A dielectric is a substance that doesn’t even allow electricity to pass, whereas a capacitor is an electronic appliance that retains electrical charges.
Because dielectrics are the polar opposite of conducting elements, they are referred to as barriers or insulators.
Apart from the basic difference, this article highlights every small difference that is there between a dielectric and a capacitor.
This article will help you understand each of the terms with distinct definitions and a comparison table too.
Key Takeaways
- A dielectric is an insulating material that resists the flow of electric current, while a capacitor is an electronic component that stores and releases electrical energy.
- Dielectric materials are essential for capacitors, as they separate the conductive plates, allowing energy storage.
- Capacitors come in various types and sizes, with different dielectric materials influencing their performance and applications.
Dielectric vs Capacitor
The difference between a dielectric and a capacitor is that a dielectric is highly resistant to electrical charges and is a very strong insulating object that is used for the layering of the outer surface of a capacitor, whereas a capacitor is a two-way conducting element that is widely used in electrical circuits. A capacitor is used for storing electrical energy in a circuit.

A substance that is dielectric when it is good in shielding or a poor carrier of electric charge.
When dielectrics are exposed to an electromagnetic current, they produce almost no current since, unlike metals and some alloys, they do not contain any loosely tied or free ions that may travel through the substance.
Electric polarisation, on the other hand, happens. Positive changes in the dielectric are pushed minimally in the direction of the applied field, whereas negative charges are transferred fractionally in a reverse way.
A capacitor is an electronic component for storing electricity that consists of two conductive materials in close vicinity. The concurrent capacitor is a small analogy of such a storage medium used in a circuit.
The capacitor does indeed have a charge Q if positive ions with an overall charge of +Q are loaded on one of the wires and an equal incidence of adverse charge -Q is placed on the other conductor.
Capacitors are useful in a variety of situations. They’re employed in electronic systems, for example, to ensure that data saved in huge computer memory isn’t lost in the event of a power outage.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Dielectric | Capacitor |
|---|---|---|
| Meaning | A dielectric insulation substance conducts electric charge poorly yet supports electromagnetic fields well. | A capacitor is a multiple-way electrical component that consists of a dielectric insulator between two conductive substances. |
| Electrical Charge Affinity | It is electrically insulated and is a weak conductor of electric current. | It is a good conductor and helps in storing electricity. |
| Property | Ability to withstand strong electric current and heat too. | To enhance the attribute of capacitance and store energy. |
| Used in | It is mainly used in fabricating capacitors. | Used in electronic appliances and inverters. |
| Cost | A dielectric is very cheap in cost when compared to a capacitor. | A capacitor is significantly costlier when compared to a dielectric material. |
What is Dielectric?
A dielectric insulation substance conducts electric charge poorly yet supports electromagnetic fields well.
It’s a medium or material that can endure high electric strain without causing significant conductivity.
When strain is increased, the dielectric stores energy in the form of an electric charge. When the tension is eliminated, the majority of this energy is maintained.
When a dielectric substance comes into touch with an electromagnetic current, it gets polarised and becomes more or less conducting.
A dielectric, like any substance, is made up of ions with opposite charges that equilibrium to maintain electroneutrality.
Positive charges are shifted in the presence of an electric field by dielectric loss, whereas negative charges shift in a reverse way.
Other electromagnetic phenomena are associated with the presence of dielectric substances.
In a dielectric medium, the interaction energy electrostatic force is less than in an atmosphere, but the energy contained in an electric field for every unit volume of dielectric material is larger.
The atoms are polarised, indicating they have a positively charged pole and a negative polarity that is aligned with the field direction since the following condition forces the electrons in each element to concentrate on one edge of the nuclei.
When a high enough electrostatic attraction is given to a dielectric, however, the forces that desire to drive the electrons can potentially defeat the force that shackles them to the elementary particle, ie.
The nuclei of an atom cause the electron particles to be ripped free.
What is Capacitor?
A capacitor is a multiple-way electrical component that consists of a dielectric insulator between two conductive substances.
It’s among the most basic passive components, capable of storing the application of an electric or an electromagnetic field.
It is their ability to store electrical power that distinguishes them. A capacitor is one of the three essential components of an electrical circuit, along with resistor and inductive loads.
When power is placed across it, it retains and releases the electrical charges as needed.
Capacitors are commonly found on elevated circuitry, but engineers are unaware of their electronic resistivity.
