The older method of storing and installing memory chips was difficult and more complex. Previously, DIPs (Dual Inline Package) were used as computer storage modules.
Sometimes due to mishandling, the pins of the DIP chip are also misaligned, which damages it and makes it unusable. Therefore, SIMM and DIMM were invented as alternatives.
Key Takeaways
- SIMM, or single in-line memory module, only has pins on one side and is used in older computers.
- DIMM, or dual in-line memory module, has pins on both sides and is used in newer computers.
- DIMM can provide greater memory capacity and faster data transfer rates than SIMM.
SIMM vs DIMM
SIMM (Single In-Line Memory Module) is a type of built-in memory. It contains pins on its sides. 32-bit channels are provided by SIMM to transfer data. The power used by it is 5 volts. DIMM (Dual In-Line Memory Module) provides 64-bit channels to transfer data. The power used by it is 3.3 volts. The storage capacity provided by it is 32MB to 1GB.

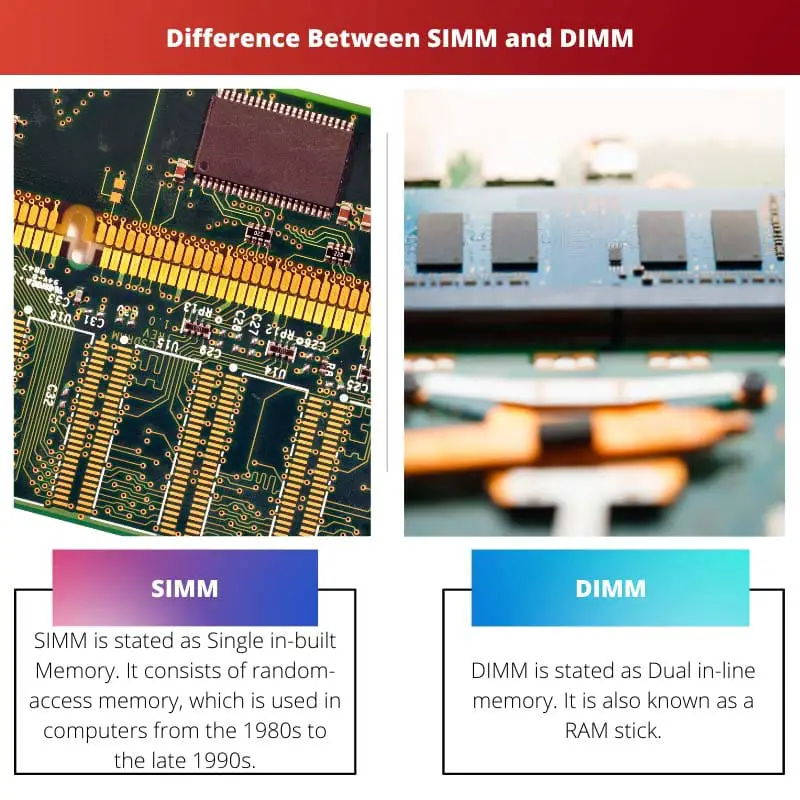
SIMM in the expanded form is known as Single in-built Memory. They were used in computers from the year 1980-the 1990s and invented by James J. Parker in 1982. The SIMM chips get their standard mark from JEDEC Solid State Technology Association.
