The scientific world and its inventions have made a great impact and difference in many fields, creating feasibility in study, analysis and management.
Before certain inventions were made, people used to make rough decisions and predictions using traditional methodologies about certain things and lacked perfection in their results. Two of such great inventions to measure atmospheric pressure are 1. Barometers, and 2. Manometers.
Key Takeaways
- Barometers measure atmospheric pressure, while manometers measure the pressure of gases or liquids in closed systems.
- Barometers are used to forecast weather conditions, while manometers are used to measure pressure in pipes, tanks, and other closed systems.
- Barometers can be mercury-based or aneroid, while manometers can be open-tube, closed-tube, or differential.
Barometers vs Manometers
A manometer is an instrument used to measure the pressure of gases and liquids. It consists of a U-shaped tube partially filled with a liquid, such as mercury or water. A barometer is an instrument used to measure atmospheric pressure. It consists of a glass tube filled with mercury or other liquid.

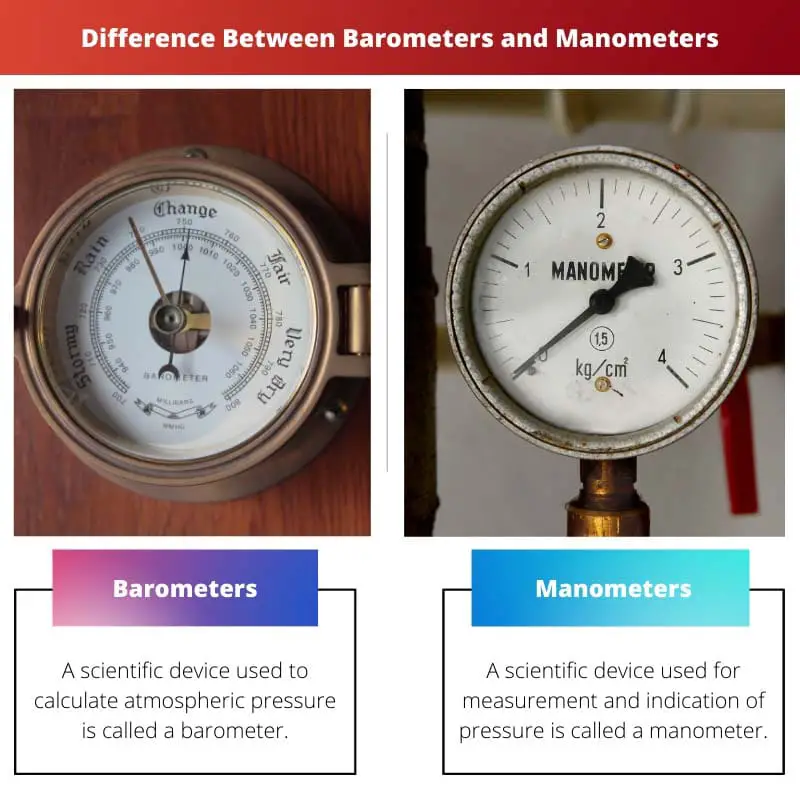
A scientific device used to calculate atmospheric pressure is called a barometer. Barometers measure the minor fluctuations in pressure caused by weather and its different elements.
A scientific device used to measure and indicate pressure is called a manometer. It is used not only to measure air pressure but also to measure other pressures that are lower than the air pressure.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Barometers | Manometers |
|---|---|---|
| Invented in/on | 1643 | 1661 |
| Inventors | Evangelista Torricelli | Otto von Guericke |
| Subtypes | Water barometers, Mercury barometers, Fitzroy barometers, Fortin barometers, Sympiesometers, Wheel barometers, Vacuum Pump Oil barometers, Aneroid barometers, MEMS barometers. | U-tube manometers, Differential U-tube manometers, Inverted U-tube manometers, Micro manometers, Inclined manometers, Ring-Balance manometers, Digital manometers, Analog manometers. |
| Uses | Measurement of atmospheric pressure, Whether forecasting, Used in scuba diving to keep track of the diver’s air tank, In smartphone’s fitness applications, or In smartphone’s GPS chip for faster locks and delivery of altitude data. | Measurements of smaller or larger pressure differences, Monitoring of gas pressure in water pipelines, and Measurement of water pressure, Mercury Absolute manometers are used for various purposes in power plants and research laboratories. |
| Advantages | High density, low vapour pressure, moderate evaporation rate, Non-sticky, Opaque surface. | Less maintenance, Fewer costs, Feasible manufacturing, Excellent accuracy and sensitivity. |
| Disadvantages | Some types of barometers are easy to transport while others are not, with High chances of liquid contamination. | Large in size and bulky, it requires levelling; condensation introduces errors and Poor dynamic performance. |
What are Barometers?
A scientific device used to calculate atmospheric pressure is called a barometer. In the year 1643, Evangelista Torricelli invented the first barometer.
The Measurement of atmospheric pressure by a barometer is called barometric pressure. The equation by which we can find the barometric pressure is “Patm= ρgh”.
Several other applications of a barometer and its subtypes include, Measurement of atmospheric pressure, Weather forecasting, Used in scuba diving to keep track of the diver’s air tank.
There are several types of barometers classified on parameters, like the material used to make them and their methods for measurements-for, for example, Water barometers, Mercury barometers, Fitzroy barometers, Fortin barometers, Sympiesometers, and Wheel barometers.
Barometers have their disadvantages and advantages. Its advantages include high density, low vapour pressure, moderate rate of evaporation, and non-sticky, opaque surface. Some of its disadvantages include high chances of contamination of the liquid.

