The word Tumor is quite popular in the medical world as well as among people. Tumors are critical medical issues. They develop in younger as well as older people.
There are different types of tumors in medicine. Some types can be cured with medications, some can be removed with surgery, but others can be life-threatening.
Key Takeaways
- Tumors and Polyps are abnormal growths that can develop in different body parts.
- Tumors can be cancerous or non-cancerous and occur in any tissue or organ. At the same time, Polyps are non-cancerous growths that occur mainly in the colon, stomach, and nasal passages.
- Tumors can be life-threatening if left untreated, while Polyps are benign but can become cancerous.
Tumors vs Polyps
Tumors are abnormal growths of cells that can be benign (noncancerous) or malignant (cancerous), forming a mass. Polyps are a specific type of benign tumor that grows in certain mucous membranes, like the colon or nose, appearing as small, stalk-like growths.
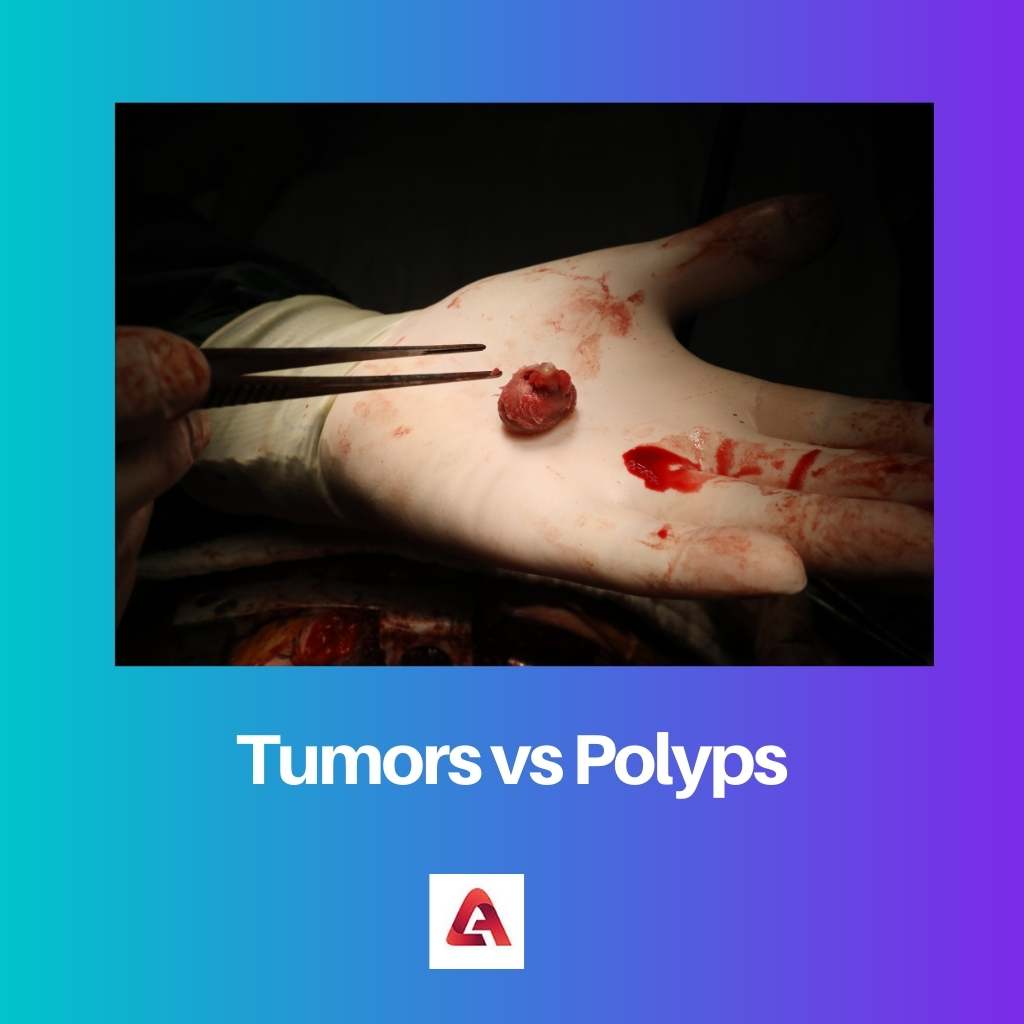
The tumor is formed by a mass of cells. Tumors look like swelling, but it is more severe. Tumors always do not develop cancerously but can become cancerous if left untreated for a long time.
