When we harm ourselves and bleed, or, to put it another way, whenever our capillaries are injured, our bodies have their own way of fighting, which is blood clotting or coagulation.
A tissue is an agglomeration or cluster of cells that work together to accomplish a certain purpose.
Since tissue is a group of cells, therefore the obvious fact is that organism is multicellular. Tissues are made up of different types of cells that enable the group of tissue to perform a particular function.
Key Takeaways
- Blood clots are solid masses formed by coagulating blood components, while tissues are collections of similar cells that perform a specific function in the body.
- Blood clots prevent excessive bleeding and support wound healing, while tissues contribute to the structure and function of organs and organ systems.
- Blood clots can become dangerous if they dislodge and travel through the bloodstream, potentially causing blockages; tissues do not pose such risks.
Blood Clot vs Tissue
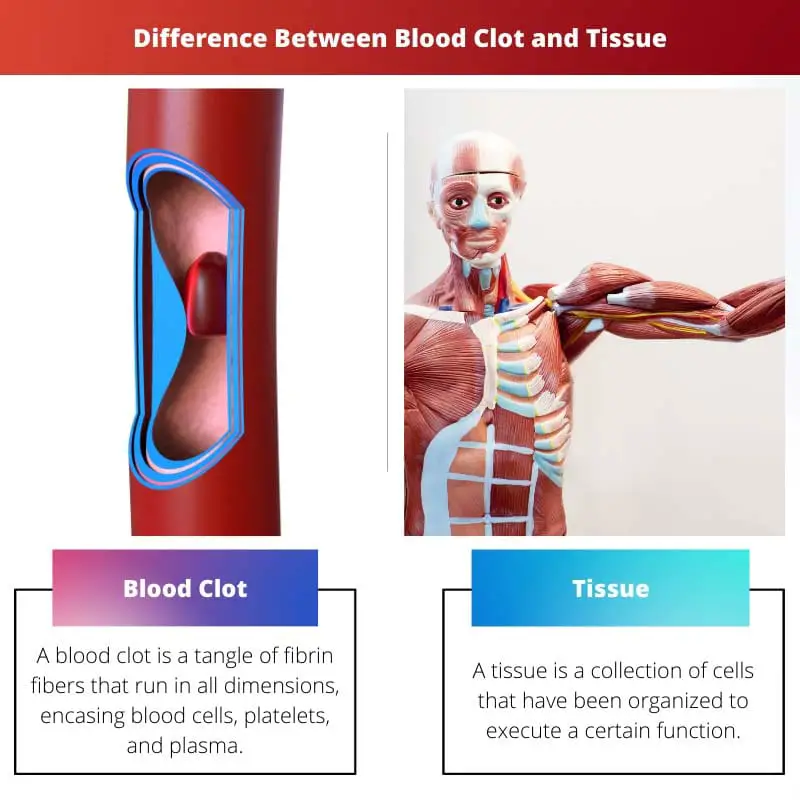
A blood clot is a clump that forms in your veins or arteries when blood hardens from a liquid to a semisolid or a gel-like state. A tissue is a group of cells of similar structure that function as a unit to perform a specific task. Different tissues get together to form an organ.
