The world is digitally revolutionized, and the data is exponentially growing. There are various models, tools, and software that work behind every click.
The two main terms with distinguishing mechanisms related to data processing, transfer, and operational performance are big data and cloud computing.
Key Takeaways
- Big data refers to large and complex data sets, while cloud computing uses remote servers to store, manage, and process data.
- Big data is used to extract insights and make informed decisions, while cloud computing provides on-demand access to computing resources.
- Big data requires specialized tools for processing and analysis, while cloud computing offers scalability and cost-effectiveness.
Big Data vs Cloud Computing
The former refers to the data which is huge in size and increased rapidly over time, while the latter refers to the on-demand availability of computing resources over the internet. The former refers to a huge volume of data and management, while the latter refers to remote IT resources and different internet service models.

Big data is used in social media data, e-commerce platforms and businesses, weather determination, IoT sensors, and other fields. Big data provides platform centralization and backup provision with an easy maintenance price.
While cloud computing is used by services like Amazon Web Service (AWS), Microsoft, Google Cloud, Azure, IBM Cloud, and many other computing vendors.
The services of cloud computing are scalable and affordable and use the internet to run.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Big data | Cloud computing |
|---|---|---|
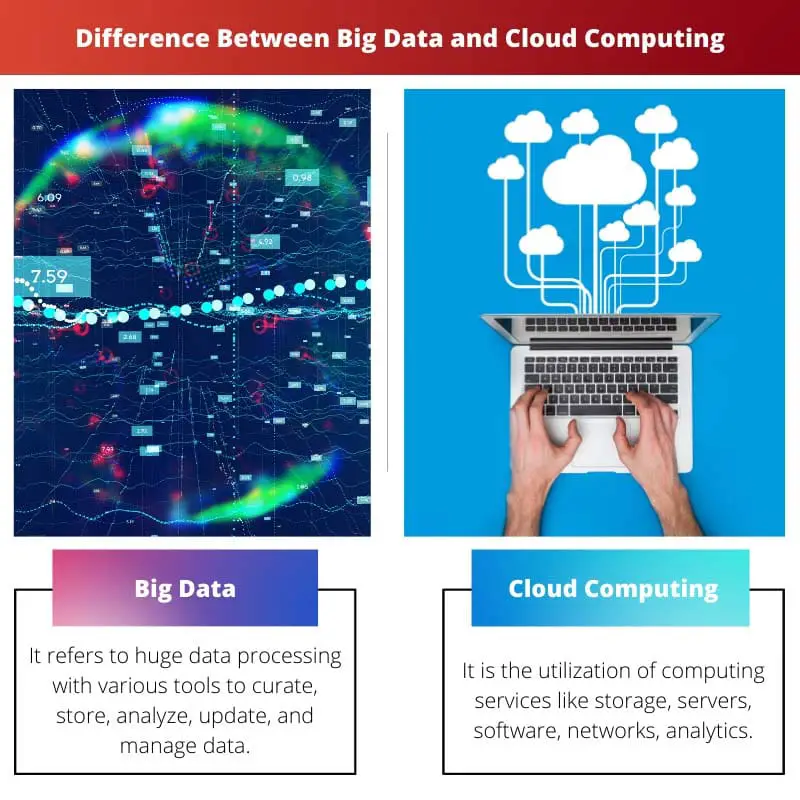
| Definition | It refers to huge data processing with various tools to curate, store, analyze, update, and manage data | It is the utilization of computing services like storage, servers, software, networks, analytics |
| Types | Three main types – structured data unstructured data and semi-structured data | Four main types – IaaS (Infrastructure as a service), PaaS (Platform as a service), SaaS (Software as a service), and Serverless |
| Function | Cost reduction, time reduction, huge data storage, innovative product development, and efficient decision making | It offers innovation, scalable economies, and flexible resources. It runs the infrastructure more efficiently and effectively |
| Characteristics | Volume, variety, velocity, veracity, value, and variability | Agility, cost reduction, device and location independence, easy maintenance, multitenancy, increased productivity, and security |
| Application | Areas like governmental processes, medical or healthcare, sports, economic productivity, crime and security, research and development, resource management, Internet of Things, education and the media industry | Sending mails, watching movies or TV, social media platforms, listening to music, healthcare services, IT services, businesses, and many other spheres |
What is Big Data?
Big data extracts, analyses, and treats large and complex data sets. In the field of big data, there are various tools to capture, curate, store, analyze, share, update, arrange and manage data.
It is also used to determine predictive analysis and user behaviour analytics. Big data has evolved from the primary concepts of volume, variety, and velocity.
Big data was popularized by John Mashey in the 1990s. Big data provides exceptional high capacity for data within a bound time and value frame.
Big data is effective for unstructured data. With the huge data generation, the global data volume is expected to reach 165 zettabytes by 2025.
According to Kryder’s Law, big data continuously evolves. The government of China, India, Israel, the United Kingdom, and the United States have actively incorporated big data to carry out various services.
Big data has also brought about innovations like Square Kilometer Away, which can gather and store 1 petabyte per day.
Big data has applications in various domains like businesses, medical and health care with computer-aided diagnosis, governmental processes, geographic information, environmental research,
crime and security, genomics, connectomics, internet searches, education, the media industry, and many other areas. Big data has grown its roots in several fields.

What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the utilization of computing services like storage, servers, processors, software, networks, analytics, and others. It enables automation and does not need individual addresses or users.
It provides agility to organizations, flexibility to the resources, and brings a reduction in costs of the existing infrastructure.
Cloud computing was introduced by Compaq in 1996. It was first referred to by the CEO of Google on 9th August 2006.
In 1977, the cloud was a term used to refer to the internet. Cloud environment gained popularity due to its easy maintenance as the server did not require centre hardware.
There are mainly three types of cloud computing – public cloud, private cloud, and hybrid cloud. Cloud computing services are of four major types – IaaS (Infrastructure as a service),
PaaS (Platform as a service), SaaS (Software as a service), and Serverless.
They are also referred to as computing stacks as they are placed one above another.
The cloud-based applications have an internet-run program, processing code, and the processes are executed in the cloud.
Cloud computing is the backbone of major online services like sending emails, editing documents, watching movies, playing games, or listening to music.
Organizations, whether startups or global level, governmental or non-profit agencies, have cloud computing incorporated in every online sphere.
Main Differences Between Big Data and Cloud Computing
- Big data includes data which is large in volume and has an exponential increase, while cloud computing involves the availability of computing resources over the internet services.
- Big data has five main characteristics that are variety, volume, veracity, velocity, and value, while the main characteristics of cloud computing are the availability of resources, cost reduction, increase in productivity, and security.
- Big data is of broadly three types – structured data, unstructured data and semi-structured data while cloud computing is of broadly four types – IaaS (Infrastructure as a service), PaaS (Platform as a service), SaaS (Software as a service), and Serverless.
- The purpose of big data is to extract, process, and organize huge data while cloud computing aims at storing and processing data in the cloud without physical intervention in IT services.
- Challenges of big data are data storage, integration, processing, and resource management, while cloud computing limits availability, security, and transformation of the charging model.
- https://dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.14778/1920841.1921063
- https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/17538947.2016.1239771