A tumor becomes malignant once it is cancerous. These tumor cells can spread and form lumps in other body parts.
Polyps are also caused by abnormal cell proliferation. They look like small bumps. They are attached to the body by a stalk. Since they have a stalk, they resemble a mushroom.
Most of the polyps are not life-threatening. But they also can develop into malignant tumors with time.
Comparison Table
| Parameters of Comparison | Tumors | Polyps |
|---|---|---|
| Location | It can occur anywhere in the body | Arise from mucosal epithelial cells |
| Diagnosis | Image tests and biopsy | Endoscopy and biopsy |
| Treatment | Radiation therapy and chemotherapy | Can be treated with drugs or removed surgically |
| Risk factors | Mutation, exposure to chemicals or radiation, genetics | Family history, lack of exercise, smoking, excessive drinking, etc |
| Success rate | Cancerous tumors return after removal and are lethal | They can be successfully treated |
What are Tumors?
The main reason for tumor production is the rapid and abnormal proliferation of body cells. Cells normally divide at a specific rate when the rate of division increases, more cells are formed.
As a result of overproduction, these cells accumulate in different body parts and are known as tumors.
The reason behind this rapid division may be mutation by physical or chemical factors, genetics, or habitual or environmental causes. The size of the tumor determines its severity of it.
Each tumor may vary in size. They can randomly develop anywhere in the body. Tumors can be classified into three types.
Benign tumors are not very critical to treat. They can be permanently removed by surgery. A premalignant tumor has not yet become cancerous but can become one if left without treatment.
Malignant tumors are very critical, and they spread to other places. They return even when they are removed surgically.
The most common types of tumors include Fibroid, Hemangioma, Adenoma, Lipoma, Sarcoma, Carcinoma, etc. Imaging tests are done to determine the position of the tumors.
Doctors conduct a biopsy to identify the type of tumor. Each type of tumor will be treated accordingly by specialists. Radiotherapy, Chemotherapy, Surgery, and Gene therapy are advanced treatments used to treat tumors.
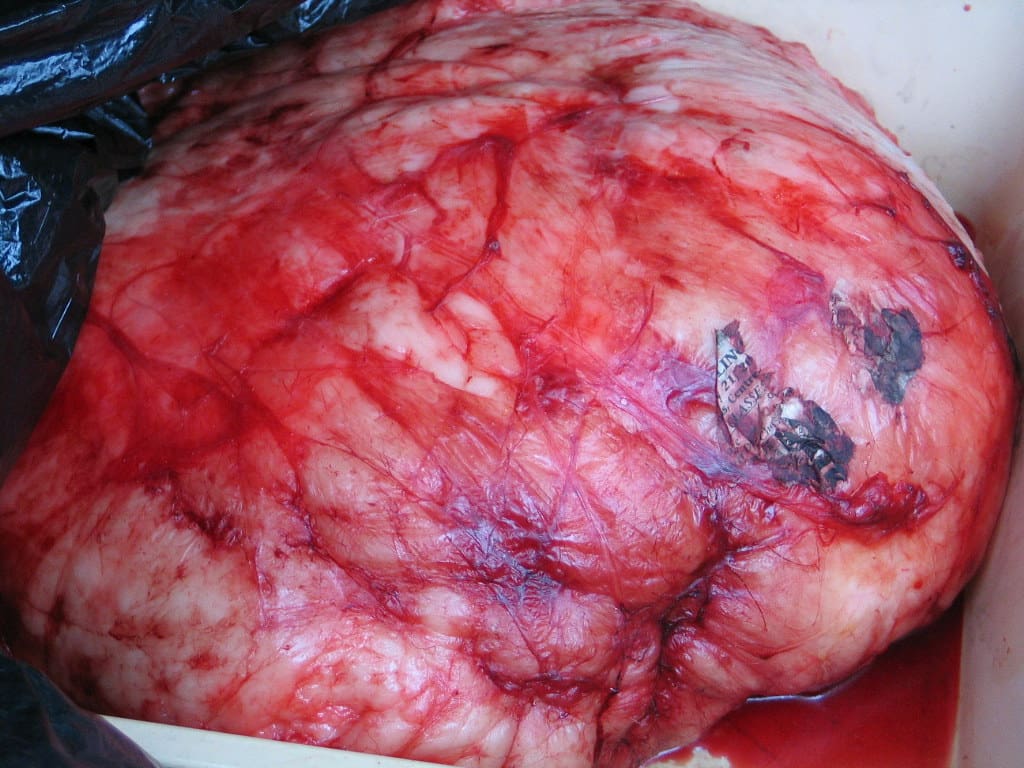
What are Polyps?