DIMM in the expanded form is known as Dual inline Memory. It is also known as the RAM stick. It is used in motherboards of modern computers.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | SIMM | DIMM |
|---|---|---|
| Full-Form | Single inline Memory | Dual inline Memory |
| Basic | The pins are present on the sides. | The pins present are independent. |
| Channel | 32 bit | 64 bit |
| Power | It uses around 5 volts. | It employs about 3.3 volts. |
| Storage | It provides a capacity of 4 Mb to 64 Mb. | It provides a capacity of 32 Mb to 1 Gb. |
| Application | Early Pentium computers and 486 CPUs uses SIMM in them. | Pentium Modern PCs uses DIMM in them. |
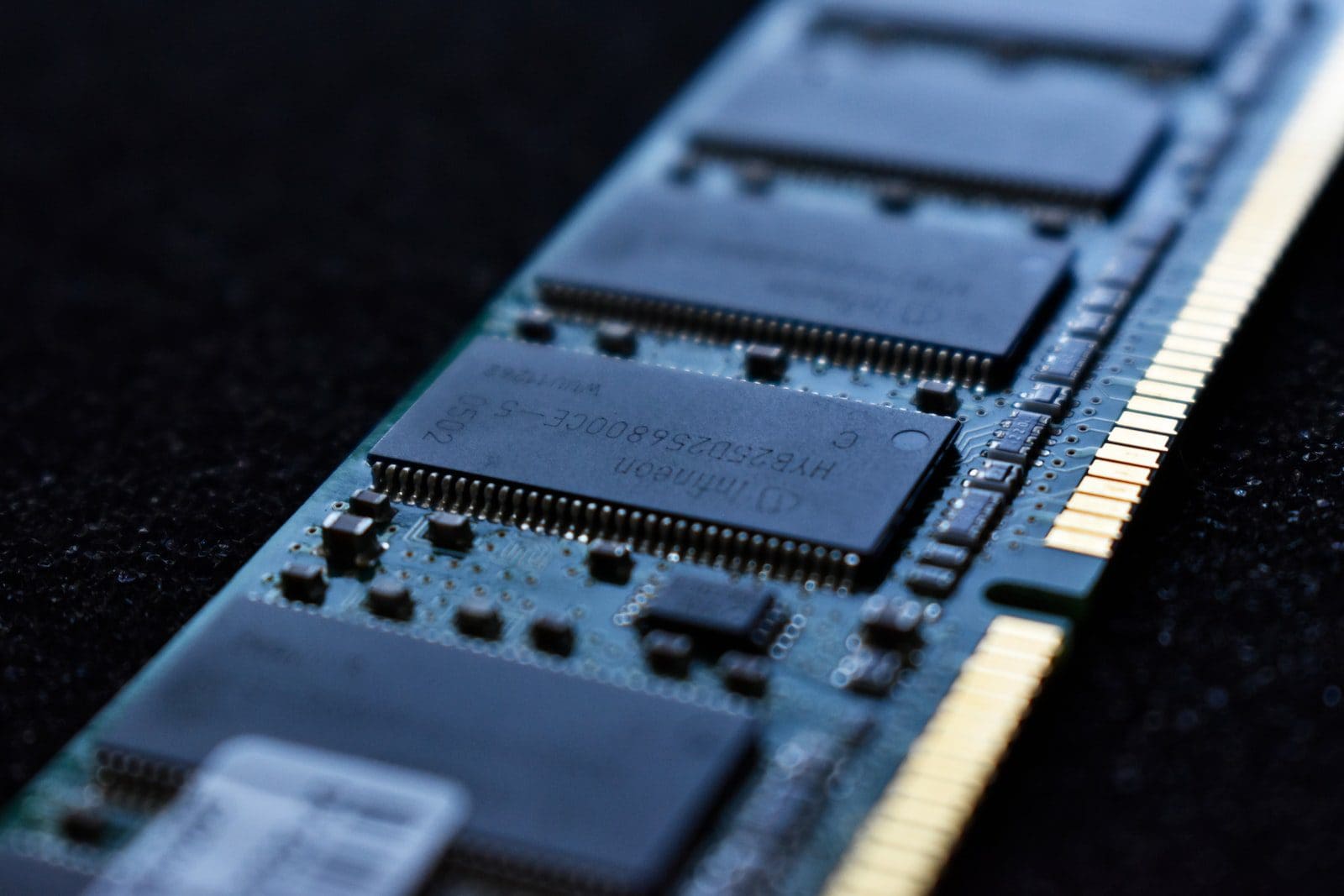
What is SIMM?
SIMM is stated as Single in-built Memory. It consists of random-access memory, used in computers from the 1980s to the late 1990s. SIMM is a module type.
James J. Parker invented SIMM in the year 1982 at Zenith Microcircuits. After their invention, Wang Laboratories became their first customer and filed for the patent, and they were also granted the patent in the year 1987, April.
These SIMM chips were standardised under the JEDEC Solid State Technology Association JESD-21C standard.
SIMMs are installed on the surface, and the pins and the SIMM connector are supposed to be of the same metal. They are only made up of gold and tin. The jagged metal should not be used for them.
