Capacitors and Resistors are two critical passive components of an electric circuit. Both play different roles in determining how the circuit behaves and are connected through conductive wires through which electricity pass.
Key Takeaways
- A capacitor is an electronic component that stores and releases electrical energy, characterized by its ability to pass alternating current (AC) signals while blocking direct current (DC) signals.
- A resistor is an electronic component that opposes the flow of electric current, helping to control voltage and current levels in a circuit.
- Both capacitors and resistors are fundamental components in electronic circuits, but they perform different functions, with capacitors managing energy storage and resistors controlling current flow.
Capacitor vs Resistor
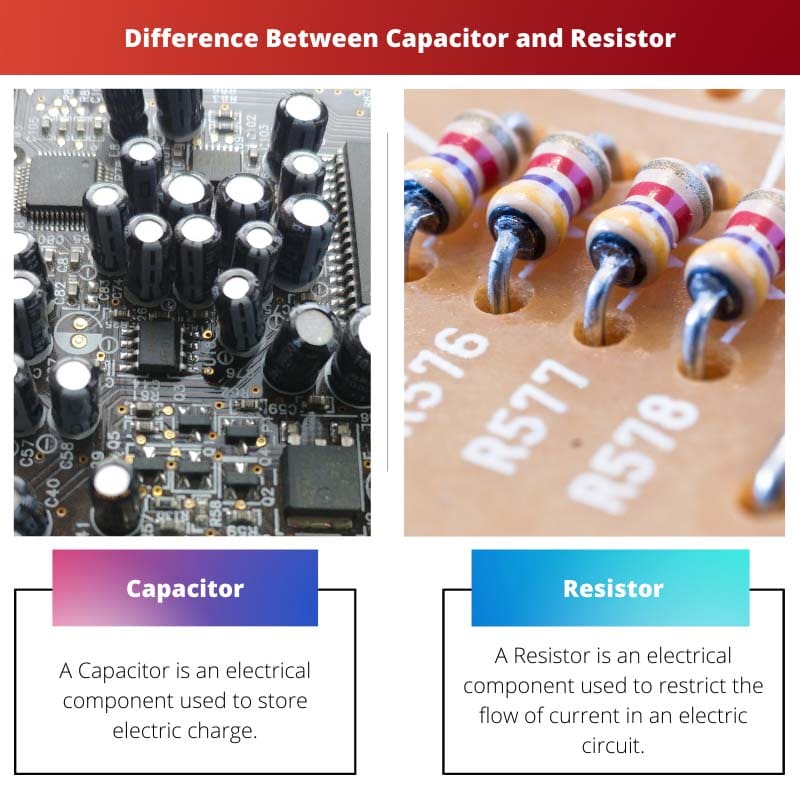
Capacitor is an electronic device used to store electrical energy in the form of charges, a resistor is an electronic device used to resist or block the current flow in a circuit. The capacitors can store an electrical account for a short period while the resistors block the wind in a course.

When a capacitor is connected to a circuit, DC Circuit can’t flow through the course because of its insulating layer and is stored in the form of charge across the conductive wires.
On the other hand, when a Resistor is connected to a circuit, it absorbs the electric current and dissipates the energy in the form of heat.
Comparison Table
| Parameter of Comparison | Capacitor | Resistor |
|---|---|---|
| What? | A Capacitor is an electrical component used to store electric charge. | A Resistor is an electrical component that restricts the current flow in an electric circuit. It creates friction like a force that blocks the current. |
| Effect on Circuit | A capacitor stores electrical energy through charges across the conductive plate when added. | When added, a Resistor absorbs electrical energy and dissipates it as heat. |
| Use | Capacitors are used for filtering, smoothening, coupling different sections of the circuit, and limiting high voltage transient across the circuit. | Resistors reduce current flow, divide voltages, terminate transmission lines, and adjust the signal level. |
| Power loss | Capacitor does not make any electrical power loss. | The resistor creates power loss and creates heat. |
| Dependence on Frequency | The opposition to the flow of current depends on the applied frequency. | The opposition to the current flow does not depend on the applied frequency. |
| Units | Capacitance is measured in farad. | Resistance is measured in ohm. |
| Formula | C=Q/V | R=V/I |
| Scope | It can block only DC Current. | It can block both DC and AC Currents. |
What is Capacitor?
A capacitor is a passive component of an electric circuit that can store energy in the form of an electrical charge producing potential differences across its plate.
Many varied sizes of capacitors are available, from tiny ones used in resonance circuits to large capacitors used in power factor correction.
It consists of two (or more) parallel metal plates which do not touch each other but are electrically spaced separately (by air or by some other good like mica, plastic, etc.). This insulating layer between conductive plates is called a Dielectric.
Because of an insulating layer, DC current cannot flow through the capacitor; instead, a voltage is developed around the plates in the form of an electric charge.
On the other hand, when capacitors are connected to the AC circuit, the current passes through the capacitor with little resistance.
It makes the electric charge by making use of external voltage. Therefore, it only stores electrons to store energy and emits the charges later whenever required.
A capacitor can be classified as Fixed Capacitors, whose capacitance shows a fixed value and does not adjust behaviour and Variable Capacitor. Such Capacitors offer adjustable behaviour to circuit operations.
The formula to find capacitance is C=Q/V. Capacitance (in farad) equals Charge (in coulomb) divided by Voltage (in volts).
What is Resistor?
A Resistor is another basic component of the electrical circuit. It restricts and blocks the flow of electric current through a circuit. The energy measures the Resistance of a Resistor. It can dissipate in the electric circuit.
It contributes to limiting the capacitor’s charging rate, adjusting the RF circuits’ frequency response, and acting as a voltage divider for the circuit.
When a resistor is connected to a circuit, it controls the flow of charge by absorbing the electrical amount and dissipating it in heat.
Two basic measurements related to resistors are resistance (measured in ohm) and power to dissipate energy (measured in watts).
A Resistor can be classified as a Fixed Resistor, in which the value of resistance is fixed and a Variable Resistor, which offers adjustable resistance when connected to any circuit.
The formula to calculate resistance is R=V/I. Resistance (in ohms) equals Voltage (in volts) divided by Current (in amperes).