Polyps are stalked lumps that are normally not life-threatening. But, they can become dangerous once they get the characteristics of cancerous cells like rapid division and proliferation.
Polyps are treatable. They don’t linger after surgical removal. However, treatment depends on the polyp’s size, type, and location.
Genetics and family history are considered the major reasons for polyps. Colon polyps are a very common type of polyp and occur due to changes in the colon’s lining.
The colon is lined with mucosal epithelial cells. Uterine polyps develop due to abnormal development of the endometrium. Cervical polyps are caused by a hike in estrogen levels, the use of allergic chemicals, or any form of infection.
Polyps also develop in Throat and Nasal cavities. Throat polyps are caused due to smoking. Shouting lead to damage of cells, inflammation, etc. Polyps in the gall bladder are also common.
Endoscopy is the major diagnostic method for polyps. A biopsy can help confirm the type. Colonoscopy is done to detect colon polyps. Throat or vocal chord polyps are checked by examining the throat with a mirror.
Most polyps don’t need treatment, and they cure without treatment. But, some polyps need to be removed surgically to ensure that it doesn’t develop into cancer tumor.
Colon polyps are removed during a colonoscopy. Progestin and Gonadotropin-releasing hormones are given to treat hormonal polyps that develop in the cervix and uterus.
Main Differences Between Tumors and Polyps
- Tumors are more or less similar in size during specific periods of growth, but tumors at different stages differ in size, while Each polyp differs in size and shape from the others.
- Tumors aren’t pedunculate, but Polyps are protrusions with a stalk.
- Tumors are highly malignant and cancerous. They become life-threatening when not treated. Whereas, Polyps are not always dangerous.
- Tumors can develop from any cell. They don’t have a specialized origin. While Polyps develop from mucosal epithelial or submucosal cells
- Tumors do not involve blood vessels. They are an aggregate of dead cells. But Polyps involve blood vessels and sometimes cause bleeding—bleeding results in blood loss and anaemia.
- https://acsjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/1097-0142(19810315)47:6%3C1241::AID-CNCR2820470602%3E3.0.CO;2-Y
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0165460893900703

As someone with a family history of polyps, this article provided crucial information on the underlying causes and diagnostic modalities for these growths. It is an essential read for those with similar concerns.
The information shared is very precise and detailed, thank you for sharing. It is imperative that people understand the important differences between Tumors and Polyps.
Indeed, the article is very educational and helpful for those seeking information about these health issues.
The thorough discussion on the main differences between tumors and polyps is enlightening, particularly in understanding their distinct characteristics and potential implications for clinical management.
I found the article to be quite alarming, especially the part about tumors becoming life-threatening if left untreated. This is a serious concern for many, including myself.
The comparison table is particularly helpful as it explains the key differences and considerations related to tumors and polyps. It is an important resource for individuals seeking to understand these medical conditions.
I could not agree more, the detailed comparison is essential for raising awareness about the potential severity of these growths and the importance of medical evaluation.
Absolutely, the information provided in the article elucidates the complexities of these conditions in a comprehensive and understandable manner.
It is concerning to learn about the potential for polyps to become cancerous over time, highlighting the need for timely medical interventions and monitoring.
Indeed, the article imparts valuable knowledge and insights that underscore the significance of early detection and management of these growths.