SIMM can be distinguished further into two types which are as follows:
- 30 pins SIMM – It has an address width of about 8-bit and has a 1 MB or 4 MB RAM capacity. For the proper and safe installation of the chip, there is a notch present at the bottom of it.
- 72 pins SIMM has an address width of about 32 or 36 bits. The notch is at the side and centre for the proper installation.
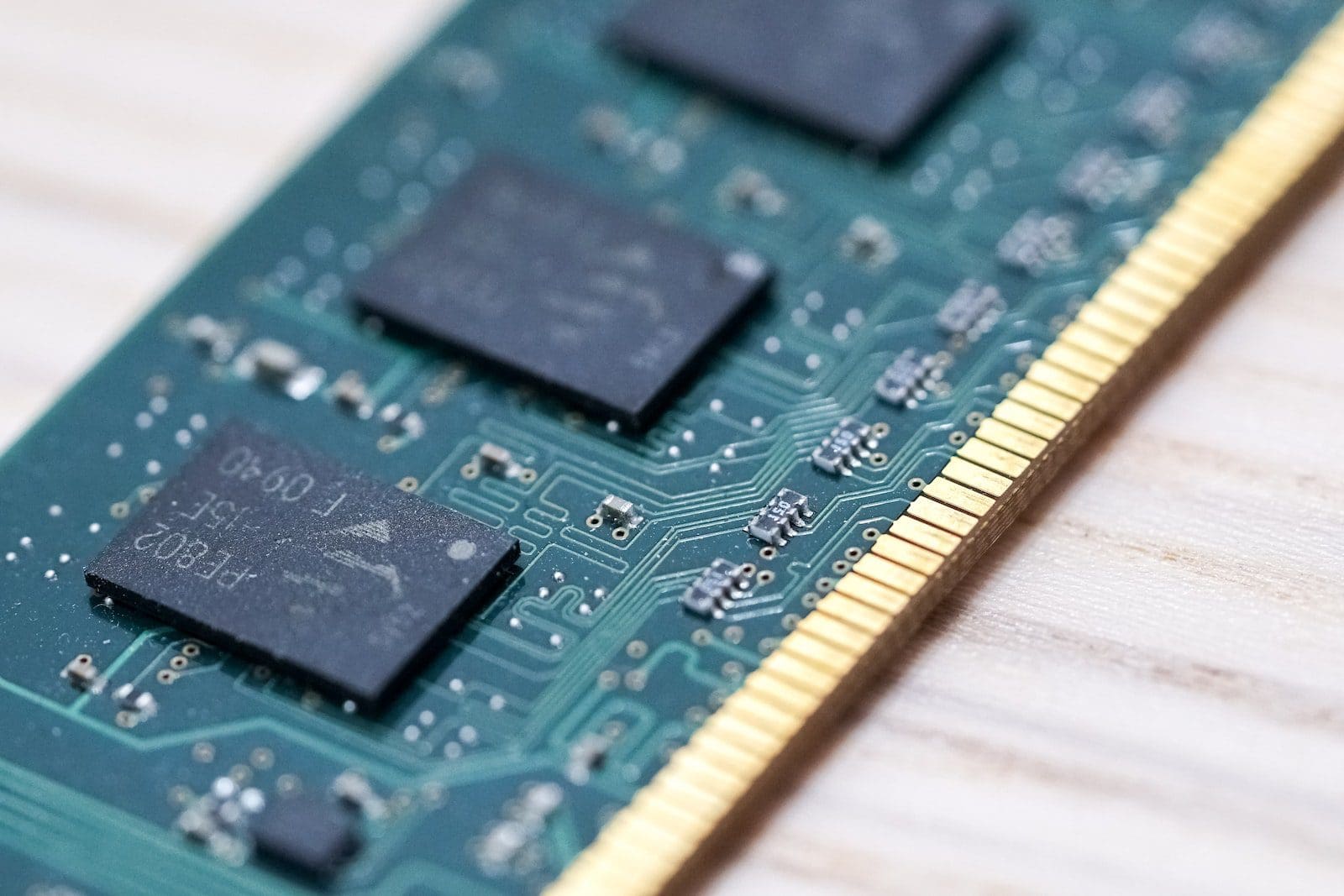
What is DIMM?