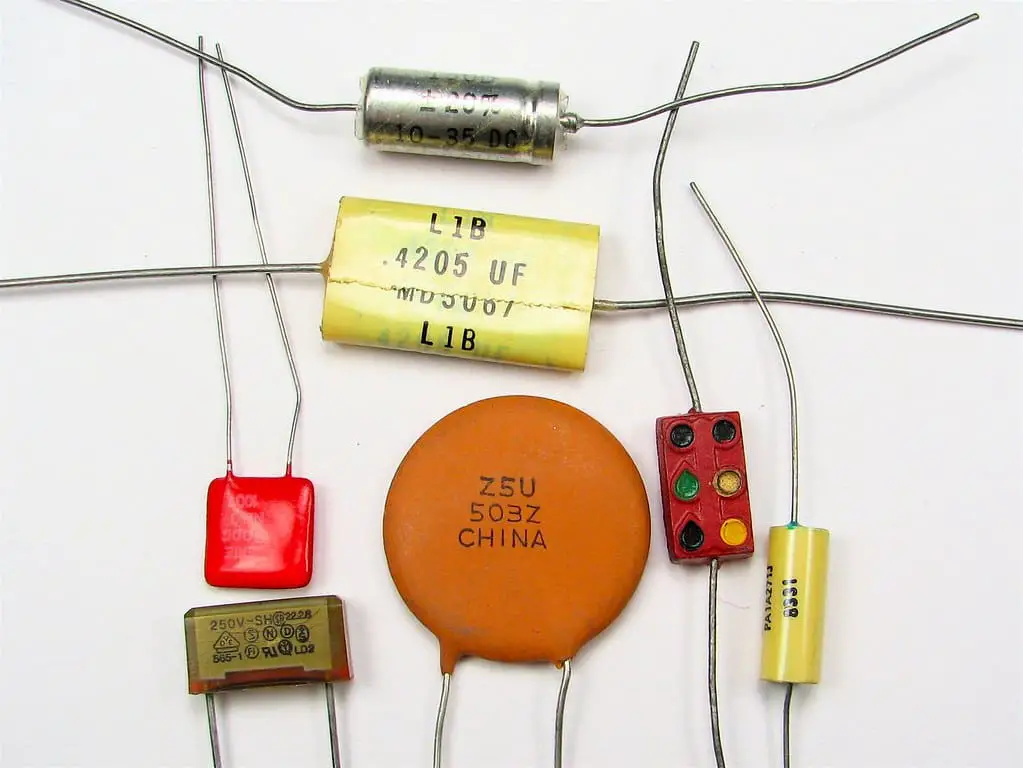
Capacitors come in a variety of sizes and shapes, but the essential design stays the same: two components that are good conductors transport equal but opposite charges.
Variable gas, sheet, mica, ceramic, polymer, tin oxide, and electrolytic capacitors are the most common dielectric materials used in capacitors.
Capacitors are even more vital as filters, diverting stray electric impulses and preventing damage to delicate electronics from electric surges.
Most power systems employ capacitors to store electrical power and then return it to the network when needed. A capacitor’s principal function is to store energy in basic words.
Capacitors come in various shapes and sizes, and they may be employed to perform various tasks in different electrical circuits.
Main Differences Between Dielectric and Capacitor
- The primary function of a dielectric is to resist electric charge, whereas the primary function of a capacitor is to store electricity.
- Dielectric is cheaper and easily available, whereas a capacitor is very costly, yet it is used in major electronic appliances.
- Every dielectric component is used in a capacitor, but not every capacitor is a dielectric component.
- A dielectric is a good insulator, but the capacitor acts as a general conductor with insulated components.
- A dielectric has more resistivity, whereas a capacitor has more conductivity numerical values.


Very informative! I had a vague understanding of these concepts, but this article has really clarified everything. Great job!
The explanation of dielectric and capacitor properties is magnificent. This article is a must-read for enthusiasts and professionals alike.
I completely agree with the level of detail presented here.
Absolutely, I found it extremely beneficial to expand my knowledge.
Excellent article! It provides a clear, comprehensive explanation of the important distinctions between dielectrics and capacitors.
An outstanding comparison of dielectric and capacitor. A highly recommended read for anyone interested in electrical components.
This article is written in an engaging way and excels in delivering a comprehensive understanding of dielectrics and capacitors.
I’m amazed by the detailed information provided here. It’s quite useful for anyone wishing to grasp this subject.
Absolutely, the depth of information is truly commendable.
Yes, I’ve learned a lot from this article. Thanks for sharing!
This is an incredibly well-articulated exposition on the differences between dielectrics and capacitors. It’s been quite enlightening.
Indeed, a thought-provoking piece for anyone interested in electrical engineering.
Absolutely, I agree with the informative depth this article offers.
I find this article to be an incredibly useful resource for understanding the fundamental distinctions between dielectrics and capacitors.