Several types of interactions exist in the environment. As a consequence, it becomes confusing to be able to differentiate between the different concepts in nature.
Magnetism and gravity refer to two such terminologies in everyday use today. There are several differences between the two terminologies.
Key Takeaways
- Magnetism is a force caused by the movement of charged particles, affecting magnetic materials.
- Gravity is a force of attraction between all objects with mass, acting on a larger scale.
- Magnetism can attract or repel, while gravity only attracts.
Magnetism vs Gravity
Magnetism is a fundamental force of nature that arises from the motion of electric charges. Gravity is a fundamental force of nature that causes all objects with mass to be attracted to each other.

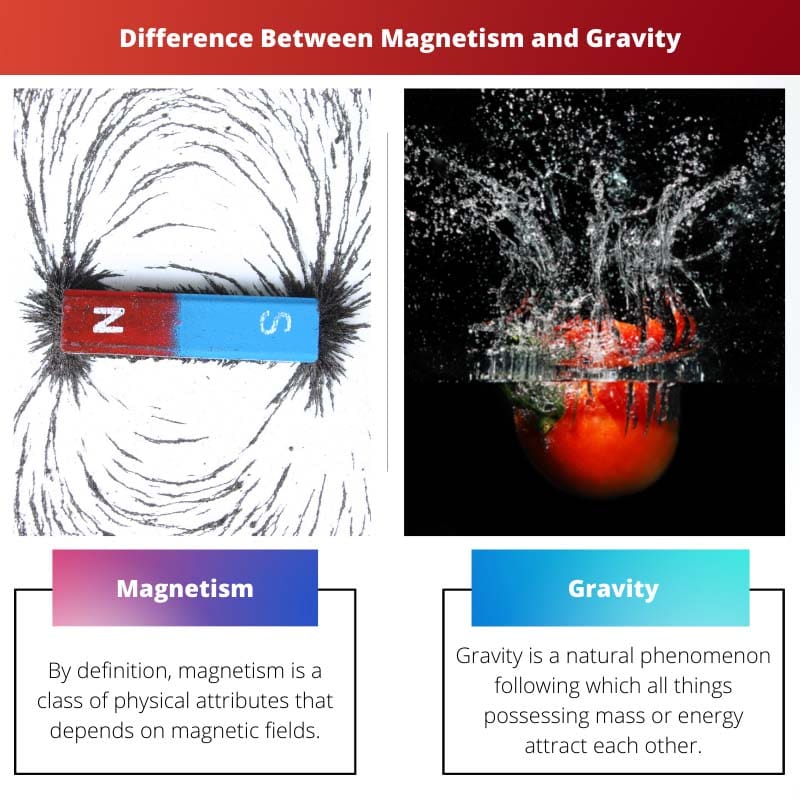
By definition, magnetism is a class of physical attributes that depends on magnetic fields. Electricity and magnetism are interlinked concepts that are an outcome of The Einstein’s Theory of Relativity.
Magnetism and electricity co-exist at most times. The magnetic behaviour of any object is characterised by its structure and temperature.
Gravity is a natural phenomenon following which all things possessing mass or energy attract each other. The basic definition of gravity takes shape from The Theory of Relativity proposed by Einstein.
In addition, the strength of gravitational force equals the acceleration of objects influenced by gravity.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Magnetism | Gravity |
|---|---|---|
| Origin of the Word | The word magnetism is derived from the Latin word magnetismus from the early 17th century. | The word gravity is derived from the Latin word gravitas meaning weight. |
| Applicability | The forces of magnetism do not apply to all objects. | The forces of gravity only follow the principle of attraction. |
| Areas of Operation | Magnetism is largely limited to man-made objects. | Gravity is a concept that has an application for heavenly objects. |
| Dependability | The forces of magnetism depend on the specific characteristics of every object. | The force of gravity acts on any two objects with mass. |
| Cause | Magnetism is an outcome of charged particles or some materials. | Gravity is an outcome of space-time curvature that results from the mass of two objects. |
What is Magnetism?
Magnetism refers to a class of physical attributes determined by magnetic fields. A magnetic field originates as a result of electric currents and the magnetic motion of elementary particles.
One of the most common items displaying magnetism is ferromagnetic materials. Just like a magnet is magnetised, it is also possible to demagnetize it.
Examples of ferromagnetic items are iron, nickel, and cobalt. Some less-known examples of ferromagnetism include neodymium and samarium. There are different types of magnetism.
Some of the common terminologies are Diamagnetism, Paramagnetism, Ferromagnetism, Antiferromagnetism, Ferrimagnetism, and Superparamagnetism.
Electricity and magnetism are two linked concepts as a result of Einstein’s Theory of Relativity. Magnetism and electricity are inconsistent in the absence of each other.
In contrast, the theory of relativity holds when we consider both magnetism and electricity. Magnetic field refers to the medium of magnetism.
The magnetic properties arise due to the magnetic moments of the object’s electrons. The magnetic behaviour of any object is characterised by its structure as well as its temperature.
The concept of magnetism came into existence when the ancient people realised that lodestones could attract iron.

What is Gravity?
Gravity refers to the natural phenomenon wherein all things that possess mass or energy attract each other. Some common examples of everyday things attracted by gravity include planets, stars, light and even galaxies.
The oceanic tides are an outcome of the gravity of the moon. Similarly, the weights are accorded to objects on Earth as a result of gravity.
An interesting feature of gravity is that it possesses an infinite range. However, the strength of gravity reduces as the distance of the object increases.
The basic definition of gravity takes shape from The Theory of Relativity proposed by Einstein. One of the most peculiar examples of gravity is the black hole that attracts light too.
The concept of gravity originates from the Greek philosopher Archimedes who discovered the centre of gravity of a triangle. The approximation of gravity takes place following the Law of Universal Gravitation proposed by Newton.
Following the law, the gravity of two objects is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
The planet Earth is surrounded by its gravitational force. The strength of gravitational force equals the acceleration of objects that are influenced by gravity.
The Law of Universal Gravitation proposed by Newton is one of the most accepted formulas for explaining the concept of gravity. Thus, the concept of gravity is commonplace today.

Main Differences Between Magnetism and Gravity
- Magnetism is the outcome of charged particles or some materials. On the other hand, gravity is an outcome of space-time curvature that results from the mass of two objects.
- The word magnetism is derived from the Latin word magnetismus from the early 17th century. In contrast, the word gravity is derived from the Latin word gravitas, meaning weight.
- The forces of magnetism do not apply to all objects. On the other hand, the forces of gravity only follow the principle of attraction.
- The forces of magnetism depend on the specific characteristics of every object. In contrast, the force of gravity acts on any two objects with mass.
- Magnetism is largely limited to man-made objects. On the other hand, gravity is a concept that has an application to heavenly objects.
- http://www.differencebetween.net/science/difference-between-magnetism-and-gravity/
- https://www.quora.com/What-is-the-fundamental-difference-between-magnetism-and-gravity

Fascinating insights into the fundamental differences between magnetism and gravity. Truly enlightening!
It’s interesting how the article has provided detailed comparisons between these two phenomena. Thank you.
I found the section on the main differences between magnetism and gravity to be particularly enlightening. Excellent work!
The references at the end of the article are great for further reading! Very useful.
The article’s detailed explanations open up a new world of understanding the differences between magnetism and gravity.
Great article! Very informative and detailed comparison between magnetism and gravity.
The explanation of magnetism and gravity is delightfully clear and precise.
This article provides a comprehensive comparison between magnetism and gravity. Well done.