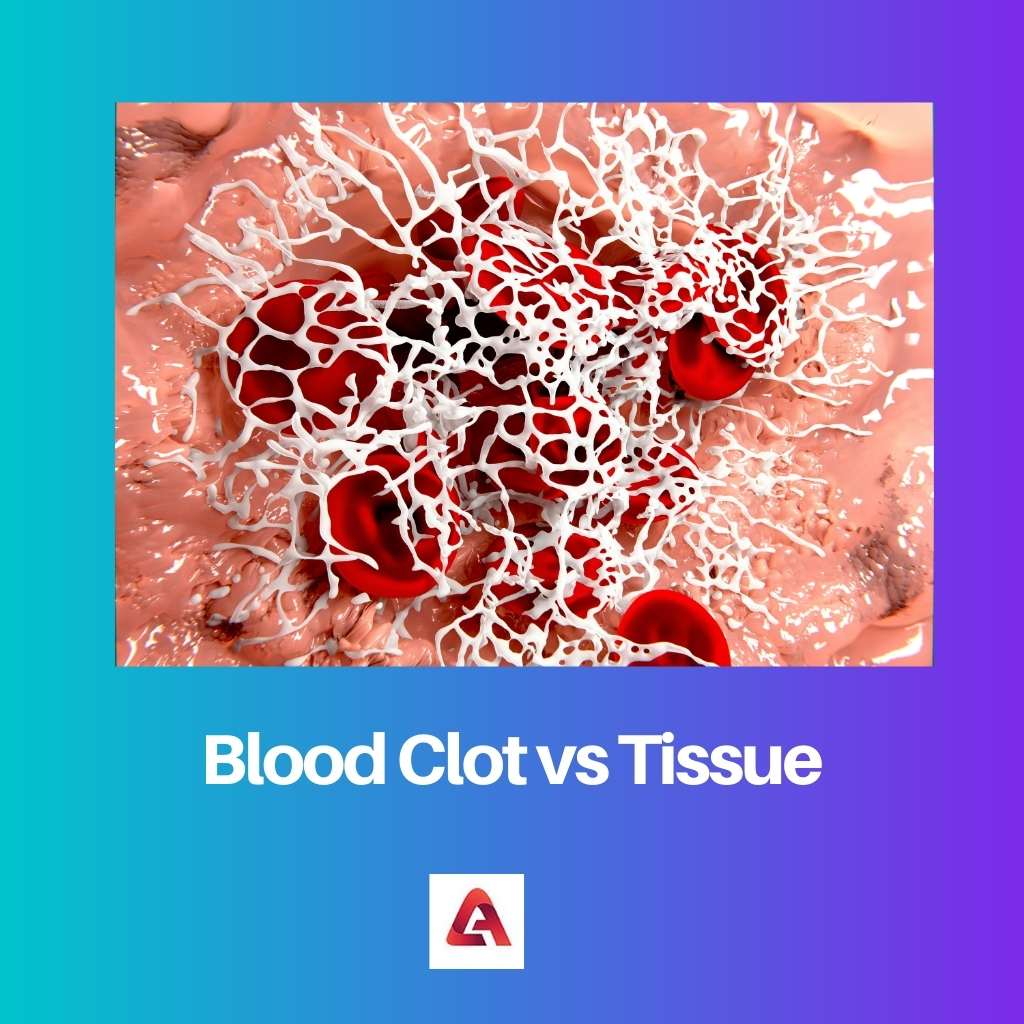
A blood clot is a web of fibrin fibers that encircles blood cells, platelets, and plasma in all ways. Blood clots are a defensive mechanism that the body uses to prevent blood loss when a blood vessel ruptures.
They are also used when the blood itself is affected by harmful chemicals.
A tissue is a collection of cells that have been organized to execute a certain function. An organ is made up of several tissues that combine to form a whole.
The cells that make up particular tissues have developed special adaptations to help them work efficiently and retain the integrity of the structure and operational characteristics. Tissue functions differ from one kind to the next.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Blood Clot | Tissue |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A blood clot is a tangle of fibrin fibers that run in all dimensions, encasing blood cells, platelets, and plasma. | A tissue is a collection of cells that have been organized to execute a certain function. An organ is made up of several tissues that come together to form a whole. |
| Composition | A blood clot is made up of fibrin fibers which form a network-like structure around the wound. | Tissues are primarily the collection or cluster of cells. |
| Occurrence | Blood clots are only restricted to multicellular animals. | Tissues are found in both plants and multicellular animals. |
| Category | Blood clots do not have any categories and types. | There are four major types of tissues which are namely epithelial, connective, muscular, and nervous tissue and each one of them has its own important roles. |
| State | Blood clots are found in the jelly-like state. | Tissues may be liquid which is the case for blood or solid in the case of muscle tissue depending upon their function. |
What is Blood Clot?
Whenever a blood vessel is damaged, a mechanism known as the extrinsic route is stimulated. When a blood vessel is damaged, the intrinsic route is initiated.