DIMM is stated as Dual inline memory. It is also known as a RAM stick. DIMM comprises a series of dynamic random-access memory, meaning it stores a single bit of data in its memory containing both transistor and capacitor with monolithic integrated circuits.
DIMM came into existence when they started to replace SIMM (Single inline Memory) after the invention of the Intel P5-based Pentium processors module in the market.
DIMM comes with the advantage of less power consumption. That is, it uses only 3.3 volts compared to SIMM. They also provide a large storage capacity of about 32 MB to 1 GB.
The pins which are present on the chip are independent. The variants which support slots of DIMMs in the market are – DDR, DDR2, DDR3, DDR4, and DDR5 RAM. DIMM is divided mainly into two types which are as follows –
- 168 pin DIMM – The structure of the 168 pin DIMM is different compared to SIMM as they consist of tiny notches along the row of the pins, which is present at the bottom of the module.
- 184 and 240 pins DIMM – It consists of only one notch but is present at a different position, so it helps in preventing the uneven placement of DIMM in the socket.
The DIMM or RAM sticks are now used in many advanced motherboards as they are surface mounted. Thus, they are present in personal computers, or at the workplace, printers, etc.
Main Differences Between SIMM and DIMM
- The storage provided by the SIMM ranges between 4 Mb to 64 Mb, while the storage of DIMM ranges between 32 Mb to 1 GB.
- SIMM is used in early Pentium computers and the 486 CPU, whereas DIMM is used in modern Pentium Computers.
- https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/1262788
- https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/471053
- https://digital-library.theiet.org/content/journals/10.1049/iet-cta.2009.0583
- https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/776247

The article delivers a clear breakdown of the functional differences between SIMM and DIMM, providing readers with a comprehensive understanding of these memory modules.
Absolutely, the clarity of the explanations enhances the accessibility of this technical information, making it an engaging educational resource.
The comparative analysis of SIMM and DIMM, along with the detailed descriptions of their technical specifications, provides a comprehensive understanding of memory module architecture.
The technical insights presented in this article are invaluable for anyone seeking a deeper understanding of computer memory technology.
Absolutely, the level of detail in the article offers a thorough exploration of memory module architecture and its impact on computing.
While the article provides a comprehensive overview, it could benefit from a more critical analysis of the impact of SIMM and DIMM on computing performance and efficiency.
I can see your point. A more in-depth look at the practical implications of these memory modules would enhance the article’s value.
The exploration of the technical specifications and historical context of SIMM and DIMM meets the highest standards of informative content. Well-crafted and enlightening.
Agreed, this article offers a commendable blend of technical depth and historical context, making it a valuable resource for anyone interested in computer memory technology.
The detailed comparison of SIMM and DIMM presented in this article is incredibly helpful for understanding the underlying technologies in computer memory modules.
Absolutely, the article’s breakdown of the technical differences provides valuable insight into the evolution of memory technology.
The historical context shared about the invention of SIMM and its subsequent evolution into DIMM is both enlightening and engaging. A compelling read!
Indeed, the historical narrative adds depth to the article and offers a fascinating perspective on the development of computer memory.
I never realized the rich history behind these memory modules. This article has shed light on a fascinating aspect of technological progress.
This is a very informative article, offering a clear comparison of SIMM and DIMM. It’s great to see the differences between these memory modules laid out so clearly.
I agree, it’s great to have all this information presented clearly and concisely!
The technological advancements that led to the development of DIMM are truly impressive. It’s fascinating to see how computer memory has evolved over time.
Absolutely! The evolution of computer memory modules is a testament to the rapid pace of technological innovation.
The comprehensive comparison table and detailed descriptions of SIMM and DIMM characteristics make this article a standout resource for understanding the evolution of computer memory.
The thorough exploration of SIMM and DIMM in this article sets a high standard for informative content, offering valuable insights with precision and clarity.
Absolutely, the side-by-side comparison of SIMM and DIMM parameters provides a clear and concise reference for understanding these memory modules.
The transition from SIMM to DIMM marks a pivotal moment in computer architecture. This article effectively captures the significance of this shift.
It’s remarkable how this shift has reshaped the landscape of computer memory and processing power. A well-articulated piece indeed.
Definitely, the move from SIMM to DIMM has had a lasting impact on the performance and capabilities of modern computing systems.