What are Manometers?
A scientific device used to measure and indicate pressure is called a manometer. It is used not only to measure air pressure but also to measure other pressures that are lower than the air pressure.
Light oils, water and mercury, are some of the liquids used in a manometer for measurement. A manometer is also used to measure smaller or larger pressure differences.
It has several other subtypes, which include U-tube manometers, Differential U-tube manometers, Inverted U-tube manometers, Micro manometers, Inclined manometers, Ring-Balance manometers, Digital manometers, and Analog manometers. These several types have several applications and have their independent properties and constructions.
Several manometer applications include measuring smaller or larger pressure differences, Monitoring gas pressure in water pipelines, and Measuring water pressure.
Some of its advantages include less maintenance, fewer costs, feasible manufacturing, excellent accuracy and sensitivity. Some disadvantages include being large in size and bulky, requiring levelling, condensation introducing errors, and poor dynamic performance.

Main Differences Between Barometers and Manometers
- The design and functionality of barometers are rather limited than the design and functions of manometers.
- Manometers have both open outlets. On the other hand, barometers have one closed outlet, which has a vacuum.
- https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=gohJZ5GlCOwC&oi=fnd&pg=PA1&dq=manometers&ots=92r3wYfsXx&sig=x1yUot31rTZ9efE-8u1hHQ_Fshs
- https://academic.oup.com/gji/article-abstract/48/3/281/615208

The article explains the differences between barometers and manometers with precision and clarity. The comparison table provides a comprehensive overview of their details and uses.
It’s fascinating to learn about the historical background and technological advancements of these scientific instruments in such a well-structured manner.
The article is a testament to the depth of knowledge about these instruments. The advantages and disadvantages section offers a balanced view of their functionalities.
The comprehensive comparison and detailed explanation of barometers and manometers in the article provide valuable scientific knowledge and insights.
The in-depth analysis of barometers and manometers showcases the depth of scientific understanding presented in the article.
The article’s thoroughness in discussing the differences and functionalities of these scientific instruments is truly impressive.
The article eloquently discusses the applications and distinguishing features of barometers and manometers. It’s a commendable piece of scientific literature.
Absolutely! The article presents a comprehensive view of the two scientific instruments with a high degree of accuracy and attention to detail.
The detailed analysis of barometers and manometers in this article is quite impressive. It’s interesting to learn about their various subtypes and applications.
The article delves deep into the functionalities and uses of barometers and manometers. The advantages and disadvantages section provides a balanced perspective on these instruments.
The article offers an intellectual discourse on barometers and manometers, bringing attention to their significance and applications in various fields.
I appreciate the level of detail in the article. The analysis of both instruments offers valuable insights into their respective capabilities and limitations.
The article provides valuable insights into the world of scientific instruments. The detailed comparison between the two inventions and their applications is enlightening.
The detailed comparison and thorough explanations provided in the article have made it clear that the two inventions are crucial for measuring atmospheric pressure and pressure in closed systems. The applications and subtypes of both instruments are intriguing.
I completely agree! The scientific information presented in the article does an excellent job at making the complex concepts easy to understand.
I’m impressed with the depth of knowledge. The historical context of the invention and the comprehensive descriptions of applications are very informative.
The informative content of the article sheds light on the significant differences between barometers and manometers. The comparison table sums up the key aspects effectively.
The article provides an insightful discussion about these instruments, making it intellectually stimulating and educational.
The detailed descriptions and thorough comparisons enhance the understanding of barometers and manometers, making the article a valuable source of knowledge.
The article skillfully presents the key differences and applications of barometers and manometers. It’s a commendable work of scientific literature.
The insightful comparisons and detailed analysis of both instruments contribute to a deeper understanding of their roles in scientific measurements.
The article provides an informative and engaging discussion about barometers and manometers. The clear explanation of their uses and differences is commendable.
I’m glad the article touches upon various aspects of these scientific devices. The details about the applications and subtypes are elucidating.
The in-depth analysis of barometers and manometers offers a great understanding of these instruments. The information is both enlightening and engaging.