Fuse, giving rise to diploid (2n) zygote. |
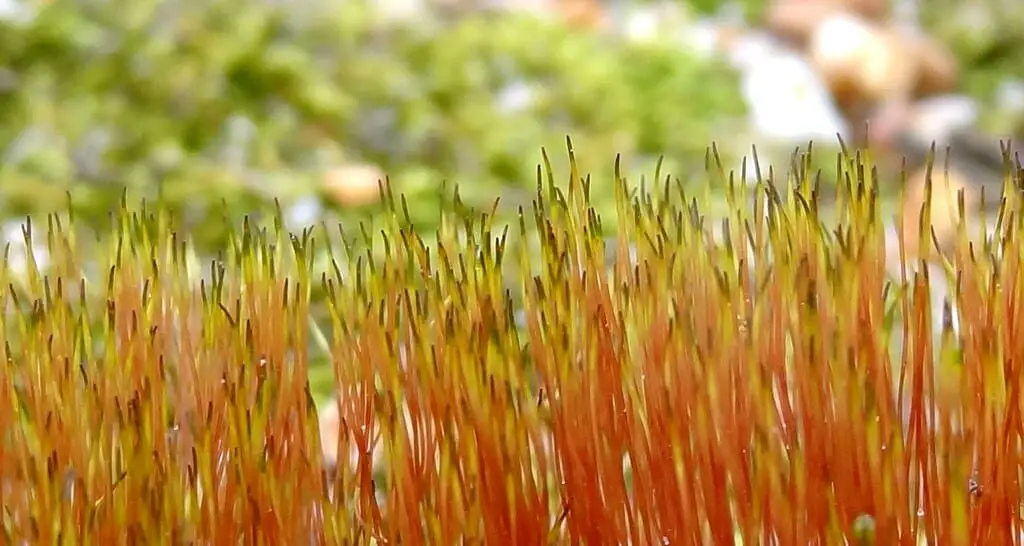
What is Sporophyte?
The word ‘Sporo’ means spores, and ‘Phyte’ means plants. The Sporophyte is the stage or segment in the plant life cycle which owns Diploid cells.
The Diploid cells own two sets of chromosomes (2n), where one set of chromosomes is the male parent’s, while the other set is that of the female parent. Sporophytes reproduce asexually.
Sporophytes, however, can produce both sexual and asexual spores. The Sporophyte produces haploid spores or meiospores by the process of meiosis.
Sporophyte receives its nourishment from Gametophytes. Plants like Angiosperms and Gymnosperms have a higher dominant phase of the Sporophyte.