Both of these mechanisms are chemical cascades that lead to the formation of a prothrombin initiator. Through a series of processes, the prothrombin activator converts fibrinogen to fibrin.
Blood clots do not form in the circulatory system under normal circumstances because there are a few counter processes in place to prevent blood from clotting unnecessarily.
The blood clot will dissolve on its own once normality is restored. Although at times it can also be seen that clots may have been formed and that too does not naturally dissolve and that can be a subject of great concern and can cause a serious hazard to health.
Blood vessels are categorized into two kinds: arteries and veins. In both cases, a clot can develop. These two types of vessels carry blood into and out of the body.
First and foremost, arteries carry oxygenated blood from the heart to the rest of the body.
The artery that distributes blood out of the heart to the remainder of the body is known as the dorsal aorta. Veins are blood channels that transport deoxygenated blood from the body to the heart for oxygenation.
A clot in a vein can prevent blood from flowing from that organ of the body to the heart, causing it to become brownish blue and cause discomfort.
That clot may separate from its origin and spread to other places of the body. If it restricts blood supply to the heart in any manner, it will endanger life.
What is Tissue?
A tissue is a grouping or cluster of cells that collaborate to achieve a specific goal. Because tissue is a collection of cells, it is self-evident that the creature is multicellular.
Tissues are composed of various cell types that allow a collection of tissues to execute a certain job.
Epithelial tissue, when it pertains to identifying the tissues because of their critical role, epithelial tissue stands at the forefront. It is the covering layer, also called the epidermal layer, which coats our skin.
It forms the skinny layer of our internal organ, also called the mucus layer. Since they are the first coating on our organs, they help to fight any immediate pathogen or foreign invasion.
Connective tissue, elastic fibers, collagen, and the ground substance, which is the other name of the matrix, are the crucial parts of connective tissue.
Although a lesser number of cells are found in the connective tissue, they are found in the outer matrix of the cell. The cells in connective tissue are relatively separated from each other except in adipose tissue.
The connective tissue also performs some of the very important functions, needless to mention is the blood and lymph without which our existence is a question. The skin, which on stretching restores itself, is only due to the fat or adipose tissue, which again is connective tissue.
To mention its other function, we can certainly recall how we are able to walk or move our hands and legs. It is due to tendons and ligaments, which again are connective tissue.

Main Differences Between Blood Clot and Tissue
- A blood clot is a protective measure that occurs in animals to keep them from bleeding to death, whereas tissue is something quite different. It is a group of cells that later form different organs of our body and perform certain functions.
- A blood clot is made up of fibrin fibers which form a network-like structure around the wound, whereas tissues are aggregates of cells.
- Blood clots are only restricted to multicellular animals. On the other hand, tissues are found in both plants and multicellular animals.
- There are four major types of tissues which are namely epithelial, connective, muscular, and nervous tissue, and each one of them has its own important roles, but as such, blood clots do not have any categories and types.
- Blood clots are found in the jelly-like state, whereas tissues may be liquid which is the case for blood, or solid in the case of muscle tissue, depending upon their function.
- https://www.annualreviews.org/doi/abs/10.1146/annurev-fluid-010814-014513
- https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Valery-Tuchin/publication/248103870_Tissue_Optics_Light_Scattering_Methods_and_Instruments_for_Medial_Diagnosis/links/5425c74b0cf2e4ce9406f647/Tissue-Optics-Light-Scattering-Methods-and-Instruments-for-Medial-Diagnosis.pdf

I found the explanation on the formation and dissolution of blood clots to be particularly informative. It clears up many misconceptions people might have about blood clots.
Blood clots and tissues are incredibly complex structures that play crucial roles in our bodies. The detailed explanation in this article really highlights the importance of these biological processes.
I wish the article had included more about the different types of tissues and their specific functions. This would provide a more comprehensive understanding of tissues.
The intricate details outlined in this article make it an excellent resource for anyone interested in gaining a deeper understanding of blood clots and tissues.
The way the article explains the occurrence of blood clots and the different functions of tissues is truly fascinating. It highlights the complexity of the human body.
This article does a great job at explaining the distinctions between blood clots and tissues. The key takeaways and comparison table really help to solidify the differences.