Main Differences Between Capacitor and Resistor
- A capacitor is an electronic component that stores electric energy in charge. At the same time, the Resistor is an electronic component that limits or regulates or blocks current in the circuit.
- A capacitor is used to keep the positive and negative charges separate, while the Resistor is used to control the flow of current to other components of the circuit.
- A capacitor stores the electrical current as charges across the conductive wires while the Resistor absorbs electrical energy and dissipates it in heat.
- A capacitor does not lead to any power loss, while Resistor does.
- Capacitance is measured in farads by dividing charge by the voltage, while Resistance is measured in ohm by dividing voltage by the current. lewd
- https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/1355709/
- https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/4768889/

I found the article to be very well-written and informative. The explanations provided are clear and concise, making it easy to understand the functions and differences between capacitors and resistors.
I absolutely agree. The author has done an excellent job of breaking down complex concepts into simple and understandable information.
This article has certainly enriched my knowledge about capacitors and resistors. The comparisons and explanations were enlightening and have broadened my understanding.
The article has effectively demystified the functions of capacitors and resistors. It’s an impressive piece of work that delivers valuable insights into these components.
I’d have to agree. The article’s detailed approach provides a clear understanding of capacitors and resistors, making it a great read.
Indeed. The author has done a remarkable job in presenting the information in an accessible and engaging manner.
The detailed comparisons between capacitors and resistors make it easier to grasp the concepts behind these components. This article has added greatly to my current understanding. Well written and very informative!
Yes, the article is very detailed and comprehensive. It’s definitely a great resource for those looking to learn more about capacitors and resistors.
The article has done a great job in shedding light on the functionality and differences between capacitors and resistors. It’s very informative and well-explained.
I couldn’t agree more. The breakdown of information makes it easier to comprehend and appreciate the roles these components play in circuits.
The article provides a comprehensive analysis of capacitors and resistors, covering all necessary aspects in an easily understandable manner. Very well-written!
It certainly does. The level of detail and clarity in the explanations make it an excellent resource for anyone interested in capacitors and resistors.
The article is a great resource for anyone seeking to understand capacitors and resistors better. It covers the fundamental concepts in a very comprehensive manner. Well done!
Absolutely. The level of detail and clarity makes this article an invaluable source of information on capacitors and resistors.
Good content, loved the detailed comparisons and the explanations. Highly educational and insightful!
The article provides a clear and accurate explanation of the differences between capacitors and resistors and how they work. It has also been explained effectively using the comparison table and the formulas. This was very informative and helped me understand these components better.
I couldn’t agree more. The level of detail and clarity in the explanation is top-notch! Very well done.
I found the information provided to be insightful and very well-structured. It has given me a broader understanding of how capacitors and resistors function.
The article is well-structured and provides a deep understanding of the differences between capacitors and resistors. It has certainly broadened my knowledge about these electronic components.
I agree. The article has succeeded in making complex concepts more approachable and understandable. An excellent piece of work.
The comparison table and detailed explanations were extremely helpful in grasping the concepts. Great job!
I found the article to be extremely informative, and the explanations were presented very effectively. It has certainly given me a deeper understanding of capacitors and resistors.
I completely agree. The clear and concise breakdown of information in the article is highly commendable.
The comparisons and detailed explanations in the article have certainly contributed significantly to my understanding of capacitors and resistors. Well done!