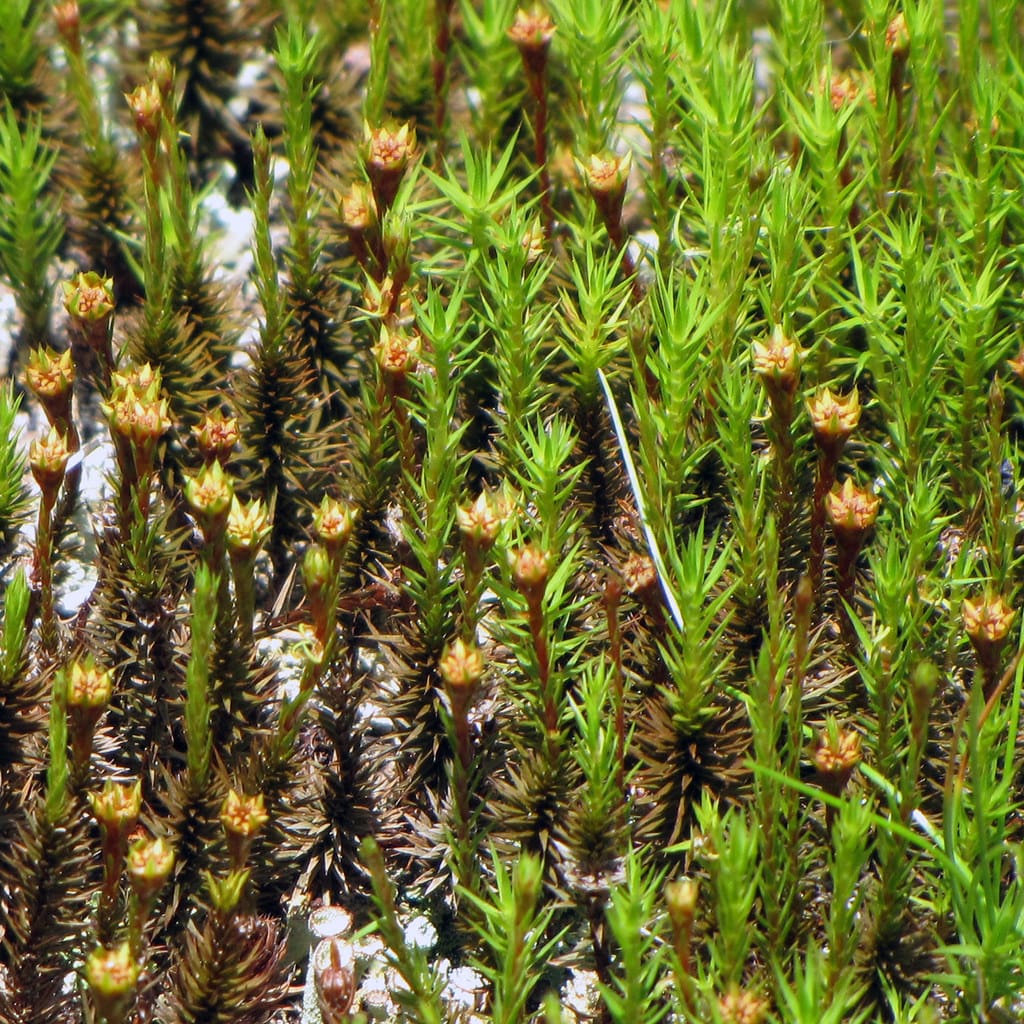
What is Gametophyte?
The word ‘Gameto’ means Gametes, and ‘phyte’ means plants. The gametophyte is the segment or stage in the plant life cycle that owns Haploid cells.
Haploid cells own one set (n) of chromosomes that carries genetic information. They produce gametes by undergoing sexual reproduction.
Gametes fuse together to take part in Fertilization and give rise to a Diploid zygote. This further grows into the next generation, known as the Sporophyte, which has diploid (2n) chromosomes.
Due to the frequent changes in plant life, there has been a rising decrease in Gametophytes, which are being constrained into small cells. Gametophytes undergo the procedure of Mitosis.

Main Differences Between Sporophyte and Gametophyte
- During the process of Meiosis, Sporophytes produce haploid spores (n) or meiospores, whereas Gametes together take part in Fertilization or Fuse, giving rise to diploid (2n) zygote.
- Sporophytes produce microspores and megaspores, whereas Gametophytes produce male gametes and female gametes.
- https://science.sciencemag.org/content/171/3976/1155.abstract
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.2307/1222089

The connection between the generations in plant life cycles is clearly explained, especially in relation to nourishment.
The dominance of Sporophytes in certain types of plants is an interesting observation.
The interdependency described is crucial to understanding the functioning of plants.
The roles of Sporophytes and Gametophytes in the plant life cycle are well articulated.
The distinction between microspores and megaspores is particularly interesting.
The main differences between both generations are well-explained and the sources help to validate the information.
The section on differences is clearly expressed.
The process of meiosis used by Sporophytes and the process of mitosis used by Gametophytes is a key distinction that is clearly described.
The difference in their reproductive methods is essential to understand.
The details about the cellular differences are highly informative.
The information on the production of spores by Sporophytes and gametes by Gametophytes is enlightening.
The significance of the roles of the two generations in plant reproduction is well emphasized.
The details provided on the main differences between Sporophyte and Gametophyte are highly informative.
The scientific literature cited is essential for further exploration of the topic.
The references provide additional credibility to the content.
The explanation of the main differences between Sporophyte and Gametophyte is very well presented.
The clear delineation of these two stages in plant life cycles is beneficial for students of biology.
The decline in Gametophytes due to changes in plant life presents an important perspective on plant biology.
The evolutionary aspects of plant life cycles are clearly presented.
The impact of environmental changes is evident through this discussion.
The comparison table provides a very comprehensive overview of the differences between Sporophyte and Gametophyte.
The complexity of the life cycle of plants is fascinating.
The table is a helpful way to simplify and understand the content.
The difference in the method of reproduction between these two generations is a fundamental concept.
The relevance of asexual and sexual reproduction in the plant life cycle is well emphasized.
The understanding of these concepts is essential in biological studies.